Software Deployment Process: Steps & Best Practices

A software deployment process is vital for the success of any project nowadays. Typically, many define it as a fixed process of deploying, configuring, and updating software applications to help ensure maximum optimization. However, today’s process can be much more complicated.
This article will help you understand the basics of a software deployment process, as well as its best practices, so you can deploy one to boost your business effectively.
What is Software Deployment?
Software deployment refers to the comprehensive process of delivering, installing, configuring, and activating a software application in a target environment where end-users can access it. This process ensures that the software moves seamlessly from development or staging environments into production, while preserving functionality, performance, and user experience.
For example, a global e-commerce company migrated its platform across multiple servers during a major update, and this deployment enabled them to handle twice the user traffic with zero downtime and improved overall system stability.
>>>Read more: What is Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
What are the Differences between Software Deployment and Release?
In many organisations, these two terms are used interchangeably even though they cover different aspects of software delivery—deployment focuses on the technical rollout, while release emphasises the user-facing availability of new features. Below are the key similarities and differences:
| Deployment |
Release |
|
| Scope | Involves installing and configuring software in environments such as staging or production. | Involves making new features available to end-users, including marketing, documentation, and user readiness. |
| Timing | Often happens multiple times a day in CI/CD pipelines with no immediate user announcement. | Generally aligns with scheduled feature launches, version numbering, or major product updates. |
| Purpose | Ensures that the technical infrastructure is ready, the code is correctly placed, and the environment works as expected. | Ensures that end-users receive the new functionality, are informed, and can adopt the changes smoothly. |
Note: “Software deployment” differs from “software release”. While a software release refers to the iterative process of any given application, a software deployment process includes more functionality, optimization to reduce bugs, and other benefits.
Why Do You Need a Software Deployment Process?
Organising a clear software deployment process provides many tangible benefits for operational efficiency, risk reduction, and business growth. Below are several key advantages:
- Reduced downtime and disruptions: A structured deployment process helps ensure that updates or releases occur with minimal interruption to users and services, thereby maintaining business continuity and customer satisfaction.
- Better quality and stability: Consistent deployment steps allow teams to perform repeated validation, version control, and roll-back planning, which leads to fewer production defects and improved system reliability.
- Faster time-to-market: A well-orchestrated deployment pipeline enables organisations to push new features, security patches, or performance enhancements more rapidly, thereby responding to market changes and competitive pressures with greater agility.
- Improved collaboration and visibility: Defined deployment processes foster clear roles, responsibilities, and communication across development, operations, and product teams, which reduces silos and aligns technical work with business goals.
- Enhanced risk management and compliance: By incorporating testing, verification, and environment controls into the deployment workflow, organisations reduce the likelihood of failures, regulatory issues, or security breaches, and therefore protect their reputation and bottom line.
Every Stage of a Software Deployment Process
A software deployment process mainly includes 3 basic stages, which are development, testing, and monitoring. However, with the increase in complexity of modern technologies, the software deployment process also requires more steps in order to ensure a successful result.

Stage 1: Plan
Making a software deployment plan is an important first step in the software deployment process. There are some questions that you need a clear answer to first at this planning stage, including:
- What software or application are you trying to deploy?
- How many end-users do you expect?
- Are there any risks involved?
Be sure to consider these questions and more before creating your plan.
Stage 2: Design
Designing a successful software deployment can be a daunting task. There are a variety of ways to approach this; however, the best option depends on your specific business needs. You might need to answer questions like:
- Which type of deployment is the safest for your company’s data?
- Do your end users need to have the updated software at the same time, or can it be rolled out slowly?
These goals can be accomplished through different types of software deployment.
Stage 3: Test
To ensure a successful software deployment process, you need to create a test environment that simulates your business. This testing allows you to detect any potential issues before they occur, ensuring a successful software installation.

Stage 4: Schedule
Breaking your software deployment plan into manageable tasks will help to ensure a successful process. Consult with your software developers or use automated software to create a schedule for when each task should be completed. Following a schedule and assigning tasks will make the software deployment process much more manageable and less prone to problems.
Stage 5: Deploy
After completing the previous steps, you’ll be ready to deploy the software to your endpoints. If you’ve followed the instructions carefully, launching your software or future patches should go smoothly. When it comes to software deployment, network-based employment and agent-based deployment are two main methods that are usually used in a software development process:
- Network- or domain-based deployment works by connecting computers, servers, and various devices together. Then, the developers release the software to the IT devices. For deployment to work, all computers which you aim to release the software must be connected.
- Agent-based deployment can successfully deploy software to any device with an internet connection. Newwave Solutions offers software deployment and software development services that have the capability of deploying your project successfully on any device.
7 Main Types of Software Deployment Strategies
There are many types of software deployment available, but here are the 7 most common software build and deployment processes that your business should focus on:
- Basic Deployment: Basic deployment is the simplest type of software deployment. This type updates all the target environments simultaneously without any process or strategy. Because it doesn’t deploy software in a slow and controlled manner, it is the riskiest.
- Rolling Deployment: In rolling deployment, applications are slowly updated by replacing the old application software with the new one. Typically, rolling deployment is completed faster than blue-green deployment, but it also carries some risk because the original application is not preserved.
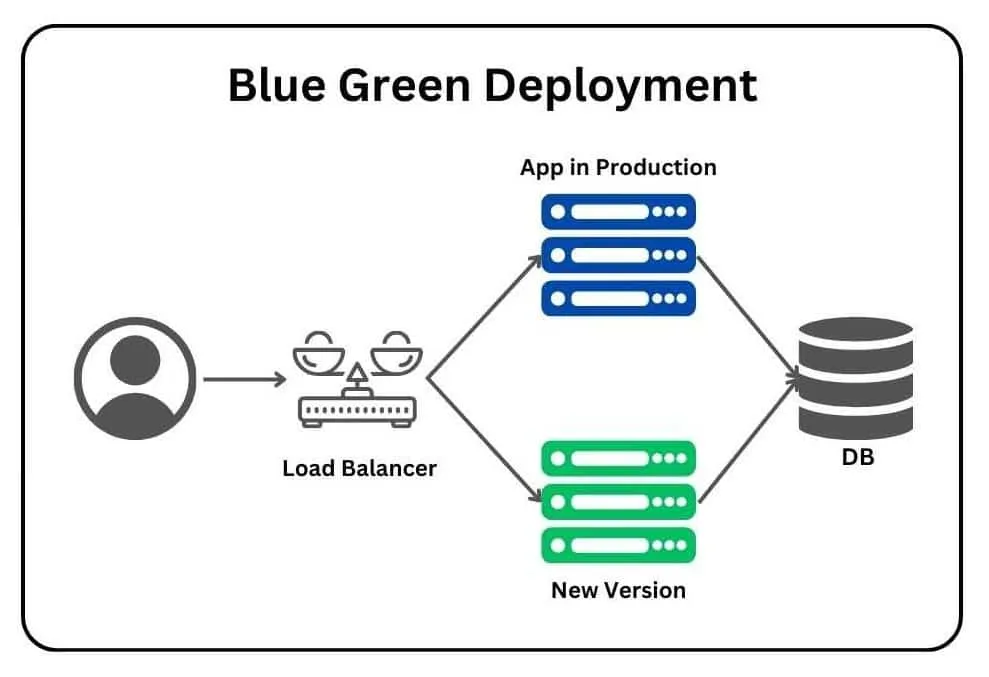
- Blue-Green Deployment: Blue-green deployment starts by having the original environment plus a duplicate environment. This enables you to preserve the old environment while deploying the new application simultaneously. Once the new application is deployed, make sure that everything runs properly. If any issues crop up, traffic can be redirected to the old environment so that it continues to run seamlessly. When you have determined that the new environment is free of issues, you can switch back to the new environment and end the old one.
- Canary Deployment: Canary deployment is when an application is deployed in small batches. Initially deployed, it only goes to a small group of people. Deployment then continues incrementally in staged releases. By doing this type of deployment, you can test the new deployment on a few users before deploying it to the rest of the users.
- Multi-service deployment: A multi-service deployment updates several interdependent services simultaneously within the target environment, which is especially useful when version dependencies span multiple modules. Although this strategy accelerates rollout of interconnected components, it still slows rollback because coordinating multiple services in reverse can become complex.
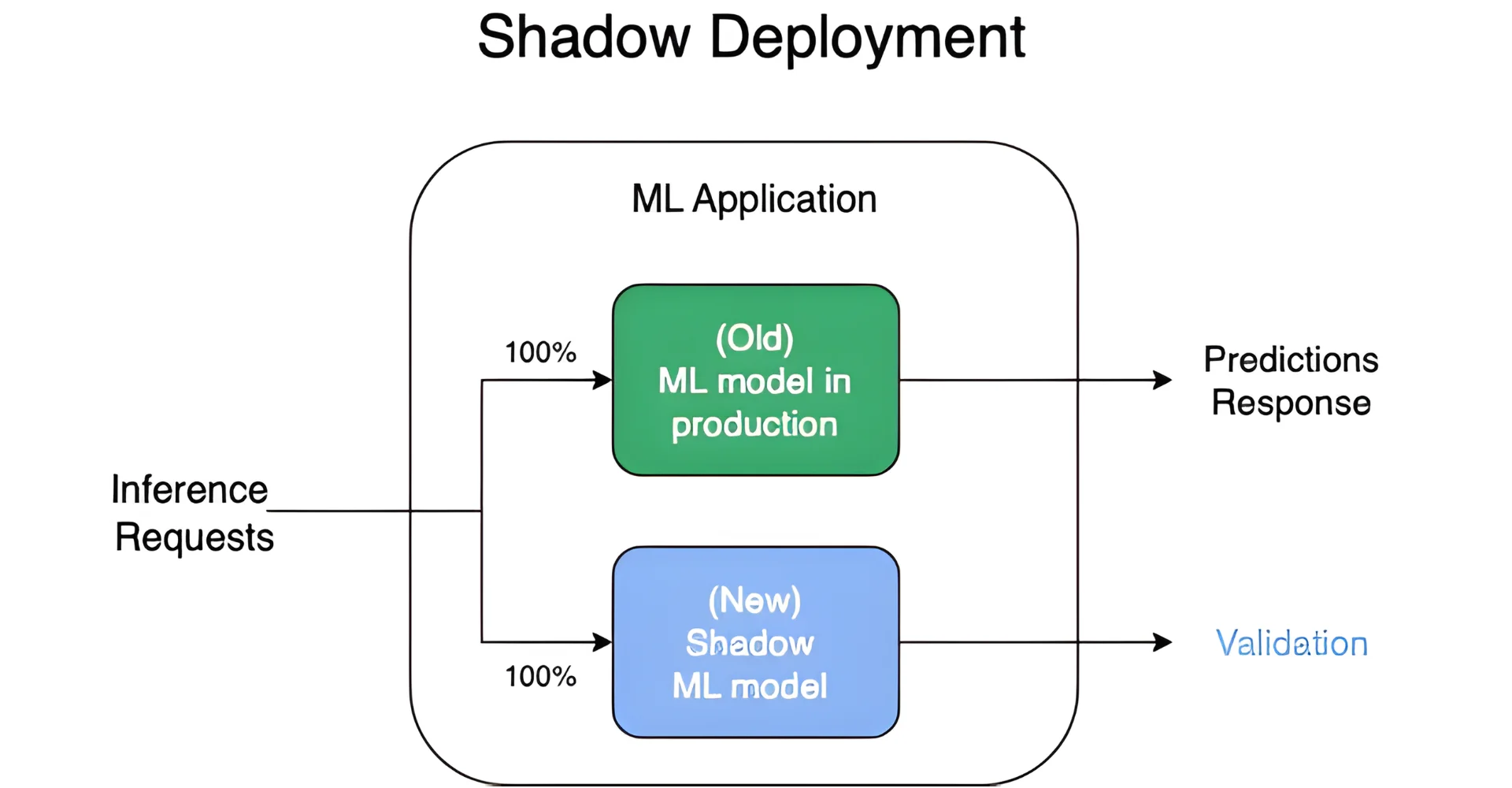
- Shadow deployment: A shadow deployment runs a new version of the application in parallel with the live version, mirroring actual production traffic for analysis while ensuring users remain unaffected. Because it allows teams to test real-world behavior without impacting live customers, this approach is low-risk and highly accurate, although the setup is specialised and demands substantial infrastructure.
- A/B testing deployment: A/B testing in deployment splits production traffic between two or more versions so that organisations can compare user responses and business metrics under realistic conditions. This method goes beyond technical validation to focus on user behaviour and conversion outcomes, providing actionable data to determine which version delivers superior results.
Key Challenges in the Software Deployment Process
- Dependency and environment conflicts: Many deployments fail due to inconsistent configurations or mismatched dependencies between environments, which lead to unexpected behaviour in production. Organizations may mitigate this by standardising environments, employing containerisation, and maintaining detailed configuration management.
- Limited automation and manual processes: Excessive manual intervention in deployment steps increases the risk of human error, slows release cycles, and reduces reliability. Applying automated pipelines and repeatable workflows ensures consistent delivery and fewer defects.
- Inadequate rollback and monitoring strategies: Without clear rollback plans and real-time monitoring, organisations struggle to respond quickly to post-deployment issues, escalating downtime and operational impact. Building robust rollback procedures and proactive alerting systems helps minimise disruption and improve recovery time.
- Scalability and load challenges: As applications grow, deployments must handle increased traffic, data volume and complexity; failure to plan for these can lead to performance bottlenecks and failures. Teams should design deployment strategies with elasticity, load testing, and scalable infrastructure to accommodate growth.
- Cultural and organisational silos: Deployment success often suffers when development, operations and business teams do not align on goals, responsibilities, or communication; this misalignment slows or blocks smooth releases. Establishing cross-functional roles, processes, and shared metrics strengthens collaboration and accelerates deployment readiness.
5 Best Practices for Software Deployment
Define clear deployment objectives and scope: A well-defined plan with stated goals, responsibilities, and rollback criteria creates shared understanding and reduces confusion.
- Use feature toggles and phased rollouts (canary/blue-green): Rolling out changes gradually to subsets of users helps validate new versions in production and minimise the risk of full-scale failures.
- Implement robust monitoring and alerting: Real-time insights into system health, user behaviour, and deployment metrics enable teams to detect issues quickly and act proactively.
- Maintain documentation, rollback plans, and environment consistency: Comprehensive documentation and tested rollback strategies ensure that teams can recover from issues efficiently and maintain traceability across deployments.
- Foster collaboration and continuous improvement: Frequent retrospectives, post-deployment review,s and shared metrics drive learning and process optimisation, which lead to more reliable and faster deployments over time.
- Automate the pipeline and leverage CI/CD: Continuous integration and automatic deployment reduce manual steps, increase release frequency, and lower defect rates.
Conclusion
Effectively implementing the software deployment process will help your business successfully carry out software management for all your devices. It supports the continuity of business operations and prevents extensive downtime. Software deployment used as part of a unified solution with other tools like patch management, endpoint management, and backups/restores can help simplify your business’s digital transformation.
Newwave Solutions software deployment allows you to manage, deploy, and patch your software at scale. Contact us today if you need to hire software developers to support your software deployment process!
Contact Information:
- Head Office (Hanoi): 1F, 4F, 10F, Mitec Building, Cau Giay Ward, Hanoi City, Vietnam
- Branch Office (Tokyo): 1chōme118 Yushima, Bunkyo City, Tokyo 1130034, Japan
- Hotline: +84 985310203
- Website: https://newwavesolution.com
- Email: [email protected]
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply