What is dApp and How to Use It in Reality?

For many enterprises and innovators exploring blockchain, the question often begins with what is dApp and how it can actually be applied in real-world scenarios. The challenge lies in balancing transparency, security, and usability, which leaves business leaders uncertain about adoption and integration. In this article, Newwave Solutions provides a clear guide for executives, startups, and global organizations to understand dApps, their benefits, and practical ways to leverage them for competitive advantage.
What is dApp?
A dApp (short for decentralized application) is a software program that runs on a distributed network such as a blockchain, instead of being managed by a single centralized server. In simple terms, dApps function much like the mobile or web apps we use every day, but they are powered by blockchain technology and smart contracts, which allow them to work without a central authority controlling the system.
This model, often referred to as what is dApp blockchain, provides users with greater transparency, enhanced control over their own data, and resistance to censorship. Today, dApps are applied across industries, including decentralized finance (DeFi), gaming, social media, healthcare, and digital content distribution, making them a cornerstone of the growing Web3 ecosystem.
Example:
One of the most popular dApps is Uniswap, a decentralized exchange (DEX) built on the Ethereum blockchain. Unlike traditional exchanges that rely on banks or intermediaries, Uniswap uses smart contracts to enable peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trading directly between users.
This model helps the business by ensuring full transparency—all transactions are publicly recorded on the blockchain—while also reducing costs since there are no middlemen. For users, it provides greater control of their assets, instant liquidity, and global accessibility, which has positioned Uniswap as one of the leading platforms in the DeFi ecosystem.
How does dApp work?
The operation of a decentralized application follows a clear flow that combines familiar user interfaces with blockchain-powered logic:
- User Interaction: A user begins by accessing the dApp through a frontend interface, which looks and feels similar to a traditional website or mobile app.
- Smart Contract Execution: When the user makes a request—such as sending funds or performing an action—it triggers a smart contract that defines the rules of the transaction.
- Distributed Processing: Instead of running on a single server, the smart contract is executed across a distributed network of computers (nodes), ensuring no single party controls the process.
- Blockchain Verification: The network of nodes validates the transaction, confirming that it meets the rules defined in the smart contract.
- On-Chain Recording: Once verified, the result is permanently recorded on the blockchain, making it visible to all participants and guaranteeing full transparency.
This flow demonstrates how dApps merge familiar app usability with blockchain’s trustless and transparent infrastructure, offering users greater security and autonomy.
6 Main features of dApps
To understand the value of decentralized applications, it is important to look at their core characteristics. Unlike traditional apps, dApps are designed with built-in transparency, security, and user empowerment. Below are the main features that define how dApps function and why they stand out in the digital landscape.
- Decentralized: dApps run on a peer-to-peer network of computers, called nodes, instead of being hosted on a single company’s server. This decentralization removes single points of failure and enhances resilience.
- Blockchain-Based: The backend logic of dApps operates on a blockchain, which makes the code and transactions publicly verifiable. This ensures transparency and trust among all users without needing intermediaries.
- Smart Contracts: dApps rely on smart contracts, which are self-executing programs where the terms of agreements are embedded directly in the code. These contracts automatically enforce rules, reducing the need for manual oversight.
- User-Owned Data: Unlike traditional apps that store data in centralized databases, dApps allow users to maintain control of their own information. This reduces risks of misuse and improves privacy.
- Censorship Resistance: Because they do not rely on a central authority, dApps are more resistant to censorship or shutdowns. This characteristic ensures continuous access and freedom of use worldwide.
- Crypto Wallets: To interact with a dApp, users typically connect through a crypto wallet such as MetaMask, Trust Wallet, or Coinbase Wallet. These wallets provide secure authentication and a gateway to decentralized networks.
Pros & Cons of dApps
Like any emerging technology, decentralized applications bring both opportunities and challenges. Understanding their advantages and limitations helps businesses and users decide whether dApps are the right solution for their needs. Below is the overview of dApps’ pros & cons.
| Pros | Cons |
| Transparency of transactions | Scalability limitations |
| User control of data | Complex user experience |
| Security through decentralization | Smart contract vulnerabilities |
| Censorship resistance | Unclear legal and regulatory frameworks |
| Trustless peer-to-peer interactions | Higher energy consumption in some blockchains |
| Global accessibility | Slower transaction speeds compared to centralized apps |
| Open-source innovation | Limited mainstream adoption |
| Token-based incentives | Dependence on cryptocurrency markets |
7 Common Use Cases of dApps
Decentralized applications are not limited to cryptocurrency trading—they are transforming multiple industries by offering transparency, security, and user empowerment. Below are the most common fields where dApps are being applied and the impact they bring.
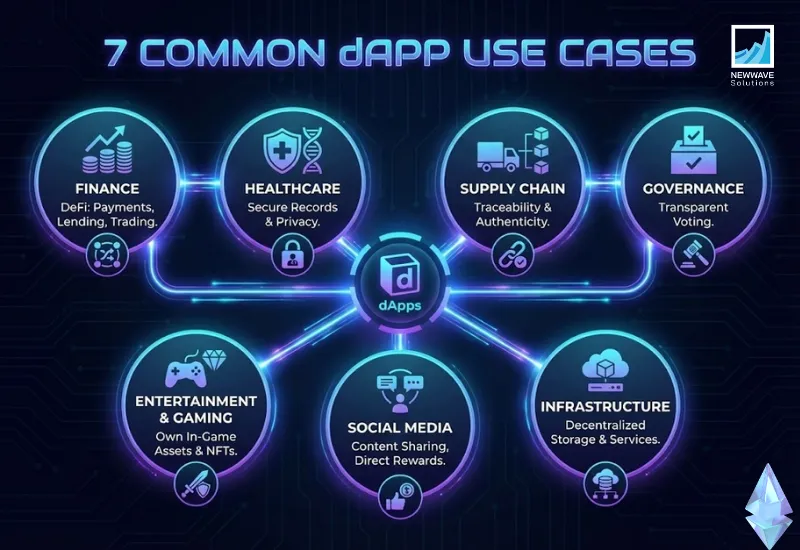
1. Finance
Financial dApps are the most widespread, enabling services such as payments, lending, borrowing, trading, and yield farming without relying on traditional banks. By replacing intermediaries with smart contracts, DeFi dApps make financial services more accessible, cost-efficient, and transparent. This shift empowers users to manage assets directly while reducing fraud and operational costs.
2. Healthcare
In healthcare, dApps can secure patient record management by storing data on a blockchain where it cannot be altered or lost. Patients and authorized professionals can access records transparently while maintaining privacy through encryption. This increases trust in healthcare systems, improves collaboration, and ensures compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
3. Supply Chain
Supply chain decentralized applications (dApps) improve traceability by documenting every stage of a product’s journey on the blockchain. Initiatives such as IBM Food Trust illustrate how tracking provenance guarantees authenticity, combats counterfeiting, and fosters consumer confidence. This impact is especially significant in sectors like food, pharmaceuticals, and luxury goods, where trust and transparency are essential. The integration of blockchain technology in supply chains not only enhances visibility and accountability but also streamlines processes, enabling faster and more secure transactions.
4 . Governance
Governance dApps support transparent voting systems where every ballot is recorded immutably on the blockchain. This eliminates tampering risks, reduces administrative costs, and boosts voter confidence. Governments and organizations can use this model for elections, shareholder voting, or community decision-making.
5. Entertainment & Gaming
Gaming dApps allow players to own, trade, and monetize in-game assets such as NFTs or tokens. Titles like Axie Infinity showcase how blockchain gaming creates new revenue streams for players and ensures true ownership of digital items. This transparency redefines engagement, shifting control from game publishers to the community.
6. Social Media
Social media dApps, such as Steemit, create decentralized platforms for content sharing and communication. Instead of relying on centralized moderation, they reward creators directly with tokens, ensuring transparent monetization. This model gives users more control over their communities and reduces the risks of censorship.
7. Infrastructure
Infrastructure dApps provide essential services that support other decentralized applications. Examples include Filecoin for decentralized data storage, identity verification systems, and blockchain oracles that connect dApps with real-world data. These building blocks are critical to the broader dApp ecosystem, ensuring reliability and transparency.
| Industry | Example | Impact |
| Finance (DeFi) | Uniswap, Aave | Transparent lending, borrowing, and trading without banks |
| Healthcare | Medical record dApps | Secure, tamper-proof patient data sharing and compliance |
| Supply Chain | IBM Food Trust | Provenance tracking, authenticity verification, and consumer trust |
| Governance | Voting dApps | Transparent, tamper-resistant elections and decision-making |
| Entertainment & Gaming | Axie Infinity, NFT games | Transparent ownership and trading of digital assets |
| Social Media | Steemit | Transparent content monetization and reduced censorship |
| Infrastructure | Filecoin | Decentralized storage, identity, and oracle services |
| Business & Supply Chains | Enterprise dApps | Streamlined logistics, transparency, and partner trust |
Potential Opportunities & Challenges of dApps
As decentralized applications (dApp) gain momentum across industries, they present both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. On one hand, dApps are reshaping how finance, healthcare, and digital services operate by enhancing transparency and reducing reliance on intermediaries. On the other hand, they face hurdles such as scalability, regulation, and user adoption that must be addressed before achieving mainstream success.
Opportunities of dApps
- Enhanced Transparency: Every transaction is recorded on the blockchain, increasing trust in industries such as finance and governance.
- User Empowerment: Users gain direct control over data and assets, reducing dependency on centralized service providers.
- Global Accessibility: dApps can be used anywhere in the world, breaking down geographical and regulatory barriers.
- Cost Efficiency: By eliminating middlemen, dApps lower transaction and operational costs for businesses and individuals.
- New Business Models: Tokenization and NFTs create revenue opportunities in gaming, entertainment, and content creation.
- Cross-Industry Innovation: From supply chains to healthcare, dApps introduce new levels of efficiency and accountability.
Challenges of dApps
- Scalability Issues: High transaction volumes can cause delays and increased fees on public blockchains.
- Complex User Experience: Many dApps require technical knowledge and crypto wallets, limiting mainstream adoption.
- Security Risks: Vulnerabilities in smart contracts can lead to hacks, undermining trust and transparency.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments worldwide are still defining legal frameworks for decentralized systems.
- Infrastructure Demands: Reliable internet and blockchain infrastructure are essential, which may be limited in some regions.
- Adoption Barriers: Educating businesses and end users about blockchain remains a key challenge.
How to create a dApp from scratch?
We’ve built and shipped multiple dApps, and the hardest part was never the code—it was choosing the right problem, chain, and security model. Once we learned to validate early with real users and keep the architecture simple, projects moved faster and launched more safely. You can take references from the steps below to go from idea to a production-ready dApp with clarity.
Step 1: Choose a use case
The first step in creating a dApp is to clearly define the problem you want to solve or the goal your application should achieve. By identifying the specific need, you can ensure that the dApp’s design and functionality directly serve a real business or user demand.
Step 2: Choose a blockchain
Next, select the blockchain network that best fits your requirements. Popular choices such as Ethereum, Solana, or Polygon each offer different advantages in terms of transaction speed, fees, and developer ecosystems. The network you choose will directly influence the scalability, cost, and usability of your dApp.
Step 3: Develop the architecture
Once the foundation is set, you need to design the architecture of your application. This includes planning the smart contracts that will handle your logic, integrating wallet connections for user interaction, and determining whether off-chain services, such as oracles or storage solutions, will be required.
Step 4: Test the application
Before going live, it is critical to thoroughly test your dApp in a safe environment such as a blockchain testnet. This allows you to check the functionality of smart contracts, validate wallet integrations, and ensure that the entire system performs reliably under different scenarios.
Step 5: Launch the dApp
Finally, once the testing phase confirms stability and security, you can deploy your dApp to the main network. After launch, it is important to continuously monitor performance, track user activity, and gather feedback so that the application can evolve and remain trustworthy for its users.
FAQs
Why is transparency important in dApps compared to traditional apps?
Transparency plays a crucial role in decentralized applications (dApps) because it allows all transactions and activities to be publicly verifiable on the blockchain. This transparency builds trust among users, as they can independently confirm actions without relying on intermediaries. In contrast, traditional applications often operate in closed environments, where data access is restricted and users must trust the platform to manage their information accurately and securely.
Are all dApps truly transparent?
While the majority of dApps are designed to be transparent, the level of transparency can differ based on the architecture of the smart contracts and the methods used for data storage. Some dApps operate on public blockchains, enabling users to view all transactions. However, if a dApp utilizes private or permissioned blockchains, this can lead to limited visibility. Thus, users should assess each dApp’s transparency features to understand how their data and transactions are handled.
How can users verify transactions on a dApp?
Users can verify transactions by utilizing a blockchain explorer, a tool that provides access to the data stored on the blockchain. These explorers allow users to search for specific transactions, wallet addresses, and block details. Since every transaction is permanently recorded and immutable, users can rely on explorers to confirm the legitimacy and history of transactions on the dApp, ensuring accountability and accuracy.
Do transparent dApps compromise privacy?
No, the transparency of dApps does not inherently compromise user privacy. While transactions are visible on the blockchain, user identities are typically anonymized and represented by cryptographic wallet addresses rather than personal information. This distinction means that individuals can participate in a transparent system without revealing their identities, thereby maintaining a level of privacy while still enjoying the benefits of blockchain transparency.
What industries benefit most from dApp transparency?
Several industries significantly benefit from the transparency provided by dApps. In the finance sector, transparency helps reduce fraud and enhances compliance; in healthcare, it ensures accurate patient records and drug traceability; the supply chain industry gains improved tracking and accountability; governance benefits from increased trust in public services; and gaming sees reduced cheating and exploitation. Overall, transparency bolsters trust, enhances fraud prevention, and promotes accountability across these varied fields.
Conclusion
By exploring what dApp is, this blog has shown how decentralized applications work, why transparency is their defining strength, and how they are applied across industries from finance to healthcare. With this knowledge, readers can evaluate opportunities, identify practical use cases, and consider how dApps might enhance trust, efficiency, and innovation within their own businesses.
For organizations and professionals ready to take the next step, Newwave Solutions offers expert guidance and end-to-end support through our DApp Development Services, helping you transform insight into real-world solutions.
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply