What is ReactJS? Building Interactive User Interfaces Efficiently

Have you ever wondered how leading web applications like Facebook and Netflix deliver such incredibly dynamic and smooth user interactions? You’re already asking the core question: What is ReactJS? This is the technology powering those experiences. Think of ReactJS as the engine that can convert a slow, clunky web application into a lightning-fast, user-friendly platform—the kind that keeps customers engaged and conversion rates climbing. This article will explore what is ReactJS and how it has become a cornerstone of web development and a pivotal factor in business digital strategy.
What is ReactJS? More Than a Library, A New Way to Build
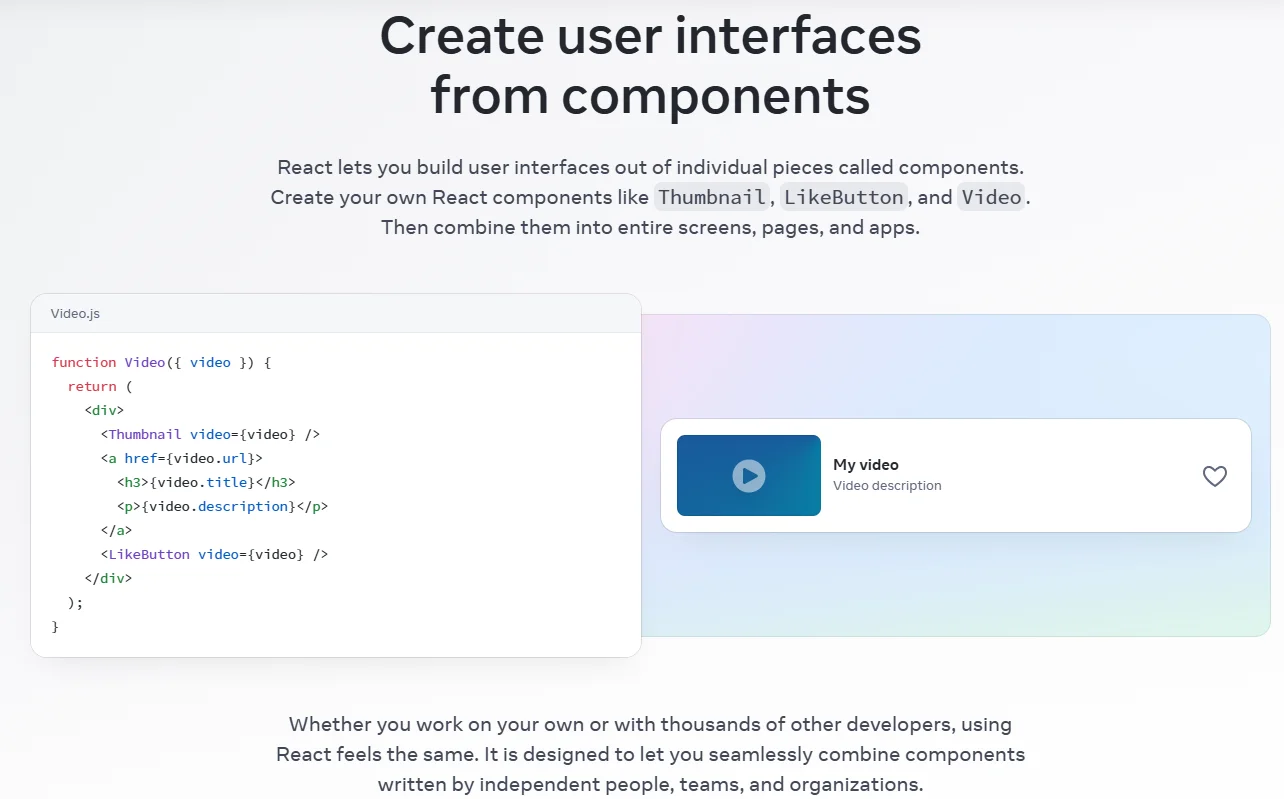
Officially, ReactJS (commonly known as React) is an open-source JavaScript library for building user interfaces, primarily for web applications. But that technical definition barely scratches the surface. Think of it not as a complete framework that dictates every aspect of your project, but as a highly specialized and powerful tool focused solely on constructing the view layer—what users see and interact with in their browsers.
React was created by Jordan Walke, a software engineer at Facebook, to address a critical performance issue. As Facebook’s advertising business grew, its codebase became increasingly complex, leading to cascading updates that were slow and difficult to manage. The solution was a novel concept: a library that could efficiently update only the parts of a web page that changed, without requiring a full page reload. Facebook open-sourced React in 2013, and it quickly gained traction because it solved a universal problem for developers building data-intensive applications.
React’s power stems from a few foundational concepts that work in concert to create a robust development experience.
- Components: The Building Blocks. Instead of writing massive, monolithic pages of code, developers use React to build applications with small, independent, and reusable pieces called components. Each component manages its own logic and appearance, like a Lego brick. This modularity makes code easier to understand, test, and maintain, a key advantage in custom ReactJS development.
- Virtual DOM: The Performance Catalyst. The Document Object Model (DOM) is a tree-like representation of a web page. Updating it directly is slow. React introduces a brilliant abstraction: the Virtual DOM. When a component’s state changes, React first updates a lightweight virtual copy of the DOM. It then compares this new virtual DOM with a previous snapshot (a process called “diffing”) and calculates the most efficient way to update the actual browser DOM. This “diffing” algorithm results in exceptionally fast and smooth performance, a core benefit of ReactJS.
- JSX: A Syntax Extension. JSX allows developers to write HTML-like syntax directly within their JavaScript code. While optional, it is widely adopted because it makes the code more readable and intuitive by visually representing the component’s structure.
This powerful combination of components, Virtual DOM, and a rich ecosystem makes ReactJS development the go-to choice for building modern, scalable, and high-performance web applications.
Ready to leverage these capabilities for your project? Hire ReactJS developers from Newwave to get started.
What are the Key Benefits of ReactJS?
The widespread adoption of React by industry giants isn’t a coincidence. It’s a direct result of tangible advantages that translate into business value. Let’s dissect the primary benefits.
1. Exceptional Performance Through Smart Updates
React’s Virtual DOM isn’t just a technical feature—it’s a performance revolution. When your application needs to update thousands of elements, React calculates the most efficient way to make those changes, updating only what’s necessary. This approach means your users experience smooth interactions even in data-heavy applications. E-commerce platforms processing real-time inventory updates or financial dashboards displaying live market data benefit tremendously from this optimization approach.
2. Reusable Components Save Development Time
The component-based architecture of React transforms how development teams approach project timelines. Instead of rebuilding similar UI elements repeatedly, you create components once and reuse them throughout your application. A button component, for instance, can maintain consistent styling and behavior across dozens of pages while being updated from a single location. This reusability translates directly into reduced development costs and faster time-to-market for your products.
3. Massive Developer Ecosystem and Community Support
React’s popularity has created an ecosystem where solutions exist for virtually every development challenge. Need form handling? Libraries like Formik or React Hook Form provide battle-tested solutions. Require complex animations? Framer Motion offers comprehensive tools. This ecosystem means your development team spends less time building basic functionality and more time crafting unique business features that differentiate your product.
4. SEO-Friendly with Server-Side Rendering
Modern ReactJS web development addresses SEO concerns through server-side rendering capabilities. Frameworks like Next.js render React components on the server, delivering fully formed HTML to search engines and users alike. This approach improves initial page load times and ensures your content is discoverable, crucial for businesses depending on organic traffic for customer acquisition.
5. Seamless Integration with Existing Systems
React’s library nature allows it to integrate smoothly with existing applications. You don’t need to rebuild your entire system to benefit from React’s capabilities. Many organizations start by converting specific pages or components to React, gradually expanding their usage as they see results. This incremental adoption path reduces risk while delivering immediate benefits.
The convergence of these benefits explains why custom ReactJS development has become the preferred approach for businesses seeking both immediate results and long-term scalability. React doesn’t just solve today’s problems—it provides a foundation that adapts to tomorrow’s challenges.
What are the Challenges of Using ReactJS?
A balanced perspective is crucial for any strategic decision. While powerful, React is not totally perfect. Acknowledging them allows for proactive planning and risk mitigation.
1. Rapid Ecosystem Evolution Creates Learning Pressure
React’s vibrant ecosystem, while advantageous, presents a double-edged reality. New libraries, tools, and best practices emerge constantly, creating pressure for development teams to continuously update their knowledge. What worked perfectly six months ago might now be considered outdated, forcing businesses to allocate resources for ongoing education and code refactoring. Offshore ReactJS development teams often mitigate this challenge by specializing in React exclusively, maintaining current expertise across multiple projects.
2. State Management Complexity in Large Applications
As your React application grows beyond simple interactions, state management becomes increasingly complex. While React’s built-in state management works well for small applications, enterprise-level projects often require additional tools like Redux or Context API, adding architectural layers that junior developers struggle to understand. This complexity can slow development velocity and increase onboarding time for new team members.
3. JSX Learning Curve for Traditional Developers
Developers accustomed to separating HTML, CSS, and JavaScript often find the JSX conceptually challenging. This “HTML-in-JavaScript” approach requires a mental shift that can initially slow development progress. Teams transitioning from traditional web development frameworks need time to adapt to React’s component-thinking methodology.
4. Configuration and Tooling Overhead
Unlike full frameworks that provide complete development environments, React requires developers to assemble their own toolchain. Choosing between webpack, Parcel, or Vite for bundling, selecting testing frameworks, and configuring development environments adds complexity to project setup. While tools like Create React App simplify initial setup, ReactJS web application development often requires custom configurations that demand deeper technical knowledge.
5. Debugging Complexity with Virtual DOM
The Virtual DOM’s abstraction layer, while improving performance, can complicate debugging processes. Traditional browser developer tools show the actual DOM, not React’s virtual representation, making it harder to trace state changes and component interactions. Specialized tools like React DevTools become essential but add another layer of complexity to the development workflow.
Despite these challenges, successful ReactJS web app development projects overcome these obstacles through proper planning, team training, and architectural decisions made early in the development process. Understanding these challenges upfront allows you to budget appropriate resources and make informed decisions about team composition and project timelines.
What is ReactJS Used For?
Modern web applications demand more than static content delivery—they require interactive, responsive experiences that feel native to each platform. React has evolved to meet these demands across diverse application types, each leveraging the library’s strengths in unique ways.
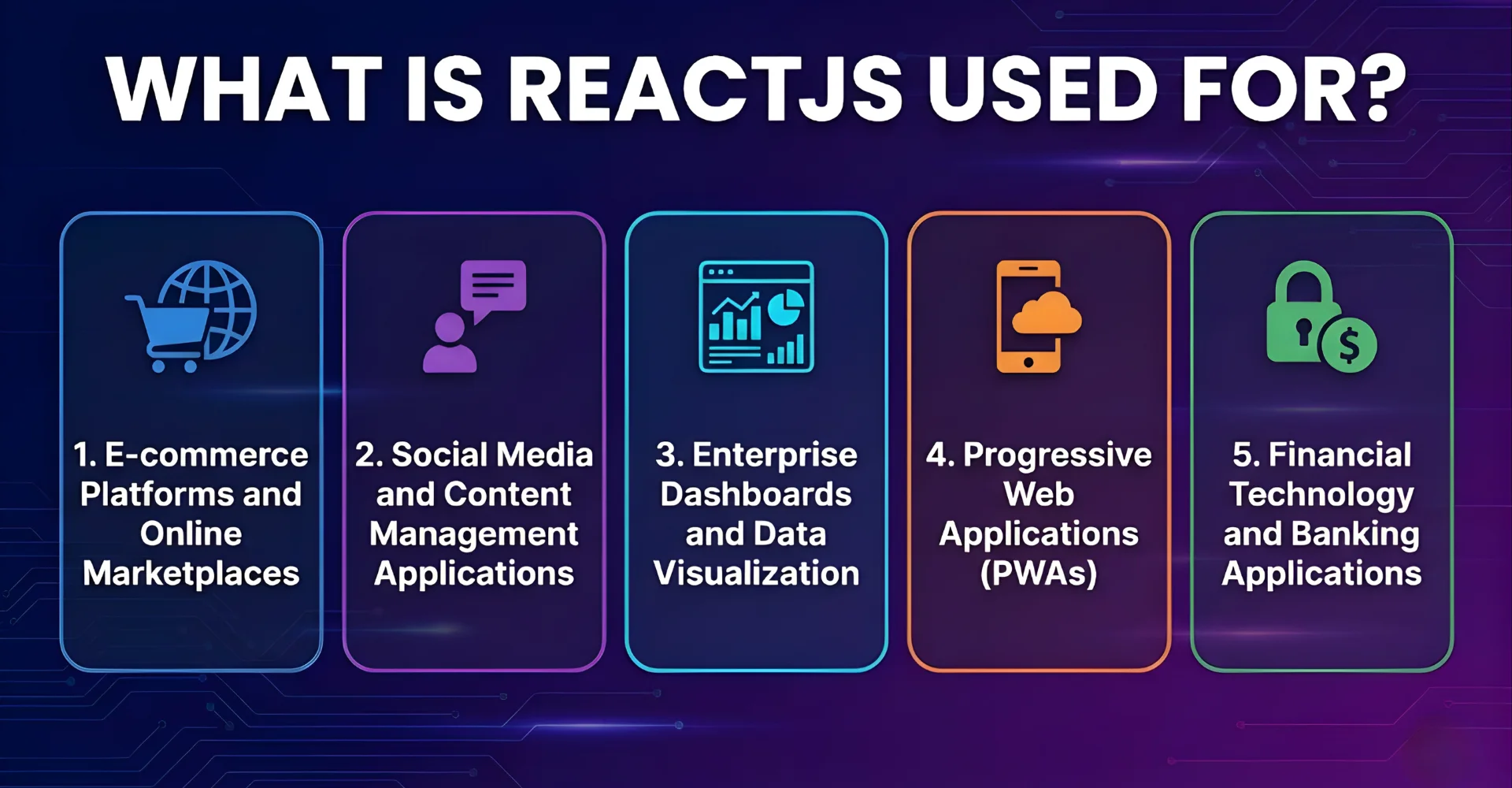
1. E-commerce Platforms and Online Marketplaces
E-commerce applications showcase React’s ability to handle complex, data-intensive user interfaces. Consider how Airbnb rebuilt its entire platform using React to manage millions of property listings, real-time availability updates, and complex booking flows. The component-based architecture allowed them to create reusable elements—property cards, booking widgets, and user profiles—that maintain consistency across their global platform while adapting to local requirements.
React’s state management capabilities prove crucial for shopping cart functionality, where users expect immediate feedback when adding items, updating quantities, or applying discount codes. The Virtual DOM ensures these interactions remain smooth even when dealing with extensive product catalogs and real-time inventory updates.
2. Social Media and Content Management Applications
Social platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp Web demonstrate React’s capacity for handling real-time data streams and complex user interactions. These applications require instant updates when users post content, react to posts, or receive messages—challenges perfectly suited to React’s efficient rendering system.
Netflix’s interface exemplifies how ReactJS web development handles content-heavy applications. Their recommendation engine constantly updates based on user behavior, displaying personalized content without page refreshes. React components manage each content tile independently, allowing for smooth scrolling through thousands of titles while maintaining responsive performance.
3. Enterprise Dashboards and Data Visualization
Business intelligence applications require sophisticated data visualization capabilities combined with interactive controls. Companies like Uber use React to power their internal dashboards, displaying real-time metrics about ride requests, driver availability, and revenue patterns across multiple cities simultaneously.
The component architecture proves invaluable for dashboard development, where different teams can build chart components, filter controls, and data tables independently while maintaining design consistency. React’s ecosystem includes powerful visualization libraries like D3.js integration and Recharts, enabling complex data presentations without performance compromises.
Looking to build engaging social or content platforms? Discover our web development expertise to create dynamic, user-centric applications.
4. Progressive Web Applications (PWAs)
React’s compatibility with PWA technologies enables businesses to deliver app-like experiences through web browsers. Twitter’s PWA demonstrates how React can power applications that work offline, send push notifications, and install like native apps while maintaining web accessibility.
The combination of React with service workers and caching strategies creates applications that load instantly, even on slow network connections. This capability particularly benefits businesses targeting emerging markets or users with limited internet connectivity.
5. Financial Technology and Banking Applications
Fintech applications demand security, real-time data processing, and intuitive user experiences. PayPal’s consumer interface leverages React to handle complex transaction flows, real-time balance updates, and secure payment processing while maintaining the responsiveness users expect from financial applications.
Predictable state management in React applications becomes crucial when handling financial data, where accuracy and consistency are paramount. React’s unidirectional data flow helps prevent state inconsistencies that could lead to transaction errors or security vulnerabilities.
Planning a fintech solution that users can trust? Explore our banking software development services to build secure, compliant financial applications.
What Are the Key Differences Between ReactJS and React Native?
The relationship between ReactJS and React Native often confuses businesses planning their digital strategy. While both technologies share React’s core principles, they serve fundamentally different purposes and target distinct platforms.
| Aspect | ReactJS |
React Native |
| Platform Target | Web browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari) | Mobile devices (iOS, Android) |
| Rendering Engine | DOM manipulation in browsers | Native platform components |
| Styling Approach | CSS, styled-components, CSS modules | StyleSheet API similar to CSS |
| Navigation | React Router, Reach Router | React Navigation, native navigation |
| Performance | Virtual DOM optimization for the web | Bridge communication with native code |
| Development Tools | Browser DevTools, React DevTools | Flipper, React Native Debugger |
| Code Sharing | Business logic and components | Logic sharing, platform-specific UI |
| Learning Curve | Web development background is helpful | Mobile development concepts required |
| Deployment | Web servers, CDNs | App stores (Apple App Store, Google Play) |
| Access to Device Features | Limited to web APIs | Full access to device capabilities |
| Updates | Instant deployment | App store approval process |
| Development Speed | Rapid web deployment | Faster than native, slower than web |
The choice between ReactJS and React Native depends on your target audience and business objectives. If your customers primarily interact with your business through web browsers, ReactJS development provides the fastest path to market with the broadest device compatibility.
However, if your application requires device-specific features like camera access, push notifications, or offline functionality, React Native offers a compelling middle ground between web development speed and native performance.
FAQs
Can ReactJS work with other technologies and frameworks?
React is designed to be technology-agnostic and integrates well with various backend technologies, databases, and third-party services. You can use React with Node.js, Python Django, Ruby on Rails, or any backend that can serve APIs. It also works alongside other frontend tools and libraries, allowing you to gradually adopt React in existing projects without complete rewrites.
Is ReactJS suitable for mobile app development?
ReactJS itself is designed for web applications, but React Native uses similar principles for mobile development. If you need a mobile app, hiring React Native developers allows you to leverage React knowledge to build native mobile applications for iOS and Android, sharing much of the code between platforms while accessing device-specific features.
What hosting options are available for ReactJS applications?
React applications can be deployed on various hosting platforms, from simple static hosting services like Netlify or Vercel for client-side rendered apps to cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure for server-side rendered applications. The choice depends on your application’s complexity, traffic requirements, and budget.
What makes ReactJS different from traditional web development?
Traditional web development often involves manipulating the DOM directly and managing application state manually, which becomes complex in large applications. React introduces a component-based approach with predictable state management and efficient rendering through the Virtual DOM, making applications more maintainable and performant.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what ReactJS is goes far beyond memorizing a definition. It’s about recognizing a paradigm shift in how we construct digital experiences—towards modular, performant, and user-centric applications. From its core principle of components to its advanced performance optimizations, React provides a robust foundation for everything from simple websites to the most complex enterprise platforms.
Ready to transform your web presence with ReactJS? Newwave Solutions brings deep expertise in custom ReactJS development, helping you leverage this powerful technology to create exceptional user experiences. Contact us today to discuss how ReactJS can accelerate your business objectives and deliver the competitive edge you need in today’s digital landscape.
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply