What Is Firebase: Google’s Backend-as-a-Service for Developers

What is Firebase? In a digital landscape where speed, scalability, and seamless user experiences define success, Firebase has emerged as a powerful Backend as a Service platform that removes the complexity of traditional backend management. Built on Google’s cloud infrastructure, Firebase enables developers and businesses to build, launch, and scale applications faster by providing real time databases, authentication, hosting, and analytics in a single integrated ecosystem. For developers, product owners, and business leaders seeking to understand how Firebase works, what it offers, and when to use it effectively, this Newwave Solutions guide breaks down everything you need to know to make informed technology decisions and build modern, high performance applications.
What is Firebase?

Firebase is Google’s comprehensive Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS) platform designed to help developers build, improve, and grow applications efficiently across multiple platforms. When considering what is the Firebase, it is best understood as a cloud-based solution that offers real-time capabilities, seamless integration with Google Cloud, and prebuilt backend services that eliminate server management complexity.
Firebase is trusted by startups and large enterprises alike because it enhances scalability, strengthens security, and accelerates application development without compromising performance.
Example: The New York Times uses Firebase to deliver real-time news updates and personalized notifications to millions of readers worldwide. By leveraging Firebase Cloud Messaging and Analytics, the company has improved user engagement and app responsiveness while reducing backend maintenance costs.
How Firebase Works?
Understanding what is Google Firebase requires exploring how its technology architecture functions beneath the surface. Firebase operates as a cloud-powered ecosystem that connects client applications with backend services through real-time synchronization and serverless computing. Its core workflow allows developers to focus on front-end innovation while Google’s infrastructure automatically manages scaling, reliability, and performance.
- Real-time data synchronization: Firebase uses WebSocket-based connections to transmit and update data instantly between clients and servers, ensuring consistency across all devices.
- Cloud-based infrastructure: The platform is fully hosted on Google Cloud, which provides automatic scalability, global availability, and enhanced data security without requiring manual server configuration.
- Modular integration: Developers can choose specific services—such as Authentication, Firestore, or Cloud Messaging—based on project needs, creating a highly flexible development environment.
- Scalable API access: All Firebase APIs are designed to automatically adjust performance capacity according to user traffic and app demand, maintaining responsiveness even under high workloads.
Core Firebase Services and Technologies
When exploring what is Firebase used for, businesses and developers quickly realize that it is more than just a database—it is a complete ecosystem of tools and cloud-based services. Through resources such as the Firebase Console and Firebase Studio, users can easily configure, manage, and monitor their projects in real time. At the core of its functionality lies the Firebase database technology, complemented by a wide range of services that streamline app development and analytics.
- Firebase Realtime Database: This database enables instant data synchronization across users and devices, making it ideal for chat applications, gaming, and collaborative tools that demand real-time interaction.
- Cloud Firestore: Firestore is a scalable NoSQL cloud database that supports complex data structures and enterprise-level workloads for both web and mobile applications.
- Firebase Authentication: This service simplifies user management through ready-to-use authentication methods, including email/password, OAuth, and single sign-on via Google, Apple, or Facebook.
- Firebase Cloud Functions: Developers can execute secure, server-side logic automatically in response to app events, enabling automation without maintaining dedicated servers.
- Firebase Hosting: Hosting provides global content delivery with integrated SSL security, ensuring fast and reliable deployment for web applications.
- Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM): This service enables real-time push notifications and cross-platform communication, improving user engagement and retention.
- Firebase Analytics (Google Analytics for Firebase): Analytics delivers actionable insights into user behavior, engagement, and performance metrics, empowering data-driven decision-making for app optimization.
Together, these technologies form a cohesive and scalable ecosystem that allows enterprises to develop high-performing applications efficiently, while maintaining control, security, and deep visibility into app performance.
Key features of Firebase
Firebase offers several advanced features that empower developers and enterprises to build scalable, secure, and high-performing applications. These capabilities go beyond basic backend services and focus on efficiency, automation, and seamless integration within modern software ecosystems.
- Seamless integration with Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Firebase connects directly with Google Cloud services, allowing unified data management, analytics, and scalable infrastructure for enterprise-grade projects.
- Real-time analytics and monitoring: Firebase provides instant visibility into user engagement, crash reports, and performance metrics, enabling faster troubleshooting and optimization.
- Multi-platform support: The platform supports iOS, Android, and web applications under a single codebase, ensuring consistent user experiences across devices and operating systems.
- Security through Firebase Rules: Developers can define data access and validation policies with fine-grained control, protecting sensitive information in compliance with enterprise security standards.
- Auto-scaling infrastructure: Firebase automatically adjusts server resources based on real-time demand, maintaining optimal app performance even under sudden traffic surges.
- CI/CD integration: The platform supports continuous integration and deployment workflows, helping teams automate testing, building, and rollout processes for improved delivery speed.
Pros & Cons of Firebase
Firebase brings numerous advantages to businesses, such as faster development, real-time performance, and lower maintenance, but it also has limitations related to flexibility and cost scaling. The table below highlights these pros and cons to help you evaluate Firebase’s fit for your project.
| Pros | Cons |
| Rapid development process: Firebase removes the need for manual backend setup, enabling faster project delivery and shorter time-to-market. | Vendor lock-in with Google Cloud: Applications are tightly integrated with Google’s ecosystem, making migration to other platforms complex. |
| Cost efficiency for startups: Its free tier and pay-as-you-go model allow smaller teams to build apps without large upfront investments. | Pricing unpredictability at scale: Costs may rise quickly with increasing users, data storage, or real-time operations. |
| Comprehensive ecosystem: The platform provides integrated services for hosting, authentication, messaging, and analytics in one unified environment. | Limited query capabilities: Firestore and Realtime Database queries are less flexible compared to relational databases. |
| Serverless architecture: Firebase Cloud Functions let developers run backend logic without server maintenance, reducing operational overhead. | Data export and structure limitations: Managing large or complex datasets may require additional customization. |
| Real-time synchronization: Data updates instantly across users and devices, improving collaboration and responsiveness. | Offline dependency issues: Some offline features require manual handling and additional configuration. |
| Strong analytics integration: Built-in Google Analytics offers deep insights into user behavior and app performance. | Customization constraints: Certain advanced backend configurations may not be possible within Firebase’s managed environment. |
| Enterprise-grade scalability: Firebase can handle millions of users through its auto-scaling cloud infrastructure. | Learning curve for beginners: New developers may need time to understand its tools, APIs, and permission rules. |
5 Common Use Cases of Firebase
Firebase has been successfully applied across multiple industries, each achieving measurable results through faster development, real-time functionality, and simplified maintenance. Below are five representative sectors where Firebase’s tools and services have made a substantial impact.
1. E-commerce and Retail
Firebase enables e-commerce brands to manage real time product data, synchronize inventory, and deliver personalized notifications to shoppers. Its cloud hosting and analytics capabilities support custom e-commerce development services by helping retailers monitor user behavior and optimize shopping experiences instantly.
Example: Alibaba Group uses Firebase to power analytics and improve mobile performance for millions of active users worldwide, increasing engagement while reducing page load times.
2. Healthcare and Telemedicine
In healthcare and telemedicine, Firebase supports secure data exchange, real time updates, and patient notifications while meeting strict privacy requirements. It allows healthcare software development services teams to rapidly build telehealth applications that connect doctors and patients through chat, alerts, and live interactions.
Example: HealthTap leverages Firebase for real time patient doctor messaging and analytics, resulting in faster response times and higher patient satisfaction.
3. Education and E-learning
Educational platforms rely on Firebase to deliver interactive lessons, real time assessments, and collaboration tools across multiple devices. Its scalability makes it a strong foundation for e-learning software development solutions, especially during peak usage periods.
Example: Khan Academy uses Firebase to manage course data and sync learner progress across devices, improving continuity and reducing technical complexity.
4. Fintech and Banking
Fintech companies adopt Firebase to support secure authentication, fraud alerts, and instant user notifications. Its analytics and monitoring tools make it suitable for fintech software outsourcing projects that require reliability, security, and performance visibility.
Example: Credit Karma uses Firebase Analytics and Cloud Messaging to deliver personalized financial insights and real time account updates, strengthening user trust and retention.
5. Media and Entertainment
Media companies use Firebase for real-time streaming updates, push notifications, and analytics-driven content delivery. These tools ensure a consistent experience across devices and networks.
Example: The New York Times relies on Firebase Cloud Messaging and Analytics to deliver instant news alerts and tailored recommendations, significantly increasing user engagement rates.
Firebase vs Other Backend Frameworks
For now, there are several backend frameworks competing with Firebase, including AWS Amplify, Supabase, and Parse. Each alternative offers unique advantages—AWS Amplify is known for deep cloud customization, Supabase provides open-source flexibility, and Parse appeals to small teams seeking simplicity. The following comparison reveals where Firebase stands out in performance, scalability, and enterprise readiness.
| Criteria | Firebase | AWS Amplify | Supabase | Parse | Verdict & Why |
| Ease of setup | Ready to use with minimal configuration through the Firebase Console. | Requires AWS IAM setup and policy management. | Easy CLI-based setup, open-source flexibility. | Simple installation, limited enterprise features. | Firebase – most developer-friendly setup for fast launches. |
| Real-time data synchronization | Built-in WebSocket-based sync for instant updates. | Uses GraphQL subscriptions with moderate latency. | Real-time updates via Postgres replication. | Lacks native real-time synchronization. | Firebase – most robust real-time engine. |
| Built-in analytics | Integrated Google Analytics with detailed dashboards. | Separate AWS Pinpoint integration required. | Requires third-party analytics tools. | Limited analytics support. | Firebase – best all-in-one analytics solution. |
| Scalability and reliability | Auto-scales via Google Cloud infrastructure. | Scales well but demands manual configuration. | Scalable to a point, limited for enterprise load. | Moderate scalability for smaller projects. | Firebase – optimal balance of automation and scale. |
| Security and compliance | Offers Firebase Rules and Google Cloud compliance standards. | Strong security with AWS Shield and encryption layers. | Customizable security via SQL permissions. | Basic security for lightweight apps. | AWS Amplify – slightly stronger for regulated industries. |
| Pricing transparency | Pay-as-you-go with predictable scaling for small to medium apps. | Complex pricing based on multiple AWS services. | Transparent and cost-effective open-source model. | Free self-hosted option, limited enterprise support. | Supabase – best for budget-sensitive projects. |
| Community and enterprise adoption | Backed by Google with a global developer community and enterprise case studies. | Large enterprise adoption, especially among AWS clients. | Rapidly growing open-source user base. | Declining adoption due to an outdated ecosystem. | Firebase – best balance of enterprise adoption and support. |
Verdict:
- Firebase: Ideal for businesses that need rapid development, real-time data handling, and scalable architecture with minimal maintenance.
- AWS Amplify: Suited for large enterprises requiring extensive customization, compliance, and deep AWS ecosystem integration.
- Supabase: Best for startups and technical teams seeking open-source flexibility and SQL familiarity.
- Parse: Suitable for small projects or prototypes that need a lightweight backend with minimal configuration.
How to set up and use Firebase?
Since Firebase offers a wide range of services, understanding and managing all its features can be complex, especially for beginners. Many developers and businesses encounter difficulties when integrating multiple tools or configuring backend settings for the first time. From our experience at Newwave Solutions, this basic guide will help you set up and use Firebase smoothly, ensuring a faster and more confident start to your development journey.
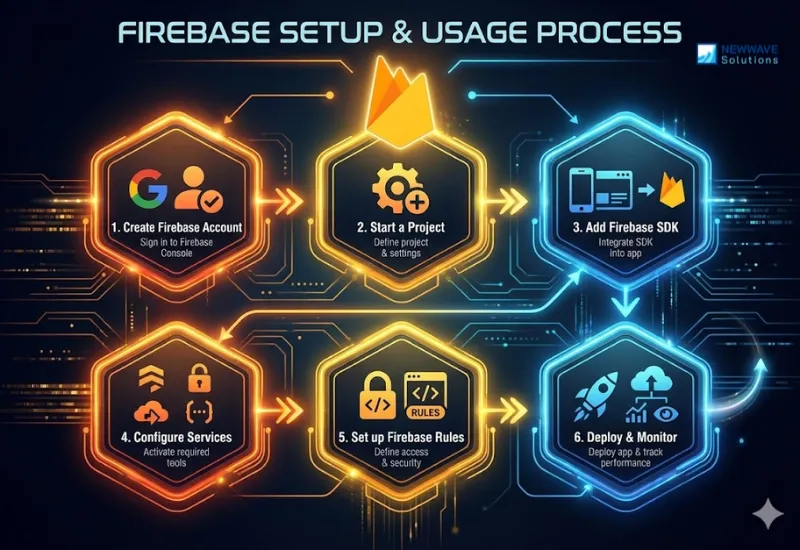
Step 1: Create a Firebase account
A developer should sign in using a Google account at the Firebase Console. This step provides access to the dashboard where all projects and configurations are managed.
Step 2: Start a project
The user must add a project name, select analytics preferences, and define the default settings for platform integration. This creates the foundation for connecting your application to Firebase services.
Step 3: Add Firebase SDK
Developers need to integrate the Firebase SDK into their mobile or web app according to the platform’s documentation. This connection enables direct communication between the app and Firebase’s backend services.
Step 4: Configure services
A project owner should choose which Firebase tools to activate, such as Firestore, Authentication, Hosting, or Cloud Functions. Selecting only the required modules helps maintain efficiency and cost control.
Step 5: Set up Firebase Rules
Developers must define data access permissions and validation logic to protect sensitive information. Firebase Rules ensure that all operations follow the required security and compliance standards.
Step 6: Deploy and monitor
Using Firebase CLI, developers can deploy their applications and continuously monitor performance through built-in analytics and real-time reports. This helps maintain stability, identify issues early, and optimize user experience.
The Future of Firebase in Enterprise Applications
Firebase’s future in the enterprise is not as a standalone, all-encompassing platform, but as a strategic accelerator for front-end and mobile app development, deeply integrated within the Google Cloud ecosystem. Its evolution is marked by a shift from a simple Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS) to becoming the preferred client-layer platform for companies building modern digital experiences. The trajectory is defined by three core, interconnected trends that address both developer velocity and enterprise-grade requirements.
Strategic Deep Integration with Google Cloud
The most pivotal trend is Firebase’s transformation into the official client development layer for Google Cloud. Enterprises are adopting a hybrid architecture where Firebase manages user-facing interactions, while GCP handles heavy-duty backend processing.
- Architecture Pattern: The emerging best practice is to use Firebase for the client layer (authentication, real-time data sync, app hosting) and seamlessly connect it to GCP for the business logic layer (Cloud Run, Cloud Functions, BigQuery, Vertex AI).
- Enterprise Value: This provides a clear, scalable path. Teams can build and validate MVPs rapidly with Firebase’s tools, then seamlessly graduate to GCP’s enterprise services as needs evolve, without a costly platform migration.
- Key Integration Points: Direct pipelines from Firebase Analytics to BigQuery for data warehousing, using Firebase Auth to secure GCP resources, and triggering complex workflows on GCP via callable Cloud Functions.
The Evolution of Firestore as an Enterprise-Grade NoSQL Database
Firestore is solidifying its role as the go-to real-time database for user-centric applications, with significant enhancements aimed at enterprise needs.
Primary Use Case: It excels for applications requiring live data sync—such as collaborative tools, live dashboards, customer-facing apps, and internal operational platforms—where its automatic scaling and strong global replication are key advantages.
- Future Roadmap: Expect continued investment in more sophisticated querying capabilities, point-in-time recovery features, and enhanced aggregation functions to bridge gaps with traditional databases.
- Cost Governance: Improved tooling for monitoring and optimizing read/write operations will be critical for financial control at scale (FinOps).
- Data Architecture: The trend is to use Firestore for operational app data, while syncing to BigQuery for analytics, forming a powerful real-time OLTP to OLAP pipeline.
Advanced Tooling for Security, AI, and Accelerated Development
Firebase is expanding beyond core services to offer embedded, specialized tooling that reduces the need for in-house expertise in complex domains.
Enhanced Security & Compliance:
- Firebase App Check is becoming a non-negotiable security layer to prevent API abuse.
- Native support for SAML and OIDC enables easy integration with corporate identity providers like Okta or Azure AD.
- Ongoing expansion of compliance certifications (SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA-ready configurations) addresses regulatory hurdles.
Democratized AI/ML Capabilities:
- Firebase Predictions allows for easy integration of user behavior forecasting.
- ML Kit and the growing suite of Vertex AI integrations enable teams to deploy custom machine learning models directly to the client-side via Firebase SDKs, accelerating intelligent feature development.
Developer Experience Focus:
- The Firebase Emulator Suite and pre-built Extensions significantly reduce development time and boilerplate code, allowing enterprise teams to focus on unique business logic rather than infrastructure.
In conclusion, Firebase’s future in the enterprise is one of strategic specialization. It is positioning itself as the essential tool for building and scaling the client interface, backed by the full power and maturity of Google Cloud. Success will hinge on its ability to maintain this seamless integration, enhance its governance and cost-control features, and continue delivering unmatched developer productivity for the most demanding enterprise applications.
FAQs
1. What is the purpose of Firebase?
Firebase is designed to help developers build, manage, and scale mobile and web applications without handling backend infrastructure. It provides tools for real-time databases, authentication, hosting, analytics, and cloud functions, all in one integrated platform. The purpose of Firebase is to let teams focus on creating better user experiences while Google manages the backend complexity.
2. What is Firebase pricing?
Firebase offers a flexible pricing model, starting with a free “Spark” plan suitable for small projects and individual developers. Businesses can upgrade to the “Blaze” plan, which follows a pay-as-you-go structure based on usage. This model allows startups and enterprises to scale their costs efficiently as their applications grow.
3. How secure is Firebase for corporate data?
Firebase is built on Google Cloud’s secure infrastructure, benefiting from its global compliance standards and encryption mechanisms. It includes Firebase Security Rules, which allow precise control over data access and validation. Enterprises can also integrate additional authentication layers to meet specific regulatory and compliance requirements.
4. Can Firebase handle large-scale applications?
Yes, Firebase can support large-scale, enterprise-grade applications through its auto-scaling architecture on Google Cloud. It adjusts resources dynamically based on user traffic and performance needs. Many global companies, including Alibaba and The New York Times, have successfully scaled their apps using Firebase.
5. How does Firebase integrate with Google Cloud?
Firebase is natively connected to Google Cloud, allowing seamless access to services like BigQuery, Cloud Storage, and Cloud Functions. This integration provides unified data management, advanced analytics, and simplified scalability. Developers can easily extend their Firebase apps using Google Cloud’s enterprise-level tools and infrastructure.
Conclusion
After analysing what is Firebase, we notice that it represents one of the most powerful BaaS platforms in today’s technology landscape, simplifying how developers and enterprises build, manage, and scale applications. By offering services such as authentication, real-time databases, and cloud functions, it enables teams to deliver high-performing and secure apps without worrying about infrastructure.
In case your business lacks in-house expertise or resources for deploying a BaaS platform like Firebase to the main website, partnering with an experienced team is often the best choice. Currently, Newwave Solutions can help solve that issue by providing comprehensive web development services, which include overall analysis, concept design, development, launching, and maintenance.
Our experts ensure your website not only looks visually stunning but also delivers measurable results through seamless performance, enterprise-grade security, and an exceptional user experience.
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply