What is Apache Struts? The Ultimate Guide to Enterprise Java Framework
In the world of enterprise Java development, where modern frameworks and microservices dominate conversations, there exists a battle-tested solution that has powered critical business applications for decades: Apache Struts. But what is Apache Struts, and why do many large enterprises still rely on this mature framework for their mission-critical systems? Understanding Apache Struts is essential for developers and businesses maintaining legacy enterprise applications or working in environments where stability and proven architecture are paramount. This comprehensive guide explores Struts’ enduring value, its enterprise capabilities, and why it remains relevant in specific business contexts.
What is Apache Struts?
Apache Struts is an open-source, enterprise-level web application framework for Java that implements the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern, designed specifically for building large-scale, maintainable web applications. Created by Craig McClanahan and donated to the Apache Foundation in 2000, Struts was one of the first comprehensive frameworks to bring structure and organization to Java web development. It provides a standardized approach to building web applications that separates business logic, data presentation, and user interaction.

So, what is Apache Struts software in practical terms? It’s a framework that extends the Java Servlet API and provides a structured architecture for building web applications. Unlike more modern approaches that might prioritize rapid development, Struts emphasizes architectural purity, separation of concerns, and enterprise-grade stability. This makes it particularly valuable for maintaining legacy systems in sectors like fintech and banking software development services, where system reliability is non-negotiable.
Key Characteristics of Apache Struts:
- Pure MVC Implementation: Strict separation of Model, View, and Controller components
- Configuration-Driven: Extensive use of XML configuration for application structure
- Tag Library Ecosystem: Comprehensive custom tag libraries for JSP development
- Enterprise Focus: Designed for large-scale, complex business applications
- Mature Ecosystem: Decades of development and refinement
Why Choose Apache Struts?
You should consider Apache Struts when working with legacy enterprise systems, maintaining large-scale Java applications, or in environments where architectural purity and separation of concerns are prioritized over rapid development. While newer frameworks offer different advantages, Struts provides unique benefits in specific enterprise contexts.
1. Proven Enterprise Stability
Apache Struts has been battle-tested in thousands of enterprise applications over more than two decades. This extensive real-world usage means the framework is exceptionally stable and reliable for ERP and CRM development services, where system downtime can have significant business impacts. The framework’s maturity makes it a safe choice for maintaining critical business systems.
2. Clear Architectural Separation
Struts enforces a strict MVC architecture that clearly separates business logic (Model), presentation (View), and application flow (Controller). This separation is invaluable for large teams working on complex software development projects where multiple developers need to work on different application layers simultaneously without conflicts or dependencies.
3. Comprehensive Tag Libraries
The framework provides extensive custom tag libraries that simplify Java Server Pages (JSP) development. These tags handle common web development tasks like form processing, data iteration, and internationalization, making it easier to build consistent user interfaces for CMS development services and other content-heavy applications.
4. Extensive Documentation and Community Knowledge
With over twenty years of community development, Apache Struts has accumulated extensive documentation, troubleshooting guides, and community knowledge. This wealth of information is particularly valuable for teams maintaining legacy systems or for organizations that need to hire Java developers for long-term application maintenance.
Apache Struts 1
Apache Struts 1 was the pioneering web framework that introduced a standardized approach to building Java web applications using the Model-View-Controller architecture. It provided developers with a structured way to organize code, separating business logic from presentation layers through specific components like ActionServlet, Action classes, and ActionForms.
During its peak, organizations chose Struts 1 because it solved the problem of unstructured Java web development. Before Struts, developers often mixed Java code with HTML in JSP pages, creating maintenance nightmares. Struts 1 brought discipline and structure, making it easier for large teams to collaborate on complex projects following a consistent SDLC.
Main Uses and Applications
Struts 1 was primarily used for building large-scale enterprise applications during the early 2000s. It became the framework of choice for banking software development, creating online banking platforms, ERP development services, building complex business management systems, and government agencies developing citizen service portals. Many insurance companies also relied on Struts 1 for their software development platforms.
Benefits
- Proven Stability: Extremely reliable for production environments
- Clear Architecture: Enforced separation of concerns through MVC
- Rich Tag Library: Comprehensive JSP tags for rapid UI development
- Form Validation: Built-in validation framework for user input
- Internationalization: Strong support for multi-language applications
Limitations
- Complex Configuration: Heavy reliance on XML configuration files
- Testing Difficulties: Hard to unit test due to tight coupling with the servlet API
- Limited Flexibility: Rigid architecture that’s hard to customize
- Single Thread Model: Action classes aren’t thread-safe by design
Apache Struts 2
Apache Struts 2 is a modernized version that combines the best features of Struts 1 and WebWork, offering enhanced flexibility, better testability, and improved architecture for contemporary enterprise applications. Released in 2007, it maintains the MVC principles of Struts 1 while introducing a more flexible, interceptors-based architecture that’s easier to test and extend.
Organizations choose Struts 2 when they need the enterprise capabilities of Struts 1 but with modern architecture features. The framework’s interceptors, improved testing support, and annotation-based configuration make it suitable for teams practicing agile SDLC methodologies and for applications that need to integrate with modern web services and APIs.
Main Uses and Applications
Struts 2 is used for modern enterprise applications requiring more flexibility than Struts 1 could provide. It’s particularly suited for fintech solutions needing robust security, CRM development requiring customizable workflows, and real estate software that needs complex form handling and validation.
Benefits
- Enhanced Testability: POJO actions are easy to unit test
- Flexible Architecture: Interceptor-based processing pipeline
- Modern Configuration: Support for annotations alongside XML
- Better Integration: Easy integration with other frameworks like Spring
- Improved Tag Library: More powerful and flexible expression language
Limitations
- Migration Complexity: Difficult to upgrade from Struts 1
- Security Concerns: Has experienced significant security vulnerabilities
- Performance Overhead: The Interceptor stack can impact performance
- Learning Curve: More complex than Struts 1 for new developers
What is Apache Struts Used For?
Apache Struts is used for building robust, scalable enterprise web applications by providing a structured framework that handles common web development challenges through its comprehensive feature set. The framework’s MVC architecture and component-based design make it particularly suited for large-scale business applications that require maintainability, security, and long-term stability.
1. Large Web Applications / Enterprise Systems
Struts provides the architectural foundation for building massive-scale business applications that serve thousands of users while maintaining code organization and team collaboration efficiency. The framework’s strict separation between business logic, presentation, and request handling allows multiple development teams to work simultaneously on different application areas. This is crucial for ERP and banking software, where complex business workflows and regulatory compliance require stable, maintainable systems. The configuration-driven approach ensures applications remain organized as they scale to hundreds of pages and features.
2. Form Handling and Validation
Struts automates user input collection, data validation, and error message handling, making form-intensive applications easier to develop and maintain. The framework automatically captures form data and converts it into Java objects while validating against business rules. For insurance software development services and fintech solutions involving complex forms with conditional logic, Struts manages validation efficiently through declarative configuration. This eliminates repetitive error-checking code and ensures data integrity across all user inputs.
3. URL Routing / Request Mapping
Struts acts as a traffic director for web applications, routing user requests to appropriate processing code based on clean, manageable URL patterns. The framework maps user-friendly URLs like “/customers/view-profile” to specific action classes, creating meaningful, bookmarkable paths ideal for CRM development. This central routing configuration also manages security rules and enables seamless URL transitions as applications evolve, maintaining backward compatibility while supporting business changes.
4. Support for AJAX, JSON, REST, and Integration
Struts bridges server-side Java development with modern web experiences through built-in support for AJAX, JSON data exchange, and RESTful web services. The framework seamlessly integrates with JavaScript frameworks, returning JSON data for dynamic updates without full page reloads. For real estate development solutions combining interactive maps with backend data, Struts serves as a reliable API provider. The REST plugin enables clean APIs for mobile apps and single-page applications, supporting modern SDLC methodologies.
5. Internationalization (i18n) and Localization
Struts simplifies creating multi-language applications with comprehensive support for different languages, date formats, and cultural contexts. The framework stores text messages and formatting rules in external resource files rather than hardcoded values. For global ERP development solutions, Struts automatically detects user preferences and serves localized content. This centralized approach makes adding new languages straightforward through additional resource files, significantly reducing maintenance effort.
6. Template & Layout Management
Struts maintains visual consistency across large applications through template systems that define common layouts while allowing page-specific customization. The templating system lets developers define headers, footers, and navigation once for reuse across multiple pages. This ensures brand consistency for CMS development and reduces duplication. When design changes occur, updates happen in template files rather than individual pages, speeding up maintenance and new feature development.
7. Extensibility and Plugin Architecture
Struts extends functionality through a robust plugin system that integrates new capabilities or custom components seamlessly. The framework allows custom plugins for specialized requirements like PDF generation, advanced caching, or domain-specific authentication. This is vital for software development services working with unique business domains, enabling clean integration of custom features without framework workarounds. The architecture future-proofs applications by supporting new technologies and evolving requirements.
How Apache Struts Works?
Apache Struts works by organizing web applications into three main components that follow the Model-View-Controller pattern, creating a clear separation between business logic, data presentation, and user interaction management. That means it splits an application into 3 clear parts:
- Model: The business logic and data
- View: What the user sees (web pages, forms, buttons)
- Controller: The traffic cop that directs requests and responses
Let’s walk through what happens when someone uses a Struts-based web app:
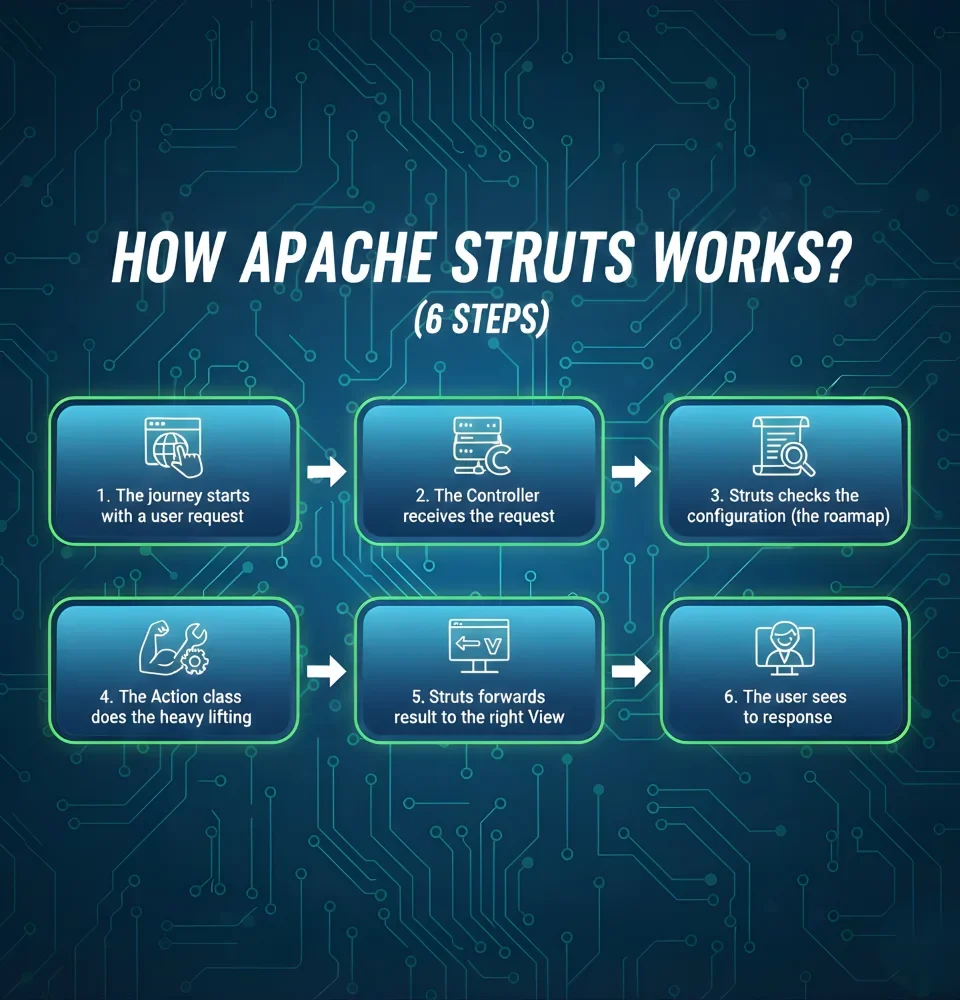
1. The journey starts with a user request
When a user clicks a link or submits a form, their action creates an HTTP request. For example, pressing “Submit Order” sends a request to the server. Instead of sending it directly to the business logic, Struts makes sure this request first goes through a central component that can manage it properly.
2. The Controller receives the request
In Struts, this role is handled by a special controller called the ActionServlet (or FilterDispatcher in Struts 2). You can think of this servlet as a traffic manager: every incoming request stops here first. It doesn’t process the order itself but checks the rules to decide which part of the system should handle it.
3. Struts checks the configuration (the roadmap)
To know where to send the request, Struts looks into a configuration file (traditionally struts-config.xml or annotations in Struts 2). This file works like a map of routes. For instance, it might say:
- If the request is for /submitOrder, send it to the OrderAction class.
- If the request is for /loginUser, send it to the LoginAction class.
This mapping system makes the application flexible and easy to expand without rewriting everything.
4. The Action class does the heavy lifting
Once the right route is identified, the request is passed to an Action class — a plain Java class that holds the business logic. This is where the real work happens. For example, in the case of submitting an order, the Action class may:
- Validate the order form data.
- Communicate with the database to save the order.
- Trigger business rules (e.g., apply a discount if conditions are met).
If everything goes well, the Action class returns a “success” result. If there’s a problem, it may return “error” or another status that tells Struts what should happen next.
5. Struts forwards the result to the right View
After the Action finishes, Struts knows which View (usually a JSP page) should be displayed. It could be:
- A confirmation page if the order was placed successfully.
- An error page if validation failed.
Here, Struts also makes sure that any important data (like user messages, error codes, or saved order details) is passed to the View so that the user sees the correct information.
6. The user sees the response
Finally, the chosen JSP page is rendered and sent back to the user’s browser. From the user’s perspective, it looks simple: they clicked a button, and the system instantly gave them the right response. But behind the scenes, Struts has carefully managed each step so the application stays reliable and organized.
>>> Why is this workflow powerful?:
By controlling the flow in this way, Struts achieves several important goals:
- Developers don’t need to mix business logic with user interface code, making applications easier to maintain.
- Large teams can work in parallel — some focus on Views, others on business logic, and others on configuration.
- Applications become more scalable and adaptable because new features can be added simply by updating the configuration and creating new Action classes.
In summary, Apache Struts works like a well-organized pipeline. A request from the user flows through a controller, is matched against a roadmap, processed by the right Java class, and finally returned as a clean response on the user’s screen. This structure is what makes Struts such a useful framework for enterprise-level web applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Apache Struts offers enterprise-grade stability and clear architectural separation, but requires significant configuration and has been largely superseded by more modern frameworks.
Advantages
- Proven Stability: Decades of real-world use in critical enterprise applications
- Architectural Clarity: Strict MVC separation makes large applications manageable
- Comprehensive Tag Libraries: Extensive JSP tags simplify view development
- Enterprise Features: Built-in support for internationalization, validation, and tiles
- Extensive Documentation: Comprehensive resources accumulated over 20+ years
Disadvantages
- Complex Configuration: Heavy reliance on XML configuration files
- Learning Curve: Requires understanding of multiple framework components
- Modern Alternatives: Newer frameworks offer more productivity features
- Security Considerations: Requires careful configuration and updates
- Less Agile: Not designed for rapid prototyping or MVP development
Why Partner with Newwave Solutions for Struts Development?
Maintaining and extending Apache Struts applications is not just about knowing Java; it requires specialized expertise in legacy frameworks, enterprise security, and strategic modernization. At Newwave Solutions, with beginning is a dedicated Java Team, we combine deep Struts knowledge with modern Java development practices to help businesses keep mission-critical systems running smoothly while planning for the future.
By choosing us, you gain more than a development partner — you gain a trusted advisor who ensures your Struts applications remain secure, reliable, and aligned with your long-term business goals.
Strategic Benefits of Partnering with Newwave Solutions:
- Legacy System Maintenance: Safe and efficient upkeep of Struts-based applications to ensure stability and performance.
- Modernization Planning: Strategic consulting on when and how to modernize, migrate, or re-architect Struts systems.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Proactive assessments and hardening against vulnerabilities to protect critical business data.
- Knowledge Transfer & Training: Clear documentation and hands-on training for in-house teams to maintain confidence and control.
Apache Struts remains a powerful framework for enterprise web applications, but maintaining and modernizing it requires expertise that goes beyond standard Java development. By choosing our hire Java developers services, you gain a reliable partner who not only keeps your Struts systems secure and efficient but also guides you toward long-term modernization. From routine maintenance to strategic upgrades, we deliver the innovation and stability your enterprise needs to stay competitive in the digital era. Ready to future-proof your Struts applications? Partner with Newwave Solutions today!
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply