Co Development Software Guide: Benefits and Best Practice

Co development software models are becoming a preferred collaboration approach because they allow internal teams and external experts to work together as one unified unit. This approach is different from traditional outsourcing or in-house development. It combines internal business knowledge with external technical capabilities. This complete guide will be all you need for the best practice before starting co-development software.
What is Co Development Software?
Co development software is a collaborative model where your internal team and an external development partner work together as a single joint team to build software solutions. Unlike traditional outsourcing, which transfers full responsibility to an outside vendor, co development software emphasizes shared ownership, transparent communication, and continuous alignment across all parties involved.
In this model, your internal product experts, engineers, designers, and stakeholders work closely with an external partner’s developers, architects, QA engineers, and project managers. Both sides contribute their strengths. Your team provides domain knowledge, customer understanding, and business logic. The external team contributes technical expertise, engineering capacity, and specialized skills that your internal team may not have.
Co development software is a strategic model used to accelerate development, improve quality, and expand technical capabilities without replacing your internal team. Instead, it augments their strengths while filling knowledge or capacity gaps.
Who Benefits Most from Co Development Software?
- Growing companies scaling faster than internal hiring allows
- Businesses lacking niche skills such as AI, IoT, cloud, security, or complex backend development
- Enterprises modernizing legacy systems but needing external support
- Startups building MVP development projects with limited resources
- Organizations needing reliable partners from offshore development countries
- Companies looking for both speed and knowledge transfer
- Teams unable to maintain full-time specialists in every technology stack
This model works for any company seeking a collaborative software development approach with shared goals and responsibilities.
Co Software Development Applications
Co development software can be applied across many areas where internal teams need external expertise or additional capacity. It works best when collaboration, innovation, and fast delivery are priorities. Below is an overview before diving into the specific applications.
Co-development blends internal business insight with external technical capability. This allows companies to deliver stronger, more competitive digital products across various project types. It ensures flexibility, continuous improvement, and balanced responsibility throughout the SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle).
Product Development
Co development software accelerates product development by allowing teams to work in parallel. Your internal team handles business logic, customer insights, and product decisions. The external partner focuses on engineering, architecture design, QA, and technical execution. This speeds up delivery and ensures your product remains aligned with both technical and business needs.
The results: The product reaches the market faster, with higher technical quality and stronger alignment with user and business needs.
Mobile and Web App Development
In mobile and web app development services, co-development software enhances development speed through shared responsibilities. Internal designers or product managers can maintain creative control, while external engineers execute the technical implementation. This reduces bottlenecks and ensures consistency across front end and back end components.
The results: Faster, more consistent mobile apps with better usability and higher performance across devices.
Legacy Modernization
Modernizing outdated systems requires both deep knowledge of legacy architecture and modern engineering skills. Co-development software helps companies transform old platforms while maintaining business continuity. Your internal team understands the existing system’s workflows, while the external team introduces modern frameworks, cloud solutions, and architecture improvements.
The results: A stable, modern system that preserves business logic while upgrading technology for future growth.
AI, IoT, and Emerging Technologies
Companies exploring AI, automation, IoT, or new digital capabilities often lack specialized engineers. Collaborative software development enables experimentation with emerging technologies solutions while reducing risk. The external partner brings technical depth. Your internal team ensures alignment with business value.
The results: A more innovative product roadmap and the ability to adopt modern technologies with lower risk and higher technical confidence.
Digital Transformation Programs
Large transformation initiatives require long-term collaboration across departments. Co development software allows internal and external teams to work as one unit throughout the SDLC, ensuring consistent progress while maintaining cost control and agility.
The results: More controlled, predictable digital transformation, with minimized disruption to operations.
Large-Scale Enterprise Platforms
Enterprise platforms require long-term development cycles, strict security, heavy integrations, and continuous enhancement. Co-development software supports this scale by enabling external engineers to handle the technical workload while internal teams oversee compliance, process alignment, and business rules. Together, both teams maintain platform stability, introduce new features consistently, and evolve the system without losing control. This approach ensures that enterprise systems stay secure, scalable, and adaptable to changing business demands.
The results: A more scalable, secure, and future-ready enterprise ecosystem.
MVP Development for Startups
Startups need to launch quickly, validate their ideas, and adapt based on market response. Co-development software is ideal for this environment because it allows the internal founder or product team to focus on strategy, customer insights, and business decisions, while the external team executes fast prototyping, technical implementation, and iteration. This collaboration dramatically shortens time for MVP development to market and increases the chances of achieving a successful proof of concept without overspending on internal hiring.
The results: A faster, more cost-effective path to market with a stronger chance of proof-of-concept success.
How Does It Work?
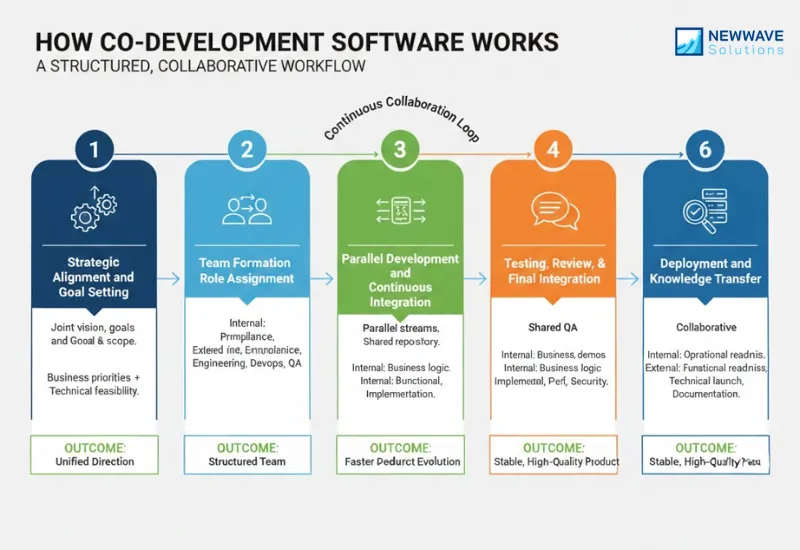
Co development software works through a structured, collaborative workflow where your internal team and the external development partner operate as one unified unit. Instead of handing over the entire project to an outside vendor, both teams stay actively involved during every stage of the SDLC. Your internal team provides business logic, domain knowledge, and product direction, while the external team contributes engineering capacity, technical expertise, and execution strength. The process emphasizes shared responsibility, transparency, and continuous alignment, ensuring that technical decisions and business objectives always move forward together.
Below is a detailed breakdown of how co-development functions across each phase.
1. Strategic Alignment and Goal Setting
The collaboration begins with both teams aligning on the product vision, project goals, scope, and measurable success metrics. This stage clarifies why the product is being built, who the users are, and what outcomes matter most. Internal stakeholders define business priorities and customer expectations, while the external partner evaluates feasibility, proposes the right architecture, and identifies technical risks. This joint understanding creates a unified direction and ensures that every later decision reflects the same strategic intent.
Outcome: Both teams commit to the same direction, same expectations, and same definition of success.
2. Team Formation and Role Assignment
Once objectives are clear, both sides agree on team structure and responsibilities. Your internal team typically owns product thinking, compliance, operational rules, and decision-making. The external team focuses on engineering tasks such as development, architecture, testing, DevOps, and performance optimization. Roles for designers, developers, QA, product managers, and project leads are mapped to avoid overlaps. This structure ensures accountability and smooth coordination when work begins.
Outcome: A unified, well-structured team with no overlapping responsibilities.
3. Parallel Development and Continuous Integration
With roles defined, development begins in parallel streams. Internal teams refine requirements, validate user flows, and clarify acceptance criteria, while external engineers build the core features, set up the architecture, and implement the technical layers. Both sides commit code to the same repository, follow shared coding standards, and integrate changes frequently using continuous integration. This approach reduces merging conflicts, accelerates progress, and maintains consistent momentum across the entire project.
Outcome: Faster delivery with fewer integration conflicts and constant technical alignment.
4. Iterative Feedback Cycles
Throughout development, both teams participate in regular reviews, sprint demos, and feedback sessions. The internal team evaluates whether features meet business rules and user expectations, while the external team updates the implementation based on the feedback. This iterative loop ensures that the product evolves in alignment with actual business needs and not assumptions. It also prevents late-stage rework by catching issues early and adjusting direction quickly.
Outcome: A product that evolves continuously and adapts to feedback without large rework.
5. Testing, Review, and Final Integration
Quality assurance is shared across both teams. Internal members verify business logic and workflows, while the external team handles functional testing, integration testing, performance validation, and security checks. Code reviews involve engineers from both sides to maintain consistency and adherence to shared standards. As development concludes, both teams conduct a final integration cycle to ensure the entire system functions as a unified, stable product.
Outcome: A stable, high-quality product that’s ready for deployment.
6. Deployment and Knowledge Transfer
Deployment is performed collaboratively, with the external partner managing the technical release process and the internal team validating operational readiness. After deployment, knowledge transfer sessions are conducted to ensure your internal team understands the architecture, codebase, and maintenance requirements. Documentation is finalized and long-term support plans are created to maintain product stability and allow future improvements. This phase empowers your team to take full ownership of the product with confidence.
Outcome: The product launches successfully, and your internal team is fully empowered to own and maintain it.
Benefits and Challenges of Co Development Software
Co development software creates strong value by combining strengths from multiple teams. Before exploring each part, it is important to understand that this model is built on partnership, not delegation. You gain access to additional expertise while keeping strategic control.
Benefits
Co development software creates value through shared ownership and blended expertise. It accelerates delivery and improves overall product quality by merging internal business understanding with external technical capabilities.
- Faster time-to-market due to parallel workstreams and continuous collaboration
- Access to advanced technical expertise such as cloud engineering, cybersecurity, AI, or IoT without permanent hiring
- Cost efficiency through scalable external resources without long-term staffing overhead
- Improved quality through cross-team reviews, diversified testing, and peer validation
- Innovation through diverse perspectives where different problem-solving styles uncover better solutions
- Reduced delivery risk by distributing responsibilities across multiple teams
- Stronger product ownership as internal teams remain highly involved throughout the SDLC
- Knowledge transfer that strengthens internal capabilities for future initiatives
Challenges
Despite the advantages, co development software requires discipline and structure to avoid misalignment.
- Coordination complexity when multiple teams work across tools, processes, and time zones
- Communication gaps that can slow development or create incorrect assumptions
- Integration difficulties if both teams use different development environments or coding standards
- Potential conflicts in priorities when internal and external teams have different timelines or expectations
- Cultural differences that affect collaboration style, feedback patterns, or problem-solving behavior
- Security and IP concerns when sharing sensitive code, data, or infrastructure
Managing these challenges requires intentional communication, shared standards, and a strong governance framework.
How to Have the Best Practice for Co Development Software?
Co development software delivers the best results when both teams—internal and external—operate with shared expectations, aligned workflows, and a consistent collaboration framework. It is a discipline that blends shared ownership, cross-team communication, strong governance, and intentional collaboration. Companies that treat co-development as a structured partnership—not a simple outsourcing extension—consistently achieve better outcomes, stronger product velocity, and higher quality releases. Below are the best practices that ensure your co-development strategy remains efficient, scalable, and sustainable:
Define a Shared Vision and Unified Goals
A successful co-development initiative begins with a common understanding of what the product must achieve. Both teams need clarity about the strategic purpose, user needs, and expected outcomes. When the vision is shared, every technical and business decision becomes easier to align.
A shared vision ensures no team overbuilds, underbuilds, or misinterprets requirements. It keeps development focused on business priorities and prevents scope drift caused by differing assumptions. With unified goals documented from the start, both teams work toward the same long-term direction, even as requirements evolve.
Establish a Clear Collaboration Framework
Co development software requires structured communication and well-defined workflows. Without an explicit collaboration framework, even skilled teams can face gaps, delays, or duplicated work. A strong framework clarifies how decisions are made, who approves deliverables, and how issues are escalated.
Establishing ownership requires:
- Defined team roles (e.g., product owner, tech lead, UI/UX lead, QA manager)
- Clear ownership of modules, features, or technical areas
- A documented RACI matrix for decision rights
- Naming escalation contacts for urgent issues
This structure helps both teams operate as one integrated unit rather than as two separate groups. A predictable workflow reduces confusion, strengthens accountability, and ensures fast resolution when challenges arise. It also builds trust—an essential foundation for a long-term collaboration model.
Use Integrated Tools Across Both Teams
Shared tools are the backbone of transparency in collaborative software development. When all teams use the same platforms for task tracking, documentation, code repositories, and communication, information becomes accessible, visible, and easy to validate.
This best practice means integrating teams into:
- Shared repositories (GitHub/GitLab/Bitbucket)
- Common CI/CD pipelines
- Unified coding standards
- Shared project management tools (Jira, Trello, YouTrack)
- Aligned testing strategies
Integrated tools prevent version mismatches, reduce communication overhead, and help teams stay aligned on priorities. They also enable real-time updates, allowing both sides to respond quickly to changes in requirements, dependencies, or technical constraints. The right tools create a single source of truth, which improves consistency and reduces risk.
Create Joint Technical Standards
Technical alignment eliminates many of the integration problems that occur when multiple teams contribute to the same codebase. Joint standards define how code should be written, documented, tested, and reviewed. They also set expectations for security, performance, and scalability.
By agreeing on architecture decisions, naming conventions, and test coverage requirements, both teams produce code that works together naturally. This leads to fewer conflicts during integration, a more maintainable codebase, and a more predictable SDLC. It also helps new developers onboard faster because the rules are consistent across both organizations.
Enable Continuous Feedback and Frequent Demos
Frequent feedback loops ensure the product evolves in the right direction. Instead of waiting until late stages for validation, both teams review progress week by week. Regular demos help the internal team confirm that the product matches business logic and user expectations, while the external team adjusts implementation in real time.
Continuous feedback reduces costly rework, keeps priorities accurate, and prevents misinterpretation of requirements. It also reinforces a culture of transparency and collaboration, ensuring that the product remains aligned with business goals throughout development.
Promote Knowledge Sharing Between Teams
Effective co-development is not only about building the software—it is also about strengthening internal capability. Knowledge sharing ensures your internal team understands the architecture, logic, and rationale behind technical decisions. It reduces long-term dependency and enables your business to maintain and grow the product confidently after release.
Workshops, joint code reviews, pair programming, and documentation sessions help both sides transfer knowledge fluidly. This practice empowers your team and builds a foundation for future phases of development without unnecessary delays or learning gaps.
Foster a Culture of Openness and Trust
Co development software thrives on honest communication and mutual respect. Since both teams share responsibility, they must feel comfortable raising concerns, proposing improvements, and collaborating on solutions. Without openness, small issues can escalate into larger problems.
Building trust encourages faster decision-making, more efficient problem solving, and smoother collaboration. It transforms the partnership from contractual to strategic, enabling both teams to contribute at their highest level.
Plan for Long-Term Scalability and Maintenance
Co-development does not end at deployment. The real value comes from the ability to continue improving, expanding, and maintaining the product over time. Planning for scalability early ensures the product can evolve with business needs, new markets, and increasing workloads.
A long-term maintenance strategy defines how updates, bug fixes, new features, and infrastructure changes will be handled. It ensures the product remains stable, secure, and future-ready. With clear expectations, both teams understand how to support the product even after the initial development cycle.
These best practices form the backbone of high-performing co-development partnerships. When companies embrace clear communication, shared workflows, defined responsibilities, and a strong collaborative culture, co-development software becomes a powerful framework for innovation, speed, and sustainable product growth.
Key Considerations Before Starting
Before engaging in co development software, companies must prepare both technically and operationally. The model works best when both sides share a clear understanding of goals and how the SDLC will be executed. Below is a mix of descriptive paragraphs and bullet points.
Co-development requires alignment on project scope, responsibilities, communication structure, and expectations. Early preparation reduces friction and increases project success.
Important Considerations:
- Clarify your internal team’s needs and skill gaps
- Identify the purpose: speed, skills, innovation, or capacity
- Evaluate external partners based on expertise and culture
- Establish a governance model for decision-making
- Decide which collaboration tools will be used
- Set rules for security, access, and IP protection
- Ensure both teams understand the SDLC steps and handovers
- Align on how progress will be measured
Understanding these key considerations prepares your organization to adopt co-development confidently and effectively. By clarifying objectives, aligning culture, validating technical fit, and establishing proper governance, you lay the foundation for a productive, high-performing partnership.
Outsourcing vs Traditional vs Co Development Software, Which Is Better?
Each development model has its strengths. The right choice depends on your goals, budget, timeline, and internal capabilities. Below is a clear explanation followed by a comparison table.
Traditional in-house development provides strong control but is costly and slow to scale. Outsourcing software services offers cost savings and flexibility but may lack internal influence. Co development software gives you the best of both models by combining shared responsibility with external expertise. It is often preferred when innovation, speed, and collaboration are essential.
Below is a detailed comparison to help you decide which model suits your needs best:
| Criteria | Traditional In-House Development | Outsourcing | Co Development Software |
|---|---|---|---|
| Team Ownership | Full internal ownership | Managed by external partner | Shared ownership |
| Cost Level | High (salaries, overhead, training) | Usually lower; flexible pricing | Moderate; shared resources |
| Speed to Scale | Slow (requires hiring) | Fast (large external talent pool) | Fast and flexible |
| Expertise Availability | Limited to internal team | Depends on vendor specialization | High – combines both teams’ strengths |
| Control Level | Maximum control | Moderate control | High control with shared decision-making |
| Innovation Potential | Depends on internal skills | Depends on vendor quality | High – diverse perspectives drive creativity |
| Risk Level | High (internal bottlenecks) | Shared but depends on vendor reliability | Distributed across teams |
| Best For | Stable, long-term products with predictable needs | Projects with clear scope and tight budgets | Complex products needing speed, innovation, and collaboration |
So which model win?
There is no universal “best” model—each fits different business contexts.
- Traditional Development (in-house development) is ideal when security, full control, and internal expertise are top priorities.
- Outsourcing works well for well-defined projects, cost efficiency, or short-term technical needs.
- Co-Development becomes the strongest model when companies need rapid innovation, specialized talent, and flexible scaling while retaining strategic control.
Co-development software is especially beneficial when building complex products, as it accelerates delivery without relying on in-house resources. This approach is ideal for navigating fast-changing markets that require quick adaptation, illustrating the benefits of in-house vs outsourcing strategies.
When Co-Development Is the Best Choice?
Co-development stands out when you want to:
- Strengthen your internal team without lengthy hiring
- Combine domain knowledge with external technical expertise
- Maintain high speed without sacrificing quality
- Improve innovation through cross-functional collaboration
- Reduce risk by distributing responsibilities
- Keep control over product direction and architecture
For companies scaling digital transformation or building large, ongoing software ecosystems—co-development is often the most balanced and future-proof choice.
Final Thought
Co development software is a powerful model that helps companies accelerate digital product delivery, strengthen innovation, and expand technical capabilities while keeping strategic control. It bridges the gap between internal knowledge and external expertise, making it ideal for businesses scaling rapidly, modernizing systems, or building complex solutions.

Newwave Solutions delivers co development software services with teams based in Vietnam, one of the strongest offshore development countries recognized for quality engineering and cost-effective collaboration. Our teams support full SDLC execution, provide specialized engineering expertise, and enable clients to hire developer services with flexible models for long-term partnership. We help businesses co-create digital products that are modern, scalable, and aligned with their strategic goals. Whether you need support with complex development, modernization, innovation, or expansion, Newwave Solutions is ready to deliver the technical partnership you need.
Ready to accelerate innovation with a co-development partner you can trust? Newwave Solutions is here to help you build smarter, move faster, and scale confidently. Let’s create your next success together.
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply