What is Spring Framework? The Essential Guide to Taming Java Complexity

Your Java application is growing, but so is its complexity. What starts as clean code can quickly become a tangled web where a simple change risks breaking everything, slowing innovation to a crawl. This complexity is the true enemy of agile development. The solution for millions has been the Spring Framework. But what is Spring Framework at its heart? It’s the essential toolkit that tames Java’s complexity, turning chaotic code into a structured, manageable, and powerful asset. Let’s strip away the buzzwords and see how it actually works.
What is Spring Framework?
Spring Framework is a comprehensive, open-source application framework designed specifically for Java platform development. At its core, Spring Framework provides infrastructure support for developing robust Java applications, allowing developers to focus on business logic rather than the underlying technical complexities.
The Spring Framework journey began in 2003 when Rod Johnson introduced it as a response to the complexity of Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB). Johnson’s vision was simple yet revolutionary: create a lightweight alternative that would simplify Java development without sacrificing power or flexibility. What started as a solution to EJB’s heavyweight approach has evolved into the most widely adopted Java framework, powering everything from small startups to Fortune 500 enterprises.
The framework operates on several fundamental principles that make it distinctive in the Java ecosystem:
- Inversion of Control (IoC) serves as Spring’s backbone, where the framework manages object creation and dependency injection. Instead of objects creating their own dependencies, Spring’s IoC container handles this responsibility, promoting loose coupling and enhanced testability.
- Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP) enables developers to separate cross-cutting concerns like logging, security, and transaction management from business logic. This separation creates cleaner, more maintainable code by allowing these concerns to be applied declaratively across multiple components.
- Dependency Injection works hand-in-hand with IoC, automatically providing objects with their required dependencies. This principle eliminates the need for manual object creation and management, significantly reducing boilerplate code and improving application architecture.
The framework’s modular architecture allows developers to use only the components they need. Whether you’re building a simple web application or a complex microservices architecture, Spring’s flexible design adapts to your specific requirements without imposing unnecessary overhead.
If you’re looking to implement these concepts effectively, establishing a clear Java Web Development Service methodology is the logical next step to ensure these principles translate into maintainable, scalable applications.
Why Should You Consider Spring Framework? The Game-Changing Benefits
Modern development teams face unprecedented challenges in delivering applications that are both feature-rich and maintainable. Spring Framework addresses these challenges head-on, offering benefits that directly impact development velocity, application quality, and long-term sustainability.
1. Simplified Development Through Dependency Injection
Spring’s dependency injection mechanism fundamentally changes how you approach application architecture. Traditional Java development often results in tightly coupled components where objects manually instantiate their dependencies, creating rigid, hard-to-test codebases.
With Spring’s dependency injection, your classes become focused purely on their business responsibilities. The framework automatically wires dependencies based on configuration, whether through XML, annotations, or Java-based configuration. This approach reduces boilerplate code by up to 60% while improving testability since dependencies can be easily mocked or stubbed during unit testing.
2. Enhanced Testability and Code Quality
Spring Framework treats testing as a first-class citizen, providing comprehensive testing support that integrates seamlessly with popular testing frameworks like JUnit and TestNG. The framework’s IoC container makes it incredibly easy to inject mock objects during testing, enabling true unit testing where components are tested in isolation.
Spring’s testing annotations allow developers to load only the necessary application context for specific tests, significantly reducing test execution time. Integration testing becomes straightforward with Spring’s test slices, which provide focused testing environments for specific application layers.
3. Flexible Architecture and Modular Design
One of Spring Framework’s most compelling advantages is its modular architecture. You’re not forced to adopt the entire framework; instead, you can selectively use only the modules that address your specific needs. This modularity prevents application bloat and ensures optimal performance.
The framework’s flexible configuration options – ranging from XML-based configuration to annotation-driven and Java-based configuration – accommodate diverse team preferences and project requirements. This flexibility proves invaluable when integrating with existing systems or when migrating legacy applications gradually.
4. Comprehensive Enterprise Integration
Spring Framework excels at integrating with virtually any enterprise technology stack. Whether you’re working with different databases, message queues, web services, or third-party APIs, Spring provides consistent abstraction layers that simplify integration complexity.
The framework’s transaction management capabilities abstract away the complexity of handling distributed transactions across multiple resources. Spring’s declarative transaction management allows developers to define transaction boundaries using simple annotations, ensuring data consistency without writing complex transaction handling code.
What Challenges Should You Expect with Spring Framework?
While Spring Framework offers tremendous benefits, understanding its challenges helps you make informed decisions and prepare your team for successful adoption. These challenges, when properly addressed, become manageable aspects of your development strategy.
1. The Learning Curve Reality
Spring Framework’s comprehensive nature means there’s substantial ground to cover for teams new to the framework. The learning curve becomes particularly steep when teams attempt to master multiple Spring modules simultaneously while trying to understand the framework’s philosophical approach to dependency injection and inversion of control.
New developers often struggle with Spring’s “magic” – the framework’s ability to wire dependencies automatically can seem mysterious when things don’t work as expected. Debugging configuration issues requires understanding Spring’s internal mechanics, which takes time to develop.
2. Configuration Complexity in Large Applications
As applications grow, Spring configuration can become increasingly complex. Managing numerous beans, understanding bean scopes, and maintaining configuration consistency across multiple environments present ongoing challenges. Large teams often face configuration conflicts where different developers create competing bean definitions or circular dependencies.
XML-based configuration can become verbose and difficult to maintain, while annotation-based configuration can scatter configuration logic throughout the codebase, making it harder to get a holistic view of the application structure.
3. Performance Overhead Considerations
Spring’s reflection-heavy approach, particularly during application startup, can introduce performance overhead. The framework’s dynamic proxy creation for AOP features and extensive class path scanning can impact startup times, especially in large applications with hundreds of beans.
Runtime performance generally remains excellent, but the initial application startup can become a bottleneck in development environments where frequent restarts are necessary.
What is Spring Framework Used For? Real-World Applications
The framework’s versatility makes it suitable for everything from simple web applications to complex distributed systems.
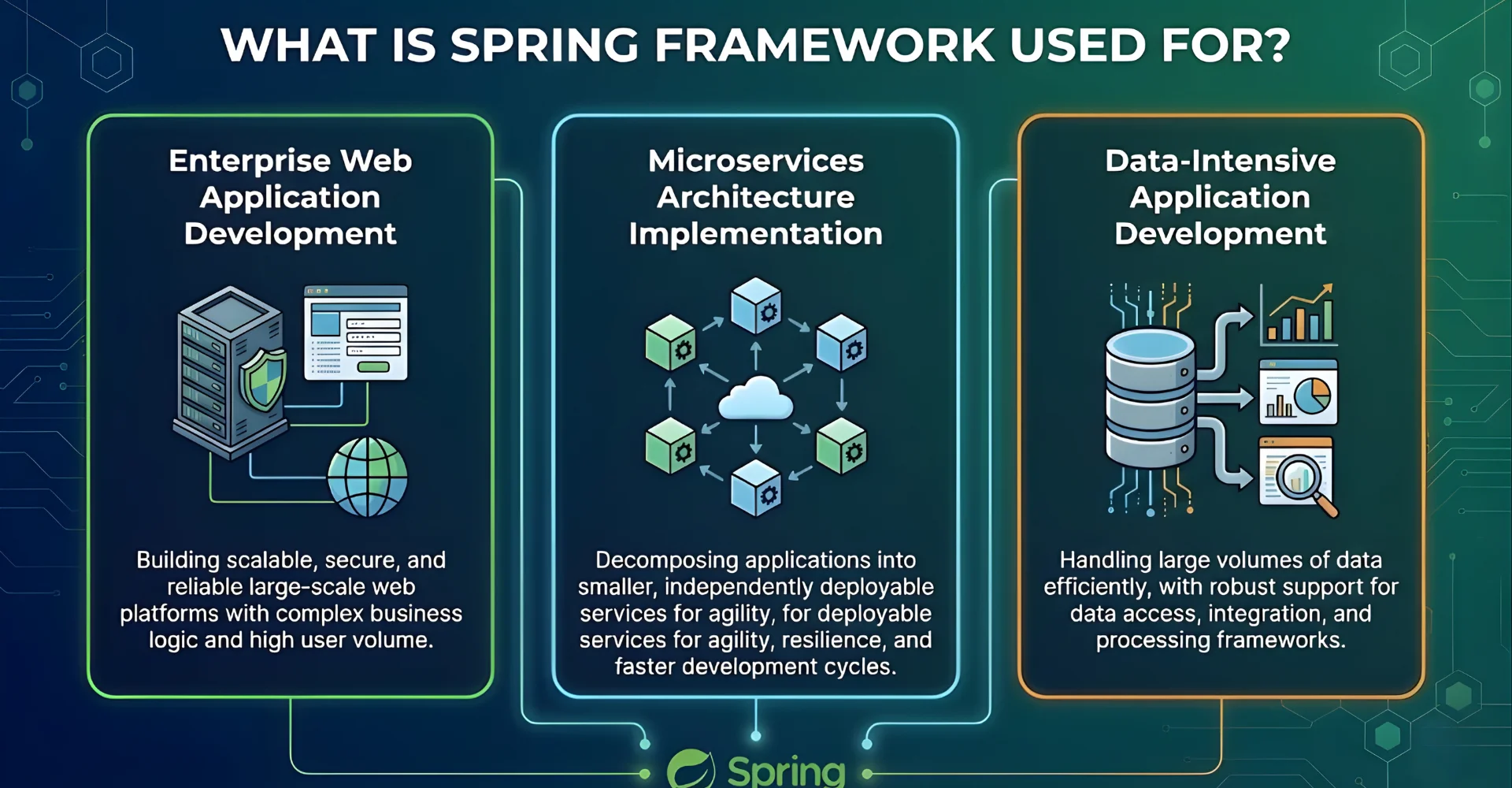
Enterprise Web Application Development
Spring Framework has become the gold standard for building scalable web applications in enterprise environments. The framework’s MVC architecture provides a clear separation of concerns, making applications easier to maintain and test. Spring’s integration with popular templating engines and its robust security features make it ideal for customer-facing applications that require high performance and security.
Key advantages that make Spring Framework ideal for enterprise web development include:
- Robust MVC Architecture: Separates presentation, business logic, and data access layers, enabling independent development and testing of each component
- Security Integration: Built-in support for authentication, authorization, and CSRF protection reduces security implementation time by 70%
- Template Engine Flexibility: Seamless integration with Thymeleaf, JSP, and modern JavaScript frameworks allows teams to choose optimal presentation technologies
- RESTful API Support: Comprehensive HTTP support with automatic JSON/XML marshalling simplifies API development for mobile and third-party integrations
The framework’s support for RESTful web services makes it particularly valuable for organizations building API-first architectures. Spring’s comprehensive HTTP support, combined with its JSON/XML marshalling capabilities, simplifies the creation of robust web services that can integrate seamlessly with mobile applications and third-party systems.
Microservices Architecture Implementation
Spring Framework, particularly through Spring Boot and Spring Cloud, has revolutionized microservices development. The framework provides essential patterns for distributed system challenges: service discovery, circuit breaking, distributed configuration, and distributed tracing.
Critical microservices capabilities that Spring Framework delivers:
- Service Discovery Integration: Native support for Eureka, Consul, and Kubernetes service discovery eliminates manual service endpoint management
- Circuit Breaker Patterns: Resilience4j integration provides automatic failure handling, preventing cascade failures across service boundaries
- Distributed Configuration: Spring Cloud Config enables centralized configuration management across hundreds of microservices with dynamic refresh capabilities
- Distributed Tracing: Sleuth integration provides end-to-end request tracking across complex service call chains for debugging and performance optimization
Spring Cloud’s integration with service mesh technologies and cloud-native platforms makes it the preferred choice for organizations transitioning to cloud-first architectures. The framework’s built-in support for containerization and Kubernetes deployment simplifies the operational aspects of microservices management.
Data-Intensive Application Development
Spring Framework’s data access capabilities make it exceptional for applications requiring complex data operations. Spring Data abstracts away the complexity of working with different database technologies while providing consistent programming models across SQL and NoSQL databases.
Essential data access features that distinguish Spring Framework:
- Multi-Database Support: Unified programming model across SQL databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle) and NoSQL systems (MongoDB, Redis, Cassandra)
- Declarative Transaction Management: @Transactional annotation eliminates boilerplate transaction code while ensuring data consistency across multiple database operations
- Repository Pattern Implementation: Spring Data automatically implements common CRUD operations based on method naming conventions, reducing data access code by 80%
- Connection Pool Management: HikariCP integration provides optimized database connection handling for high-throughput applications
Spring’s support for batch processing through Spring Batch enables organizations to handle large-scale data processing operations efficiently. This capability proves invaluable for industries like healthcare, finance, and telecommunications, where processing millions of records daily is routine.
Spring Framework vs Spring Boot: Which is the Key difference?
A common point of confusion is the difference between the Spring Framework and Spring Boot. They are not competitors but complementary parts of the same ecosystem. Understanding their distinct roles is critical for making the right architectural choice.
| Aspect | Spring Framework |
Spring Boot |
| Configuration Approach | Requires extensive manual configuration through XML or Java config classes. Developers must explicitly configure components, data sources, and security settings. | Provides auto-configuration based on classpath dependencies. Automatically configures common scenarios with sensible defaults. |
| Dependency Management | Manual dependency management requiring explicit version specification and compatibility checking across multiple Spring modules. | Opinionated dependency management through starter packages that bundle compatible versions of related dependencies. |
| Embedded Server Support | Requires external application server deployment (Tomcat, JBoss, WebLogic). Applications are packaged as WAR files. | Includes embedded servers (Tomcat, Jetty, Undertow) enabling standalone JAR deployment with java -jar command. |
| Development Speed | Longer development setup time due to extensive configuration requirements. Higher initial learning curve for new projects. | Rapid application development with minimal configuration. New projects can be running in minutes using Spring Initializr. |
| Production Readiness | Requires additional configuration for monitoring, health checks, and metrics. Manual setup of production concerns. | Built-in production-ready features including health checks, metrics, externalized configuration, and monitoring endpoints. |
| Flexibility vs Convention | Maximum flexibility allows complete customization of application architecture and component configuration. | Convention-over-configuration approach with opinionated defaults that can be overridden when necessary. |
| Deployment Complexity | More complex deployment requiring application server management, WAR deployment, and server configuration. | Simplified deployment model with self-contained executable JARs or Docker containers. |
| Learning Curve | A steeper learning curve requiring deep understanding of Spring’s core concepts before productive development. | A gentler learning curve allows developers to be productive quickly while learning Spring concepts gradually. |
The evolution from Spring Framework to Spring Boot represents a maturation of enterprise Java development practices. Spring Boot doesn’t replace Spring Framework; rather, it builds upon it to eliminate common pain points and accelerate development velocity.
FAQs
Can Spring Framework work with other Java frameworks?
Spring Framework integrates exceptionally well with other Java technologies and frameworks. It works seamlessly with Hibernate for ORM, Apache Kafka for messaging, Redis for caching, and various database technologies. Spring can integrate with legacy systems, third-party APIs, cloud services, and Java app development services. This integration capability is one of Spring’s strongest features, allowing organizations to adopt Spring gradually without replacing their entire technology stack immediately.
Is Spring Framework suitable for small applications or only enterprise systems?
Spring Framework scales excellently from small applications to large enterprise systems. Spring Boot makes it particularly suitable for small applications by providing rapid setup and minimal configuration. Many successful startups begin with Spring Boot for quick development and scale seamlessly as their applications grow. The framework’s modular design means you only include the components you need, avoiding unnecessary complexity in smaller applications.
Is Spring free to use?
Yes, the Spring Framework is completely open-source and free to use, even for commercial applications, under the permissive Apache License 2.0.
How can you handle external configuration in a microservices architecture with Spring?
For a few services, configuration files per environment suffice. For a large-scale microservices architecture, a centralized configuration server like Spring Cloud Config Server is essential. It provides a central place to manage properties for all environments and services. Services can pull their configuration at startup or, with Spring Cloud Bus, can be refreshed at runtime without a full restart.
To sum up
Spring Framework represents more than just a technology choice – it embodies a philosophy of enterprise development that prioritizes maintainability, testability, and architectural flexibility.
Ready to leverage Spring Framework for your next project but need expert guidance to ensure optimal implementation? Consider the options to hire professional Java developers from Newwave Solutions to smoothly apply the Spring framework to your project for the best results. We ensure our experts can help you accelerate delivery, reduce operational costs, and build scalable, high-performance solutions across industries.
Let us assist you in delivering the best Spring framework ever!
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply