Smart Contracts in Real Estate: Unlocking Benefits & Future Potentials

You are buying a house without the mountain of paperwork, the weeks of anxious waiting, or the hefty fees paid to a small army of intermediaries. What if the entire process, from offer to ownership, could be secure, transparent, and completed in days instead of months? This isn’t a distant future fantasy, it’s the reality being built today using smart contracts in real estate. This transformative technology is reshaping the property market, making it more efficient, accessible, and secure for everyone involved. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a real estate investor, or a business professional exploring your next project, this guide will demystify how smart contracts and blockchain are revolutionizing one of the world’s oldest industries.
What is a Smart Contract in Real Estate?
A smart contract for real estate is a self-executing digital agreement where the terms between a buyer and seller are written directly into code and stored on a blockchain network. Think of it not as a traditional paper contract, but as a digital vending machine: you submit the required input (like a payment), and the machine automatically delivers the output (like ownership rights) without any human intermediary. In real estate, this code can automate critical steps like payments, title transfers, and escrow services, executing them only when predefined conditions are met.
The evolution of blockchain smart contracts real estate applications has moved from theoretical concept to tangible reality. Initially confined to cryptocurrency, blockchain technology proved its ability to handle complex, high-value transactions with trust and security. Pioneering companies began applying this to property, moving beyond simple records to manage entire transaction lifecycles. This shift is turning the dream of a seamless, digital property sale from a prototype into a practical tool for the global market.
A famous real-world example for using smart contracts in real estate is the sale of a luxury apartment in Kyiv, Ukraine, by Propy in 2021. The entire transaction, which from the initial offer to the final deed registration was handled via a smart contract on the blockchain. The buyer, from a different country, purchased the property as an NFT (Non-Fungible Token), which represented the digital title. The contract automatically executed the transfer of ownership once the payment was confirmed, showcasing a complete, cross-border real estate deal with unprecedented speed and reduced complexity.
Why Are Smart Contracts Changing Real Estate?
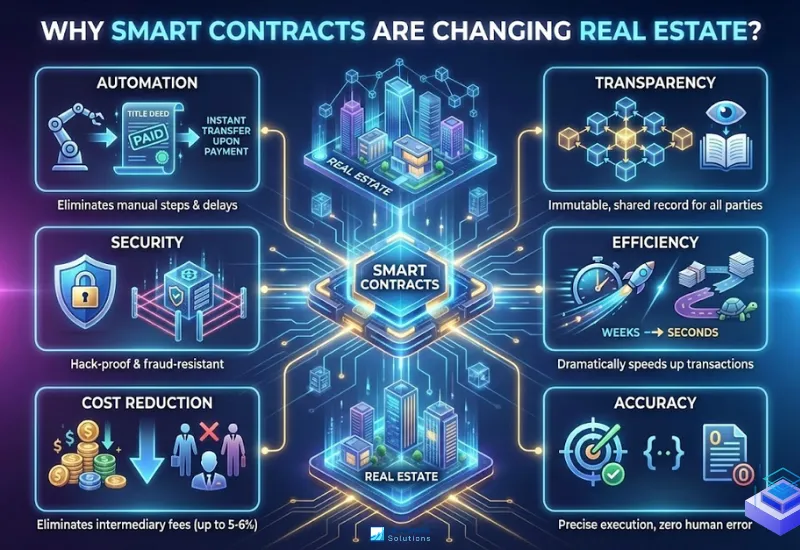
The traditional real estate process is notoriously slow, paper-heavy, and opaque, relying on a chain of intermediaries who each add time, cost, and potential points of failure. Smart contracts for real estate software development solutions disrupt this model entirely by introducing a decentralized, automated, and trustless system. They revolutionize the industry by fundamentally altering how we verify information, execute agreements, and transfer value, replacing manual verification with cryptographic proof and automated code execution. This creates a paradigm shift towards a more efficient and democratic market.
1. Automation
This is the core of the revolution. Smart contracts automatically trigger actions when conditions are met. For instance, the contract can be programmed to instantly transfer the digital property title to the buyer the moment it receives confirmation that the full payment has been made. This eliminates the need for manual follow-ups, checks, and authorizations, streamlining the entire closing process.
2. Transparency
Every term of the agreement and every action taken is recorded on the immutable blockchain ledger. This means all permitted parties—the buyer, seller, lender, and agent—can view the same information in real-time. This shared source of truth drastically reduces misunderstandings and disputes, as no single party can alter the recorded history without consensus from the network.
3. Security
Blockchain technology uses advanced cryptography to secure data. Once a transaction is recorded on the chain, it is nearly impossible to hack, alter, or delete. This protects against common real estate frauds, such as title fraud where someone tries to sell a property they don’t own, because the ownership history is transparent and verifiable by everyone.
4. Efficiency
By cutting out weeks of back-and-forth communication and manual processing between lawyers, brokers, and title companies, smart contracts dramatically speed up transactions. Processes that traditionally take 30-45 days can be compressed into a matter of days or, for simpler terms, even seconds. This frees up capital and resources much faster for all parties.
5. Cost Reduction
Each intermediary in a traditional transaction charges a fee. Smart contracts reduce or even eliminate the need for many of these middlemen. This can save participants up to 5-6% of the property’s value in intermediary fees alone, making transactions more affordable and opening up investment opportunities.
6. Accuracy
Human error in manual paperwork is a significant source of delays and legal issues. And this problem is solved by smart contracts, which are defined by precise code, ensuring that the agreement is executed exactly as written, without typographical errors, misplaced documents, or misinterpreted clauses.
How Smart Contracts Work in Real Estate?
We’re both know the beginning and the result if using real estate applications which apply smart contracts, but what about the details process and how these applications handle data? Understanding how smart contracts work in real estate is key to appreciating their power. The process transforms a physical asset and a legal agreement into a streamlined, digital workflow. It replaces manual, sequential steps with a synchronized, automated sequence of events that are verified and executed by the blockchain network itself, ensuring trust and precision from start to finish.
1. Agreement Creation
The buyer and seller negotiate and agree on all terms of the sale—price, closing date, contingencies (like inspections or financing), and more. Instead of a lawyer drafting a text-based document, a developer (or a user-friendly platform) encodes these exact terms into the logic of a smart contract, which is then deployed to a blockchain like Ethereum or Hedera.
2. Tokenization
The property rights are converted into a digital token on the blockchain—a process known as tokenization. This token (often an NFT for a whole property or a security token for fractional shares) is a digital representation of ownership. It is held in a secure digital wallet, much like a digital deed.
3. Condition Verification
The smart contract constantly checks its predefined conditions using “oracles”—secure external data feeds. For example, an oracle can confirm that a bank wire has been received in an escrow account or that a home inspection report has been successfully uploaded and approved.
4. Automatic Execution
Once all conditions are verified as met, the smart contract self-executes. This means it automatically performs the required actions simultaneously. For example, it instantly transfers the property token (ownership) from the seller’s wallet to the buyer’s wallet and releases the payment funds from escrow to the seller. This is the “if-this-then-that” logic at work.
5. Recording on Blockchain
The entire transaction, the transfer of the token and the funds is permanently and immutably recorded on the blockchain. This creates a verifiable and auditable history of ownership (a “chain of title”) that is transparent to authorized parties and resistant to tampering.
How Property is Tokenized in Real Estate?
Tokenization is the bridge that connects physical real estate to the digital world of smart contracts. It is the process of converting the value of a real-world property into a digital token that can be stored, transferred, and traded on a blockchain.
Get to know the Tokenization Process
- Asset Selection & Valuation: A property is identified, and its market value is established through a professional appraisal.
- Legal Structuring: The property is often placed into a legal entity, like an LLC or a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV). This entity is then owned by the tokens, simplifying ownership transfer and ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Token Creation: Digital tokens representing ownership shares of the legal entity are created on a blockchain. Each token is programmable, containing information about the asset, ownership rights, and share of revenue.
- Token Offering & Distribution: These tokens are then offered to investors through a regulated Security Token Offering (STO) or private sale. Investors purchase tokens using cryptocurrency or fiat money.
- Management & Payouts: The smart contract can automatically manage distributions. For example, it can collect rental income and instantly distribute it proportionally to all token holders’ wallets.
Examples of Tokenization
- Fractional Ownership: Platforms like RealT and Lofty AI tokenize rental properties in the U.S. Investors can buy tokens for as little as $50, representing a fractional share of the property, and receive a proportional share of the monthly rental income automatically through smart contracts.
- Full Asset Tokenization: As with the Propy example in Kyiv, an entire property can be tokenized as a single NFT, allowing the whole asset to be bought and sold in one transaction on the blockchain, streamlining the process for high-value deals.
What are Core Technologies Behind?
The entire ecosystem of blockchain smart contracts real estate is powered by a stack of interconnected technologies. The foundation is the blockchain itself—a decentralized, distributed digital ledger that records transactions across many computers. Smart contracts are the application layer on top of this ledger. They rely on token standards (like ERC-721 for unique NFTs or ERC-20 for fractional tokens) to represent assets and oracles (like Chainlink) to bring real-world data onto the blockchain to trigger contract execution.
Let’s take a summarize of table for Key Technological Components as below:
| Component | Role in Smart Contracts | Example in Real Estate |
| Blockchain Platform | Provides the secure, decentralized infrastructure for deploying and running contracts. | Ethereum, Hedera, Polygon |
| Token Standards | Define how property is represented digitally on the chain (e.g., as a unique asset or fractional shares). | ERC-721 (NFTs), ERC-20 (Fractional Tokens) |
| Oracles | Act as bridges, fetching verified off-chain data (e.g., payment confirmation, KYC checks) to trigger execution. | Chainlink |
| Digital Wallets | Software that holds the cryptographic keys to access and manage digital tokens and assets. | MetaMask, Ledger |
Advantages of Smart Contracts and Tokenization in Real Estate
The benefits of integrating this technology are profound and multi-faceted:
- Enhanced Efficiency and Speed: Smart contracts automate processes like title transfers and payments, reducing transaction times from weeks to days or even seconds. For example, Propy reduced closing times by 30% and costs by 50% in some transactions.
- Cost Reduction: By eliminating intermediaries (e.g., brokers, lawyers), smart contracts save 5-6% of property value in transaction fees. Tokenization also reduces administrative costs associated with traditional financing.
- Increased Liquidity: Tokenization enables fractional ownership, allowing investors to buy and sell shares of properties easily on secondary markets. This unlocks liquidity in traditionally illiquid assets.
- Transparency and Trust: All transactions are recorded on an immutable blockchain, providing a clear audit trail. This reduces disputes over ownership and title defects.
- Accessibility and Democratization: Fractional tokens lower the barrier to entry for real estate investment, enabling small investors to participate in high-value markets. Global access allows cross-border investments without jurisdictional hurdles.
- Security: Blockchain’s cryptographic security minimizes fraud risks, while smart contracts ensure automatic, error-free execution of terms
For the clearly compare with traditional Real Estate, let’s take a look at the below table:
| Aspect | Traditional Real Estate | Tokenized Real Estate with Smart Contracts |
| Transaction Time | 30-45 days (due to paperwork, approvals, and intermediaries) | As low as seconds or days (automated processes) |
| Cost Structure | High (5-6% in intermediary fees; additional administrative costs) | Lower (reduced intermediary fees; automated administration) |
| Ownership Model | Whole-asset ownership predominates; high entry barriers. | Fractional ownership; low minimum investments (e.g., $50) |
| Market Accessibility | Localized and limited by geographical and regulatory barriers. | Global access; cross-border investment facilitated |
| Liquidity | Low (illiquid asset class; slow sales processes). | High (tokens traded on exchanges; near-instant settlements) |
| Transparency | Opaque processes; reliance on centralized records prone to errors or fraud. | Immutable blockchain records; transparent transaction history |
>> View more what can we offer in Blockchain Development Services
Challenges and Risks
Despite the potential, the path to adoption has hurdles:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The legal status of tokenized assets is still evolving. Most are considered securities, requiring compliance with complex regulations that vary by country (e.g., SEC in the U.S., MiCA in the EU).
- Technical Complexity & Integration: Bridging the gap between cutting-edge blockchain systems and legacy government land registries is a significant technical challenge.
- Security of Code: While blockchain itself is secure, smart contracts are only as safe as their code. Bugs or vulnerabilities in the contract’s code can be exploited by hackers.
- Limited Adoption and Education: Widespread understanding of the technology is still low. Overcoming skepticism from traditional industry players is crucial for growth.
The Future of Real Estate with Smart Contracts
The integration of smart contracts and tokenization is not merely a niche innovation, it represents a fundamental restructuring of real estate capital markets. The trajectory is set for explosive growth, with analysts from Boston Consulting Group (BCG) and Citi projecting the market for tokenized real estate assets could reach a staggering $16 trillion by 2030. This growth will be fueled by the unlocking of vast, previously illiquid capital and the democratization of a historically exclusive asset class. The future will be defined by several interconnected and powerful trends:
- AI Integration: AI will supercharge smart contracts with predictive analytics for property valuation, automated risk assessment, and intelligent compliance checks.
- Evolving Regulatory Clarity: As governments establish clearer frameworks (like the EU’s MiCA regulation), institutional investment will flood in, legitimizing and stabilizing the market.
- Interoperability: Solutions will emerge to allow seamless trading of tokenized assets across different blockchain platforms, solving liquidity fragmentation.
- Expansion into New Assets: Tokenization will expand beyond developed properties to include real estate debt, undeveloped land, and other illiquid assets, unlocking new financing models.
Conclusion
Smart contracts in real estate are far more than a buzzword; they are the foundational technology for a more efficient, transparent, and accessible global property market. They solve long-standing industry pain points by automating trust, reducing friction, and unlocking capital. While challenges around regulation and adoption remain, the potential for transformation is undeniable.
For businesses and investors looking to stay ahead of the curve, the time to explore this technology is now. Understanding its mechanics and potential is the first step. The next step is implementation. Our emerging technologies services are designed to guide you through this complex landscape, from initial strategy and legal structuring to smart contract development and deployment. Let Newwave Solutions help you turn the revolutionary potential of blockchain into your next successful business project.
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply