What Is Apache Hadoop? Core Technologies & Business Uses

Many B2B companies and large firms struggle with the challenge of processing massive data sets, but cannot find the right technology to manage them effectively. What is Apache Hadoop? It is an open-source framework designed to store, process, and analyze big data across clusters of affordable hardware, making it both powerful and cost-efficient. In this article from Newwave Solutions, you will learn about Apache Hadoop’s components, pros and cons, business use cases, and challenges to see whether this solution can help your company handle large-scale data operations more efficiently.
What Is Apache Hadoop?
First of all, let’s explore a summary of Apache Hadoop if you are unfamiliar with this technology. Apache Hadoop is an open-source framework that allows businesses to store and process large-scale data sets across clusters of commodity hardware. It is designed to handle both structured and unstructured data, enabling enterprises to manage big data efficiently and cost-effectively with scalability and fault tolerance.
For example, Yahoo was one of the earliest adopters of Apache Hadoop, using it to process billions of search queries and user data daily, which significantly improved their ability to deliver faster, more accurate search results at a massive scale.
4 Core Components of Apache Hadoop
Apache Hadoop works by distributing large amounts of data across clusters of low-cost servers and processing them in parallel, which makes it highly scalable and cost-efficient. Its architecture is built on several core components, each serving a specific role that allows enterprises to manage and analyze big data effectively.
The 4 main modules of Apache Hadoop include:
- HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System): HDFS stores massive data sets across multiple machines and replicates them for fault tolerance. Enterprises use it to ensure data remains available and reliable even if hardware fails.
- YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator): YARN manages system resources and schedules tasks across clusters. This allows enterprises to maximize hardware utilization and balance workloads efficiently.
- MapReduce: MapReduce provides a programming model to process large data sets in parallel. Companies apply it to analyze big data quickly, from log analysis to business intelligence reports.
- Common Utilities: Hadoop’s common libraries and utilities provide essential tools that all its modules depend on. These ensure smooth integration and seamless operation across the Hadoop ecosystem.
Pros & Cons of Apache Hadoop
When businesses ask what is Apache Hadoop in big data, the answer often includes both opportunities and challenges. Like any technology, Apache Hadoop comes with several pros and cons that can affect how effectively a company manages its data. The table below outlines these points so you can match them with your current business status, development process, and long-term data demands.
| Pros |
Cons |
| High Scalability – Apache Hadoop can easily process petabytes of data by adding more servers, making it suitable for enterprises with growing data needs. | Complex Deployment – Setting up and maintaining Hadoop clusters requires skilled professionals, which can increase implementation challenges for enterprises. |
| Strong Cost Efficiency – It runs on commodity hardware instead of expensive servers, which reduces infrastructure costs significantly for large organizations. | Limited Real-Time Performance – Hadoop is designed for batch processing and may not perform well for real-time data or small workloads. |
| Built-in Fault Tolerance – Hadoop automatically replicates data across nodes, ensuring data availability and reliability even when hardware failures occur. | High Resource Consumption – Running Hadoop clusters often requires significant storage and processing power, adding to operational overhead. |
| Data Flexibility – The framework supports structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, giving businesses freedom to store and analyze any type of information. | Security Challenges – Older versions lacked strong built-in security features, and enterprises often need extra configurations to secure sensitive data. |
| Rich Ecosystem Integration – Hadoop works well with tools like Hive, Pig, Spark, and HBase, allowing companies to extend its capabilities for advanced analytics. | Ongoing Maintenance Needs – Large Hadoop clusters demand continuous monitoring, tuning, and updates, which can add to long-term costs. |
| Open-Source Advantage – As an open-source technology, it benefits from a global developer community that continuously improves features and provides support. | Steep Learning Curve – Non-technical teams may find Hadoop difficult to adopt quickly due to its complex architecture and operations. |
4 Common Use Cases of Apache Hadoop
Many major businesses have already applied Apache Hadoop to strengthen their big data management strategies and improve decision-making. If you are unsure which areas Hadoop can cover or what is Apache Hadoop used for, the following examples will show you how this technology supports different industries and drives measurable results.
1. Data Warehousing & Analytics
Apache Hadoop provides scalable storage and parallel processing power, making it a strong fit for data warehousing and analytics. Retail companies use it to analyze customer behavior, track inventory, and forecast demand with greater accuracy.
Example: Walmart applies Hadoop to process millions of transactions daily, which helps them improve stock availability and optimize supply chains.
2. Fraud Detection in Finance
Financial institutions rely on Hadoop to analyze massive volumes of transaction data and detect suspicious patterns that could indicate fraud. Its ability to process structured and unstructured data in real time makes it a powerful tool for enhancing security.
Example: Major banks such as JP Morgan use Hadoop frameworks to flag anomalies in customer transactions, reducing financial risks and protecting customer assets.
Explore end-to-end financial software development services to assist your enterprises in streamlining operations, strengthening security, and accelerating digital transformation.
3. Healthcare Data Management
Hospitals and healthcare organizations use Hadoop to manage patient records, medical images, and research data at scale. By applying predictive analytics to healthcare software development solutions, they can identify treatment trends, improve diagnosis accuracy, and enhance patient outcomes.
Example: The Cleveland Clinic has used Hadoop systems to analyze clinical data and support better healthcare delivery.
4. IoT & Sensor Data Processing
Telecommunications companies and manufacturers leverage Hadoop to manage the flood of sensor and IoT data generated by connected devices. Moreover, its distributed architecture enables fast ingestion and analysis of high-velocity machine data.
Example: Verizon has utilized Hadoop to process telecom network data, which improves service reliability and helps monitor equipment performance in real time.
4 Major Challenges of Using Apache Hadoop
Many businesses that adopt Apache Hadoop encounter challenges ranging from technical complexities to performance bottlenecks. If you are facing similar issues, do not worry—these challenges are common, and the troubleshooting guides below will help you resolve them effectively.
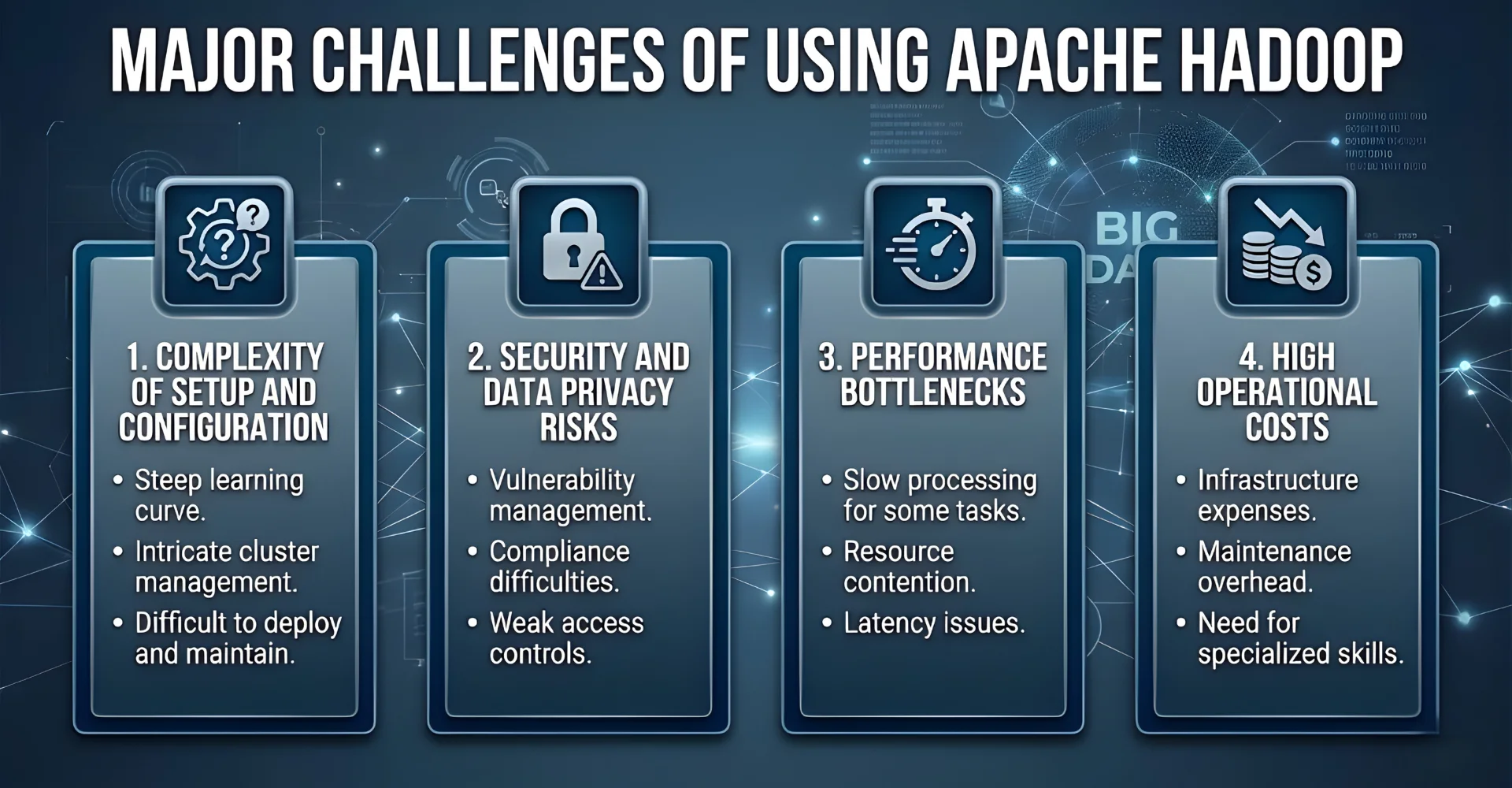
1. Complexity of Setup and Configuration
One of the biggest concerns with Hadoop is its complex installation and configuration process, which requires in-depth technical expertise. This can delay project timelines and overwhelm IT teams that lack Hadoop specialists. As a result, businesses may struggle to get their clusters up and running efficiently.
The best solution is to rely on managed Hadoop services or cloud-based Hadoop offerings such as Amazon EMR or Azure HDInsight. These solutions simplify setup and reduce the need for manual configuration, ensuring faster deployment. Investing in staff training or partnering with experienced vendors also helps maintain smooth operations.
2. Security and Data Privacy Risks
Hadoop’s open-source nature and distributed environment can expose businesses to data privacy and security risks if not configured properly. Unauthorized access, lack of encryption, or poorly managed user roles may result in data leaks. This is especially critical in industries like finance or healthcare, where compliance is mandatory.
Organizations should implement strong security frameworks, including Kerberos authentication, data encryption at rest and in transit, and regular audits. Leveraging Hadoop’s native tools, such as Ranger or third-party solutions, enhances security. Additionally, setting clear role-based access controls can mitigate misuse and unauthorized data exposure.
3. Performance Bottlenecks
As datasets grow, Hadoop clusters may face performance bottlenecks due to inefficient MapReduce jobs, poor resource allocation, or slow hardware. These bottlenecks can lead to delays in data processing and increased costs. If unresolved, businesses risk losing real-time insights, which can impact decision-making.
The solution is to optimize MapReduce workflows, apply caching strategies, and leverage in-memory tools like Apache Spark alongside Hadoop. Proper hardware scaling and cluster monitoring also improve performance. Businesses that continuously fine-tune resource allocation can maintain consistent efficiency even with large-scale workloads.
4. High Operational Costs
While Hadoop is open-source, managing clusters, scaling infrastructure, and hiring skilled personnel can become expensive. Businesses often underestimate the ongoing operational costs, leading to budget overruns. Over time, this may reduce the cost-efficiency advantage of Hadoop.
To overcome this, companies can adopt hybrid models by combining on-premise Hadoop with cloud-based storage and processing. Cloud solutions allow flexible scaling and reduce the need for large upfront investments. Careful cost planning and workload assessment before implementation can also help avoid unnecessary expenses.
Step-by-step on using Apache Hadoop from scratch
For businesses and users who are not yet familiar with this technology, here is a quick and simple guide to get Apache Hadoop set up and running in your system.
- Step 1: Install Prerequisites – You need to set up Java and a Linux environment first, since Hadoop relies on them to function. This ensures that the framework will run smoothly later on.
- Step 2: Download and install Hadoop – Visit the official Apache website to learn how to download Apache Hadoop, then extract and configure the package on your server. Following the installation guide carefully avoids common errors for first-time users.
- Step 3: Configure Hadoop Environment – Edit configuration files such as core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml to define how the system stores and processes data. These settings will allow you to manage nodes and storage effectively.
- Step 4: Format and Start HDFS – Run the command to format the Hadoop Distributed File System, then start the NameNode and DataNode services. At this point, your cluster is ready to handle distributed storage.
- Step 5: Run Sample Jobs – Try simple MapReduce examples like word count to practice how to use Apache Hadoop for processing data. This will give you a hands-on feel for how Hadoop handles parallel tasks.
- Step 6: Add Real Business Data – Once you are confident with sample jobs, upload your company’s datasets into HDFS and run analytical tasks. This step integrates Hadoop into your business system for real use cases.
- Step 7: Monitor and Optimize – Use monitoring tools like Hadoop’s built-in Web UI or third-party tools to track performance. Regular tuning and scaling ensure that your Hadoop system grows with your business needs.
Apache Hadoop vs Other Big Data Technologies
In the last few years, lots of major firms and corporations are on a race to master big data, with advanced technologies emerging to solve complex problems. In such case, while Apache Hadoop remains a major player, the business faces strong competition from platforms like Apache Spark and Google BigQuery. If you want to see how these solutions stack up, the comparison table below highlights the key differences to help you decide the optimal choice.
| Criteria | Apache Hadoop | Apache Spark |
Google BigQuery |
| Speed | Hadoop uses disk-based storage with MapReduce, which makes processing slower for iterative tasks. | Spark uses in-memory computation, which significantly increases processing speed for real-time and batch data. | BigQuery leverages Google’s cloud infrastructure to deliver near real-time query performance for large data sets. |
| Scalability | Hadoop scales horizontally across thousands of commodity servers, making it suitable for very large data volumes. | Spark also scales efficiently, but it requires more memory resources to achieve its best performance. | BigQuery scales automatically in the cloud, offering seamless scaling without user intervention. |
| Ease of Use | Hadoop requires detailed configuration and a steeper learning curve for new users. | Spark is easier to program with APIs in multiple languages, like Python and Scala, but still needs cluster management knowledge. | BigQuery is the easiest, as it offers a serverless model where users only need to write SQL queries without managing infrastructure. |
| Cost | Hadoop is open source and free to use, but managing and maintaining on-premises clusters can lead to hidden costs. | Spark is also open source, but running it at scale (especially in memory) can be expensive. | BigQuery uses a pay-as-you-go model, which can be cost-effective for variable workloads but expensive for constant heavy queries. |
FAQs
1. What is Apache Hadoop tutorial?
An Apache Hadoop tutorial is a step-by-step learning guide that explains how to download, set up, and use Hadoop for storing and processing big data. It is often designed for beginners to understand the basics of the framework and practice with examples.
2. Is Apache Hadoop free?
Yes, Apache Hadoop is an open-source framework, which means it is free to use. However, businesses may still incur costs for hardware, infrastructure, or cloud services needed to run it.
3. What industries benefit most from Hadoop?
Industries that manage massive amounts of data, such as finance, healthcare, retail, telecommunications, and e-commerce, benefit most from Hadoop. They use it to analyze customer behavior, detect fraud, and optimize operations.
4. How is Hadoop different from Spark?
Hadoop relies on disk-based storage and MapReduce for processing, making it slower for iterative or real-time tasks. Spark, on the other hand, uses in-memory processing, which makes it much faster for analytics and streaming data.
5. Can Hadoop be integrated with cloud platforms?
Yes, Hadoop can integrate with cloud services like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. This integration allows businesses to scale storage and computing resources more easily while reducing the need for heavy on-premise infrastructure.
Final thoughts
So far as we have explored about What Is Apache Hadoop?, which is a scalable, flexible, and cost-efficient big data framework built for enterprises managing massive and complex data sets. With its core technologies like HDFS, YARN, and MapReduce, Hadoop offers both power and reliability for industries ranging from finance to healthcare.
In case your enterprise is lacking quality professionals to apply the Apache Hadoop framework smoothly to your current project, consider the option to hire developers from Newwave Solutions. With 14+ years of experience in the IT outsourcing field, Newwave Solutions ensures to deliver exceptional developer resources to assist your entire IT-based project from scratch effectively.
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.



Leave a Reply