Benefits of Blockchain: How This Technology Transforms Businesses

From finance to supply chains, the benefits of blockchain are quietly transforming the way businesses build trust and operate. As companies look for faster, safer, and more efficient ways to handle transactions and data, blockchain is proving its value beyond cryptocurrency — enabling transparency, automation, and secure record-keeping at scale. Let’s explore the key advantages that make blockchain a game-changer across industries today.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain represents a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that maintains a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked and secured using cryptographic principles. At its core, blockchain functions as a decentralized database that stores information across multiple computers in a network, ensuring that no single entity controls the entire system.
Blockchain is not a replacement for databases. It becomes valuable where multiple independent parties need to operate on a shared source of truth with auditability and automated trust. If you’re curious about the mechanics behind it, our comprehensive guide to blockchain technology goes deeper.

Which are the Top Benefits of Blockchain
The revolutionary potential of this technology becomes most apparent when examining its practical benefits across various use cases. These 5 advantages of blockchain technology address long-standing challenges that traditional systems have struggled to resolve, offering novel approaches that create tangible value for organizations.
1. Enhanced Security
Centralized databases remain easy targets because compromising a single control point can expose entire systems. Blockchain strengthens security by distributing data across nodes, protecting each block with SHA-256 hashing and digital signatures, and enforcing network-wide consensus to prevent unauthorized changes.
- Distributes control across nodes: Eliminates single points of failure, making attacks exponentially harder.
- Secures records with cryptography: Hashing and digital signatures ensure data integrity and authentication.
- Prevents unauthorized changes: Consensus mechanisms validate all transactions before recording.
JPMorgan’s JPM Coin has processed over $1 billion in daily transactions with zero security incidents since launch, demonstrating blockchain’s security advantages over traditional correspondent banking systems.

2. Greater Transparency
Lack of transparency in supply chains, finance, and healthcare creates mistrust and inefficiencies. It provides a shared, tamper-proof ledger that allows participants to verify and audit transactions in real time, increasing accountability and confidence.
- Creates immutable, auditable records: Transactions cannot be altered, enabling reliable audits.
- Provides a single source of truth: All participants see the same data, reducing disputes.
- Enables efficient verification: Structures like Merkle trees allow rapid validation of large datasets.
Walmart’s food traceability system reduced contamination source identification time from weeks to seconds during the 2018 romaine lettuce outbreak, demonstrating how transparency enables rapid crisis response.
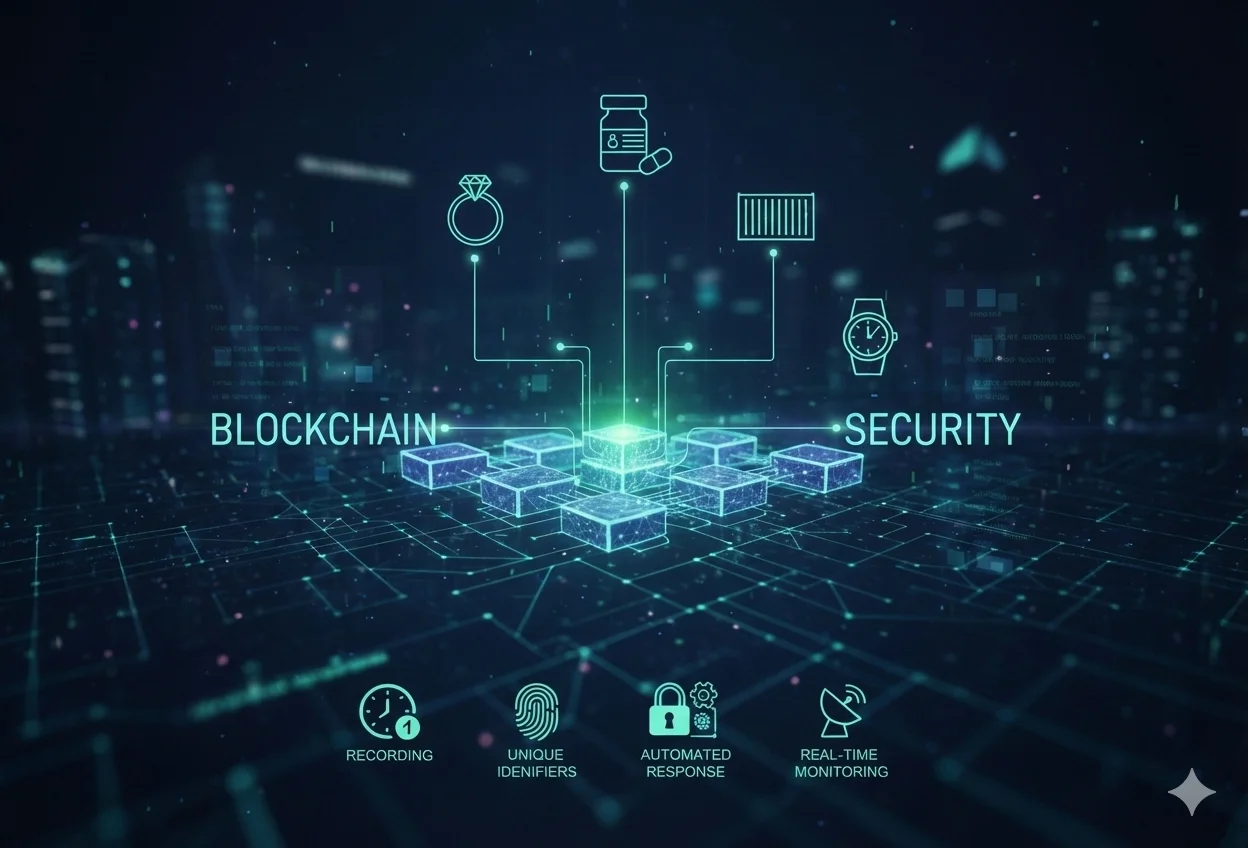
3. Instant Traceability
For industries dealing with regulated products, luxury goods, or sensitive assets, tracking provenance is critical. This technology ensures every product and transaction has a permanent, timestamped record, enabling end-to-end traceability and accountability.
- Recording: Data is permanently timestamped and cannot be altered, ensuring a reliable audit trail.
- Links to unique identifiers: Each asset is connected to its original information, guaranteeing authenticity.
- Automated response: Smart contracts proactively address issues as they occur without manual intervention.
- Real-time monitoring: IoT sensors continuously feed accurate data to the blockchain for up-to-date tracking.
De Beers’ Tracr platform tracks diamonds from mine to retail, reducing diamond fraud by over 95% and increasing consumer confidence through complete authenticity verification.
4. Increased Efficiency and Speed
Traditional transactions involve multiple intermediaries and lengthy settlement times. This technology accelerates operations by enabling peer-to-peer transactions, automating processes with smart contracts, and validating transactions simultaneously across participants.
- Eliminates intermediaries: Cuts processing delays and manual verification.
- Reduces settlement time: Moves transactions from days to minutes or seconds.
- Automates workflows: Smart contracts handle predefined rules automatically.
Ripple’s blockchain network processes international transfers in under 4 seconds with fees below $0.01, compared to traditional 3-5 day wire transfers costing $25-50, representing 99.9% improvements in both speed and cost.
5. Automation
Manual processes introduce bottlenecks, errors, and resource overhead. It automates contract execution, compliance checks, and payments, reducing human intervention and ensuring consistent rule-based operations.
- Executes smart contracts automatically: Triggered when predefined conditions are met.
- Removes manual oversight: Eliminates delays and human errors.
- Integrates with external data sources via oracles: Ensures actions are based on real-world information.
AXA’s flight delay insurance automatically processes claims and payments using smart contracts triggered by flight data, reducing processing time from weeks to hours while eliminating administrative costs.
Seeing these benefits in action shows how blockchain can truly transform business operations. With the right approach, your organization can leverage blockchain development services to boost security, transparency, and efficiency across real-world processes.
How Industries Benefit from Blockchain
Understanding industry-specific applications demonstrates how the advantages of using blockchain technology translate into real-world improvements and competitive advantages across diverse sectors.
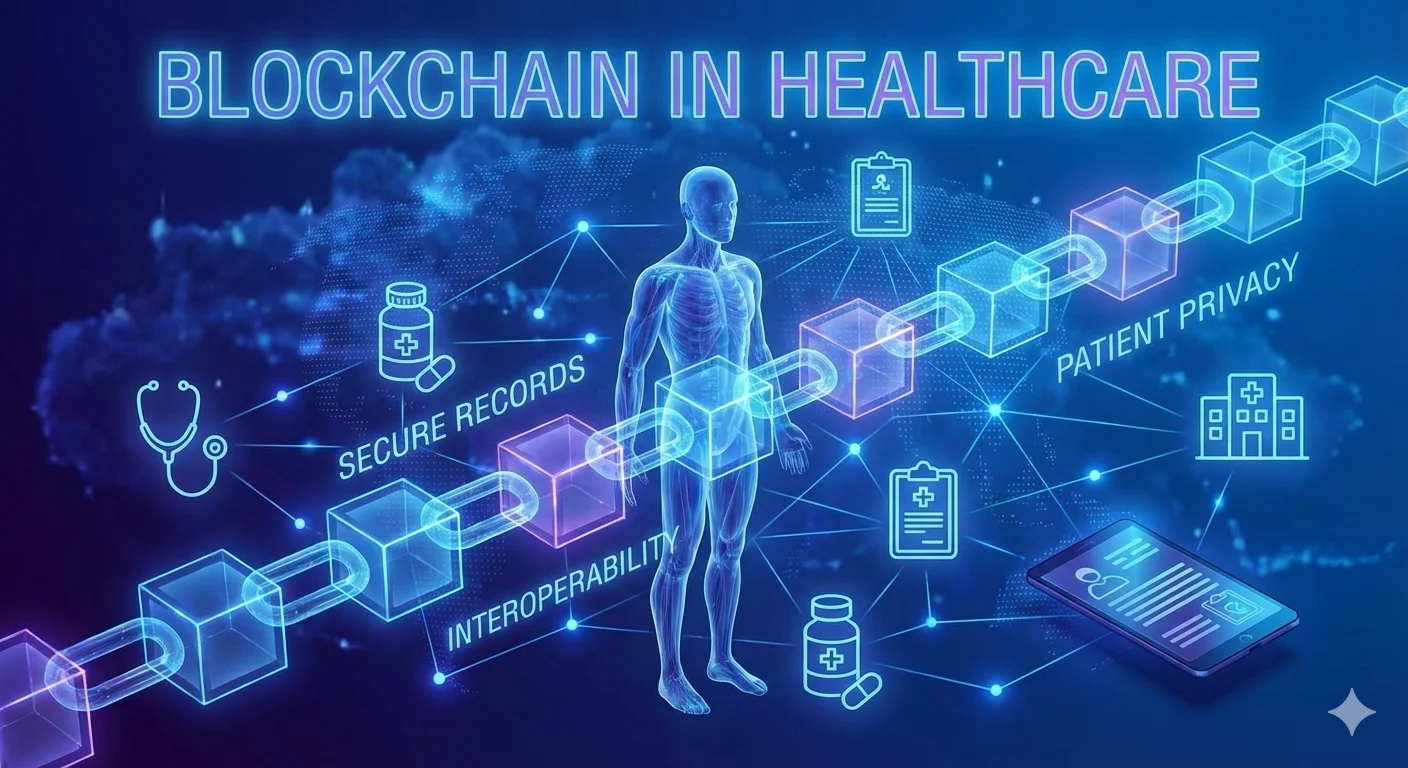
1. Healthcare
The healthcare sector is leveraging blockchain to tackle its long-standing struggle with fragmented and insecure patient data. Medical records are often siloed across separate providers, leading to incomplete histories and operational inefficiencies. It enables the creation of a unified, patient-centric ledger where individuals can grant secure, auditable access to any provider.
This wasn’t just a concept; the MIT Media Lab’s MedRec prototype demonstrated how the network could act as a decentralized access-control manager. Rather than storing medical records on-chain, MedRec stores only cryptographic hashes and access metadata on the blockchain while keeping actual patient data in off-chain secure storage. The implementation has demonstrated a 30% reduction in medical record sharing time between healthcare institutions while providing patients with a complete, immutable audit trail of all data access.
2. Financial Services
Financial institutions face regulatory pressures, high transaction costs, lengthy settlement times, and increased fraud risks. Cross-border payments remain slow and expensive, while trade finance involves cumbersome documentation processes.
Its applications include:
- Faster, cheaper cross-border payments
- Automated trade finance through smart contracts
- Shared KYC databases reducing compliance costs
- Fraud prevention through immutable records
- Decentralized lending platform
The ASX embarked on an ambitious project to replace its legacy CHESS clearing and settlement system with a blockchain-based solution developed using Digital Asset’s DAML technology. The new system was designed to provide real-time settlement, reduce counterparty risk from days to minutes, and lower operational costs by an estimated 30-40%. While the project faced implementation challenges and was ultimately delayed, it successfully demonstrated the technical viability of blockchain for mainstream financial market infrastructure.
3. Logistics and Supply Chain
Global supply chains are notoriously opaque and inefficient, suffering from a lack of visibility that leads to delays, fraud, and high costs. It tackles these issues by creating a single, shared source of truth for all partners.
This makes blockchain is an ideal solution because
- It creates a single, shared source of truth for all supply chain partners.
- It automates documentation (smart contracts can auto-pay upon delivery confirmation).
- It provides real-time, tamper-proof tracking of goods, from raw materials to finished products.
BHP Mining Operations – the world’s largest mining company implemented a blockchain-based system to track the movement of wellbore rock and fluid samples from drilling sites to laboratories. Using IoT sensors and QR code tracking, each sample’s journey is recorded on a hyperledger-based blockchain, creating an immutable chain of custody. The implementation reduced sample tracking administration costs by 45% and decreased data reconciliation errors by 92%. More significantly, it reduced the time required to verify sample authenticity from weeks to minutes, enabling faster geological analysis and decision-making.
Want to see how these blockchain benefits work in real-world projects? Explore our blockchain case studies to learn how businesses apply this technology in practice.

What Are the Challenges and Risks of Blockchain?
Despite its benefits, blockchain faces challenges such as scalability, privacy, governance, operational risks, and regulatory uncertainty:
- Scalability: Public blockchains often struggle to match the throughput of centralized systems. Layer-2 solutions and permissioned networks are emerging to address this.
- Privacy: Immutability can conflict with regulations like GDPR’s “right to erasure.” A common approach is to keep sensitive data off-chain and use on-chain hashes with techniques such as zero-knowledge proofs.
- Governance Complexity: Multi-party systems require clear rules for membership, upgrades, and dispute resolution. Without this, blockchain may create more friction than it removes.
- Operational Risks: Mismanaged keys or poorly written smart contracts can lead to major losses. Strong custody solutions (HSM, MPC) and rigorous audits are essential.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Legal frameworks vary widely by jurisdiction and continue to evolve. Businesses need flexible architecture that can adapt to new rules.
These challenges don’t diminish blockchain’s potential but highlight the need for careful design and governance. The organizations that succeed will be those that approach blockchain not just as technology, but as a strategic system requiring policy, security, and compliance alignment.
How is Blockchain Evolving?
Current trends indicate blockchain’s expanding influence beyond cryptocurrency, driven by technological maturation and regulatory clarity. Market adoption has accelerated dramatically, with nearly 90% of businesses surveyed reporting deployment of blockchain technology in some capacity, while 87% of surveyed businesses are likely to invest in a blockchain solution in the next 12 months according to Deloitte.
Technological advances address previous adoption barriers:
- Layer-2 solutions enable thousands of transactions per second, competing with traditional processors
- Proof-of-stake consensus reduces energy consumption by 99%
- Interoperability protocols connect different blockchain networks
Regulatory frameworks provide the clarity enterprises need for confident investment. The EU’s MiCA regulation creates standardized compliance, while similar frameworks emerge globally. Over 80 central banks are researching CBDCs, demonstrating government confidence in blockchain’s reliability for critical infrastructure.
Future projections show remarkable growth potential. According to Grand View Research, the blockchain market is projected to reach $1,431.54 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 90.1%, while integration with AI, IoT, and 5G creates unprecedented autonomous system capabilities.
The convergence of technological maturation, regulatory clarity, and institutional investment positions blockchain as a fundamental digital infrastructure rather than niche technology.
FAQs
What makes blockchain different from traditional databases?
Traditional databases operate under centralized control with single administrators managing access and security. Blockchain distributes control across network participants, creating immutable records through cryptographic linking and consensus mechanisms. While traditional systems require trust in controlling entities, blockchain establishes trust through mathematical verification, eliminating intermediary dependence.
Where do the benefits of blockchain in business show up on the P&L?
The value appears in lower reconciliation costs, faster settlement cycles, reduced compliance expenses, and new revenue from tokenization. Executives can measure improvements through metrics such as time-to-cash, exception rates, and audit hours. These are the direct financial outcomes of blockchain adoption.
Is blockchain right for my use case or is a normal database enough?
If a single organization owns the workflow, a database is usually sufficient. Blockchain adds value when multiple independent parties must share trusted records without relying on one central operator. It is best suited for industries with high reconciliation and compliance costs.
Can blockchain integrate with ERP and CRM systems?
Yes, blockchain acts as a settlement or trust layer while ERP and CRM handle business operations. Data can flow between them via APIs or event streams, with sensitive records stored off-chain. This integration lets enterprises keep using familiar tools while gaining blockchain’s auditability.
How do we quantify ROI for a blockchain initiative?
ROI is measured by comparing costs and revenues before and after implementation. Savings often come from fewer reconciliation hours and faster settlements, while new revenue may arise from tokenized products. A risk-adjusted view also includes reduced fraud losses.
How do we ensure interoperability and avoid vendor lock-in?
Interoperability relies on open standards and modular design. Sensitive data should stay off-chain with anchors stored on-chain to preserve portability. Using common identity and messaging protocols helps ensure systems can connect without dependence on a single vendor or chain.
Blockchain is no longer just about cryptocurrencies; it is becoming the backbone of secure, transparent, and efficient digital ecosystems. At Newwave Solutions, our blockchain development services help enterprises turn blockchain from concept into measurable business value through tailored solutions, smart contract development, and system integration. If you’re ready to explore how blockchain can streamline your operations and create measurable impact, get in touch with us to discuss your project.
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply