What Is Apache Cordova? A Complete Guide for Building Multi-Platform Mobile Apps
In today’s mobile-first world, businesses are increasingly turning to hybrid frameworks to cut costs and streamline multi-platform app development. Apache Cordova stands out as an open-source solution that empowers developers to create mobile applications using familiar web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript—all while accessing native device features through simple plugins. This Newwave Solutions’ article explores what is Apache Cordova, how it works, and why tech leaders and enterprises should consider it to unify development workflows and accelerate app delivery.
What is Apache Cordova?

Apache Cordova is an open-source mobile application framework developed by the Apache Software Foundation that allows developers to create mobile apps using standard web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It serves as a bridge between web applications and native device features, enabling hybrid mobile app development without requiring full native coding.
This flexibility makes Apache Cordova app development a popular choice for businesses seeking to reach multiple platforms with a single, cost-effective codebase.
Example: Spotify once used Apache Cordova in early versions of their mobile web app to rapidly prototype hybrid features before fully integrating into native environments. This demonstrated how Cordova helps enterprises test concepts efficiently across multiple platforms, saving both time and resources.
How Apache Cordova Works?
Apache Cordova operates on a hybrid architecture that combines web and native app capabilities, allowing developers to reuse existing web code while accessing device hardware. This architecture enables a seamless bridge between web technologies and native functionalities.
- WebView Container: Hosts the app’s HTML, CSS, and JavaScript inside a native wrapper, allowing it to run like a native mobile app.
- Plugins: Provide access to device APIs such as the camera, GPS, accelerometer, file system, and storage.
- CLI Tools: Enable developers to create, build, and deploy Cordova apps efficiently across multiple platforms.
- Bridges: Translate JavaScript commands into native device calls, ensuring smooth communication between the web layer and device hardware.
What is Apache Cordova Used For?
Understanding what Apache Cordova is used for helps businesses and developers identify how this hybrid framework can meet their goals. The section below highlights the core use cases where Cordova simplifies development, reduces costs, and accelerates deployment across multiple platforms.
- Cross-Platform Mobile Apps development solutions: Cordova allows enterprises to deploy a single codebase across Android, iOS, and Windows, minimizing development overhead.
- Enterprise Dashboards: Businesses use Cordova to create mobile dashboards for analytics and data visualization using existing web assets.
- Rapid Prototyping: Developers leverage Cordova to quickly test app concepts before committing to full-scale native development.
- IoT and Hardware Interfaces: The framework integrates with device sensors and hardware APIs, making it suitable for IoT and connected solutions.
- Hybrid Web-to-App Conversion: Enterprises transform their web portals into mobile apps without starting from scratch, extending usability and customer engagement.
Key Features of Apache Cordova
To fully grasp the power of this framework, it’s essential to explore its key features — the tools and capabilities that make Cordova a strong choice for building mobile apps efficiently. Below are the most important features that drive performance, flexibility, and integration across enterprise environments.
- Single Codebase Development: Cordova allows teams to write once and deploy everywhere, significantly reducing duplication and speeding up release cycles for mobile apps.
- Extensive Plugin Library: It includes a vast range of community and enterprise plugins that provide access to native features such as geolocation, camera, push notifications, and secure storage.
- Open Source & Free: As an open-source framework, Apache Cordova has no licensing costs—making it a cost-efficient solution for startups and SMEs looking to scale mobile presence.
- Command-Line Interface (CLI): The CLI simplifies project setup, plugin management, and build automation, enabling integration into continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) environments.
- Integration with Frontend Frameworks: Cordova easily connects with popular frontend frameworks like Angular, React, and Vue, enhancing UI/UX consistency across web and mobile.
- Support for Enterprise Plugins: It provides access to specialized plugins for security, data encryption, and offline functionality, vital for enterprise-grade applications.
- Cordova WebView (WKWebView): The optimized webview engine improves app performance and rendering speed on both iOS and Android devices.
Pros & Cons of Apache Cordova
Exploring the advantages and disadvantages of Apache Cordova Android helps businesses determine whether this framework aligns with their mobile development strategy. Below, we analyze how Cordova excels in simplifying hybrid app development and where it faces practical limitations for enterprise-grade solutions.
| Pros | Cons |
| Cross-Platform Efficiency – Cordova allows developers to write code once and deploy it across multiple platforms like Android, iOS, and Windows, saving significant time and resources. | Performance Limitations – Because Cordova apps run in a WebView, performance can lag for complex or graphics-intensive applications. |
| Web Developer Accessibility – Developers familiar with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript can easily transition to mobile development without learning new native languages. | Native Dependency – Advanced features depend on third-party plugins, which may become outdated or unsupported over time. |
| Cost Reduction – Maintaining a single codebase minimizes costs associated with separate development teams for each platform. | UI Inconsistency – Visual and interactive elements may not appear identical across devices, affecting user experience. |
| Fast Prototyping – Cordova enables rapid development of MVPs and prototypes, helping businesses validate concepts quickly. | Maintenance Complexity – Managing multiple plugins, OS updates, and dependencies can increase long-term maintenance efforts. |
| Plugin Ecosystem – A wide range of plugins provides access to device functionalities such as GPS, camera, and file system without writing native code. | |
| Open Source & Free – Being completely open-source, Cordova eliminates licensing costs, making it an excellent option for startups and SMBs. |
4 Common Use Cases of Apache Cordova
Apache Cordova has been widely adopted across multiple industries for its flexibility, speed, and ability to reuse existing web resources. Below are examples of how this framework has been applied effectively in real-world business environments.
1. Retail & E-commerce
Apache Cordova helps retail brands accelerate mobile app delivery by reusing existing web codebases and design assets. This approach reduces development time while ensuring consistent user experiences across web and mobile channels. For e-commerce development services, Cordova enables faster launches, unified product displays, and synchronized shopping journeys that support customer retention and conversion growth.
Example: Walmart Labs used Cordova based prototypes to align web and mobile development workflows, enabling rapid feature testing and quicker deployment cycles for its shopping platforms.
2. Logistics & Supply Chain
In healthcare, Apache Cordova supports the development of secure mobile applications that require offline access, device integration, and rapid updates. Healthcare software development services teams use Cordova to build patient apps, internal dashboards, and field data collection tools that function reliably across devices, even in low connectivity environments.
Example: Healthcare providers have adopted Cordova based solutions for patient monitoring and internal reporting apps, improving data availability for clinicians while reducing development and maintenance complexity.
3. Banking & Fintech
Banks and financial institutions use Apache Cordova to develop lightweight internal applications such as reporting tools, compliance dashboards, and employee facing systems. Banking software development services benefit from Cordova’s cross platform capabilities, which reduce costs while maintaining security controls and consistent performance across mobile devices.
Example: Barclays implemented Cordova based hybrid apps for internal transaction monitoring and compliance tracking, shortening development timelines while adhering to strict security and regulatory standards.
4. Education & E-learning
Apache Cordova simplifies the creation of cross platform learning applications that deliver consistent educational experiences on smartphones, tablets, and desktops. Edtech software development solutions leverage Cordova to expand accessibility, support multimedia learning, and reach global users without maintaining multiple native codebases.
Example: Coursera’s early mobile applications used Cordova’s plugin ecosystem to enhance video playback and ensure consistent learning experiences across devices, improving access for learners worldwide.
Apache Cordova vs Other Frameworks (React Native, Flutter, Ionic)
While Apache Cordova focuses on hybrid web-based app development, frameworks like React Native, Flutter, and Ionic provide alternative methods with different strengths. The table below compares them on key criteria to help businesses decide which best suits their needs:
| Criteria | Apache Cordova | React Native | Flutter | Ionic |
| Codebase Type | Uses web technologies (HTML, CSS, JS). | Uses JavaScript and React. | Uses the Dart language. | Uses web stack (HTML, CSS, JS). |
| Rendering Engine | WebView-based rendering. | Native rendering bridge. | Skia rendering engine for native-like visuals. | WebView and native hybrid approach. |
| Performance | Moderate; best for simple and data-driven apps. | High; close to native performance. | Excellent; ideal for animations and complex UIs. | Moderate; faster with Capacitor plugins. |
| Plugin Support | Extensive plugin ecosystem, but dependent on community updates. | Built-in and third-party modules available. | Built-in libraries maintained by Google. | Integrates well with Capacitor and native APIs. |
| Learning Curve | Easy for web developers. | Moderate for React developers. | Higher due to the Dart language. | Easy transition for web developers. |
| Enterprise Usage | Popular for rapid hybrid deployment. | Common in corporate mobile apps. | Used for scalable enterprise-grade apps. | Preferred for cross-platform PWA and hybrid apps. |
| UI Flexibility | Web-based components; less native feel. | Native components; consistent UX. | Custom widgets; highly adaptable UI. | UI flexibility depends on the chosen framework (Angular/React/Vue). |
Verdict:
Apache Cordova remains the most accessible and cost-efficient solution for businesses with strong web teams aiming to build hybrid apps quickly. However, enterprises seeking more advanced UI performance may prefer Flutter or React Native, while Ionic offers a middle ground with enhanced flexibility and modern web support.
How to use Apache Cordova?
Many developers and IT teams find Cordova challenging at first due to its diverse functionality and multi-platform build processes. Based on extensive user experience, this Apache Cordova tutorial outlines the basic setup steps to help you get started with confidence:
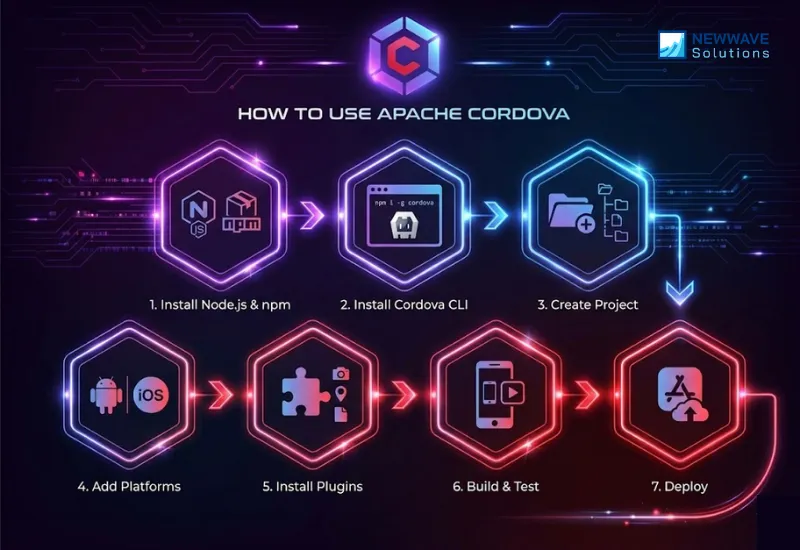
Step 1: Install Node.js and npm.
Apache Cordova relies on Node Package Manager (npm) for managing dependencies and plugins. Download and install both from the official Node.js website.
Step 2: Install Apache Cordova via CLI.
Use the terminal or command prompt and run: npm install -g cordova. This installs Cordova globally for easy project creation and management.
Step 3: Create a New Project.
Run cordova create appname to generate a base project structure. You can later customize folders for assets, scripts, and configurations.
Step 4: Add Target Platforms.
Use commands like cordova platform add android or cordova platform add ios to build for different operating systems.
Step 5: Install Necessary Plugins.
Add plugins such as camera, GPS, or file access using the CLI (cordova plugin add plugin-name) to enable native features.
Step 6: Build and Test the App.
Compile your app using cordova build and test it directly on simulators or connected mobile devices to check functionality and performance.
Step 7: Deploy to Marketplaces or Internal Systems.
Package your app using cordova run for direct deployment to app stores or distribute it within your enterprise system securely.
Apache Cordova’s Future in Hybrid App Development
Apache Cordova’s future is one of managed decline and niche specialization. It will persist primarily as a legacy maintenance tool and a bridge for simpler applications, while ceding ground to modern frameworks for new, performance-sensitive enterprise development.
- Legacy Maintenance & Targeted Simplicity: Cordova’s primary role is now supporting thousands of existing enterprise apps. Its future is in maintaining these legacy systems and building very simple internal tools or MVPs where a pure web skill set is the absolute top priority.
- Superseded by Modern Successors: Frameworks like React Native, Flutter, and Capacitor (a direct, modern evolution of Cordova by Ionic) now dominate new projects. They offer superior performance, better developer experiences, and more modern architectures, making them the preferred choice for new enterprise applications.
- Constrained by a Performance Ceiling: Cordova’s WebView-based architecture inherently limits UI fluidity and complex interactivity. As user expectations for native-like performance rise, this ceiling makes it a less viable choice for competitive, customer-facing applications.
- Evolving into a Plugin Ecosystem: Cordova’s most enduring legacy will be its standardized plugin system. Modern tools like Capacitor maintain compatibility with Cordova plugins, allowing this ecosystem to live on as a foundational bridge for accessing native device APIs, even as direct Cordova usage decreases.
FAQs
Is Apache Cordova free to use?
Yes, Apache Cordova is completely free and open-source, maintained by the Apache Software Foundation. Businesses can use it without licensing fees, making it highly accessible for startups and large organizations alike.
Can Apache Cordova be used for enterprise apps?
Absolutely. Many enterprises use Cordova to create secure internal tools, dashboards, and client-facing mobile apps. Its plugin system allows integration with authentication, encryption, and data storage modules, ensuring enterprise-grade functionality.
What programming languages does Apache Cordova use?
Cordova relies primarily on standard web technologies — HTML, CSS, and JavaScript — to build mobile applications. This makes it easy for web developers to transition into mobile development without learning new native languages like Swift or Kotlin.
How does Cordova differ from React Native?
Cordova runs apps inside a WebView, using web technologies, while React Native renders components using native UI elements for better performance. Cordova is simpler and faster to prototype with, while React Native offers a more native-like experience for complex apps.
Does Cordova work offline?
Yes, Cordova supports offline functionality through local storage and caching mechanisms. This is particularly useful for logistics, retail, and enterprise apps where internet access may be intermittent.
What is the future of Apache Cordova?
Although newer tools like Capacitor have gained attention, Apache Cordova still holds relevance due to its wide adoption and plugin ecosystem. Developers continue to use it for hybrid app projects that prioritize simplicity, cost efficiency, and cross-platform deployment.
Conclusion
As we have analysed what is Apache Cordova, it is a powerful open-source framework that has transformed the way developers build and deploy cross-platform mobile applications, bridging the gap between web and native environments. From our point of view, businesses that aim to develop hybrid or multi-platform applications but lack an in-house team with deep technical expertise should partner with experienced professionals to achieve successful outcomes.
Currently, Newwave Solutions offers cross-platform as well as hybrid app development services designed to deliver high performance, security, and a seamless user experience across iOS, Android, and multiple platforms. By leveraging advanced frameworks like Flutter and React Native, our team creates scalable and cost-effective applications that accelerate development while maintaining exceptional quality and reliability.
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply