What is HTML5? Core Technology for Interactive Websites

Many businesses today face growing pressure to deliver seamless, cross-device experiences that meet rising user expectations. Older markup languages struggled with multimedia and mobile responsiveness, creating clear limitations. Solutions like HTML5 were introduced to address these gaps with more flexibility and power. This article will deliver what is HTML5, its key features, benefits, use cases, and how companies are adopting it to overcome these challenges.
What is HTML5?
HTML5 is the latest version of Hypertext Markup Language, serving as the global standard for structuring and presenting content on the web. It improves the web development technology by introducing semantic markup, native multimedia support, and cross-platform adaptability, making it easier for enterprises to build scalable and interactive applications.
Example: YouTube adopted HTML5 development to replace Flash for video playback, enabling smoother performance across devices without external plugins. According to Google, this shift significantly improved loading speed and accessibility for millions of global users.
HTML vs HTML5: Key differences
HTML is the standard markup language used to structure and display content on the web, while HTML5 is the latest version that expands on HTML with modern features such as multimedia support (audio, video), semantic elements, offline storage, and cross-platform compatibility. In application, HTML is limited to basic page layouts, whereas HTML5 enables businesses to build interactive, mobile-friendly, and media-rich web applications without relying on external plugins.
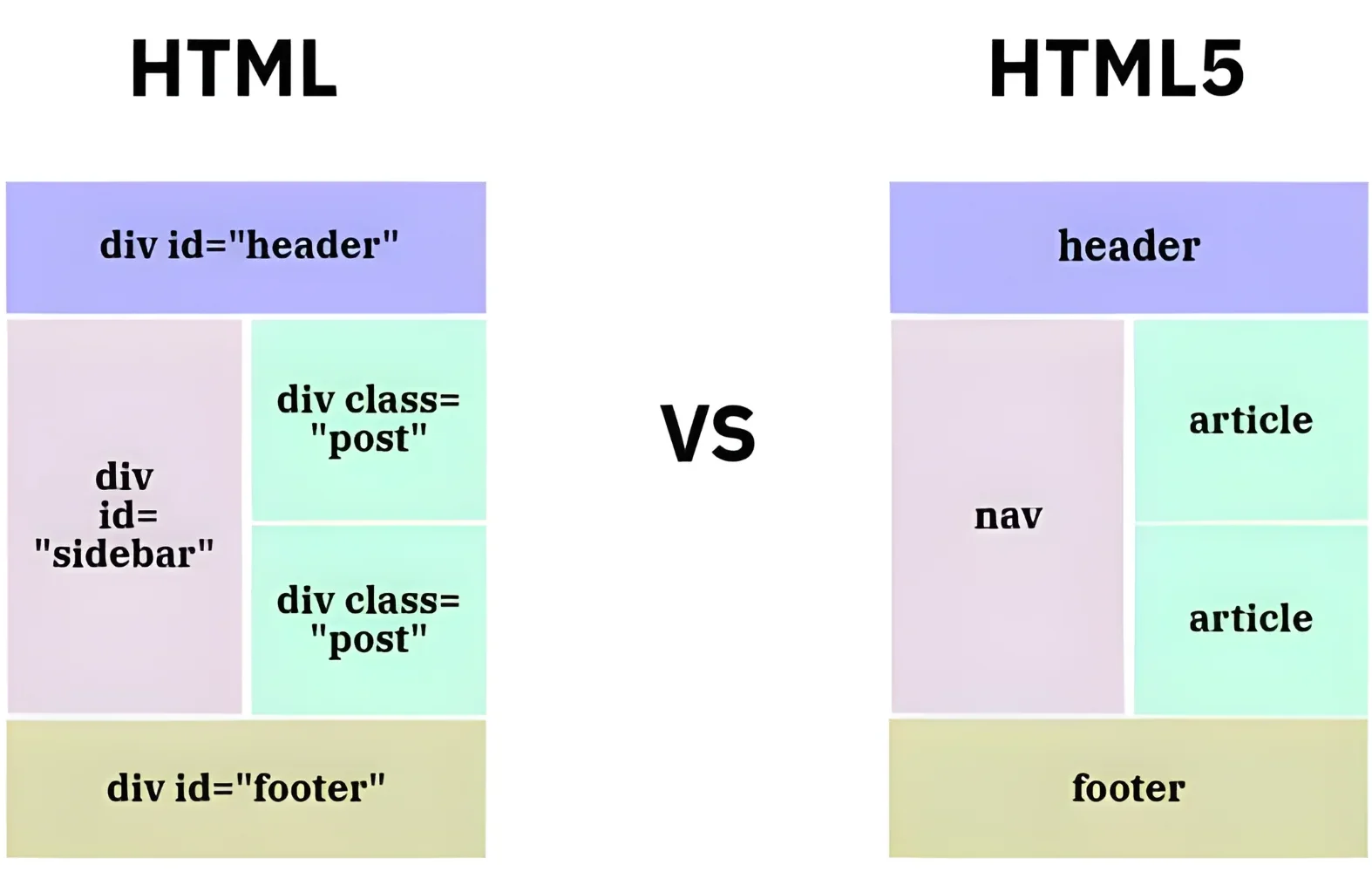
How does HTML5 work?
HTML5 works as the foundation layer of web development, using tags, semantic elements, and APIs to define the structure and behavior of web pages. It integrates seamlessly with CSS3 for styling and JavaScript for interactivity, ensuring responsive and dynamic experiences across devices.
- Content layer: HTML5 structures the content and layout of the web page.
- Style layer: CSS3 defines design, layout, and responsiveness.
- Logic layer: JavaScript powers interactivity, automation, and real-time user interactions.
This layered approach helps developers create modern, flexible, and device-agnostic web applications.
What is HTML5 used for?
HTML5 can be applied in multiple cases and industries, serving as a versatile technology for both simple websites and enterprise-grade applications. Below are the most common use cases:
- Rich multimedia (audio, video without plugins): Developers can embed media directly into websites with <video> and <audio> tags, eliminating reliance on third-party plugins like Flash.
- Mobile app development with hybrid frameworks: HTML5 works with frameworks such as Apache Cordova or Ionic to build cross-platform mobile apps.
- Cross-browser compatibility: Applications built with HTML5 function across all modern browsers, improving accessibility for users worldwide.
- Offline storage & caching with local storage: Businesses can offer offline experiences using local storage and IndexedDB, improving usability for apps that need continuous access.
- Interactive web apps (games, dashboards): HTML5 Canvas and APIs allow the creation of dynamic games, analytics dashboards, and real-time interfaces.
- Enterprise apps requiring accessibility & compliance: HTML5 semantic elements and ARIA support ensure that applications meet accessibility standards for users with disabilities.
Main Features of HTML5
If you want to know whether this technology fits your business needs, exploring its key features is an essential step. From responsive websites to HTML5 mobile app development, the framework provides powerful tools that help organizations build modern, secure, and scalable applications.
- Semantic elements (e.g., <header>, <article> for cleaner code): These elements provide clear meaning to content, making it easier for developers to maintain code and improving SEO performance for businesses.
- Built-in multimedia tags (<video>, <audio>): HTML5 allows video and audio embedding without third-party plugins, enabling smoother user experiences and reducing security risks.
- Offline support (localStorage, IndexedDB): With built-in offline storage, businesses can ensure that users can still access critical data or functions even without an internet connection.
- Cross-platform & mobile-friendly design: HTML5 supports responsive layouts and works seamlessly across browsers and devices, allowing enterprises to deliver consistent experiences on desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
- Improved forms (date pickers, sliders, validations): Built-in form enhancements simplify user input and reduce errors, making applications more user-friendly and efficient for data collection.
- API integration (Canvas, Geolocation, WebSockets): HTML5 APIs enable advanced functionality like real-time graphics, location-based services, and live data communication for enterprise applications.
- Accessibility improvements for compliance: With ARIA support and semantic structures, HTML5 helps organizations meet accessibility standards, ensuring inclusivity for users with disabilities.
Pros & Cons of HTML5
Like all technologies, HTML5 has strengths and trade-offs; businesses should carefully evaluate both to determine if it is appropriate for their development goals. Below, we break down the benefits of HTML5 alongside its limitations:
| Pros |
Cons |
| Wide browser support: HTML5 is supported by all modern browsers, ensuring that applications can reach the widest possible audience without compatibility issues. | Inconsistent browser support for advanced features: Some advanced APIs and capabilities may not work consistently across older browser versions, requiring additional testing. |
| Reduces dependency on plugins: Native support for multimedia eliminates the need for third-party plugins like Flash, improving security and lowering maintenance costs. | Security challenges: Features like local storage and offline caching may create vulnerabilities if not implemented carefully. |
| Mobile-ready: HTML5 is designed to be responsive, allowing businesses to create websites and apps that adapt seamlessly across devices. | Limited offline storage vs. native apps: HTML5 offers local storage, but its offline capabilities are more restricted compared to fully native mobile apps. |
| SEO-friendly: Semantic tags provide better structure for search engines, improving discoverability and visibility for enterprise websites. | Heavy reliance on JavaScript for complex apps: While HTML5 defines structure, complex business logic often requires significant JavaScript development, which increases complexity. |
| Cost-effective: Being open-source and plugin-free reduces licensing and infrastructure costs, making it budget-friendly for startups and SMEs. | |
| Future-proof standard: As the W3C-recommended markup standard, HTML5 is continually updated to meet evolving business and user demands. |
HTML5 is ideal for most modern websites and enterprise applications, offering flexibility, scalability, and accessibility. However, for highly complex or performance-intensive systems, businesses may still need to combine HTML5 with native or specialized technologies.
5 Common Use Cases of HTML5
From enterprise websites to mobile platforms, HTML5 app development enables businesses to deliver responsive, secure, and interactive applications. Below are five common industries where HTML5 proves its value.
1. Banking & Financial Services
Financial institutions use HTML5 to create responsive online banking dashboards, secure customer portals, and mobile-ready payment platforms. Its cross-platform adaptability ensures clients can access services seamlessly from any device.
Example: Barclays Bank implemented HTML5 in parts of its online banking applications and financial software development services, resulting in faster load times and improved accessibility across browsers and devices.
2. Automotive Industry
Automotive companies leverage HTML5 to power in-car infotainment systems, dealership websites, and online booking platforms. The framework’s multimedia support enhances interactive experiences for customers.
Example: Ford adopted HTML5 for its in-car apps, improving real-time navigation and entertainment features while ensuring compatibility across devices.
3. Retail & E-commerce
Retailers rely on HTML5 to create engaging product catalogs, interactive shopping carts, and responsive checkout processes. The ability to integrate multimedia makes it easier to showcase products effectively.
Example: eBay used HTML5 in its mobile web interface, delivering a faster and more responsive shopping experience to millions of users worldwide.
4. Education Technology
EdTech services/ platforms use HTML5 for building learning management systems, interactive course content, and mobile-first education apps. Its accessibility features ensure inclusive experiences for all learners.
Example: Khan Academy incorporates HTML5 to deliver interactive exercises and educational content that works seamlessly across devices and browsers.
5. Travel & Tourism
The travel sector applies HTML5 to booking engines, customer self-service portals, and interactive destination guides. Its offline storage capabilities ensure that users can access important travel information even without connectivity.
Example: TripAdvisor implemented HTML5 features in its platform to improve mobile browsing performance, enhancing user engagement for travelers worldwide.
How to Set Up & Use HTML5 in Projects
Even if you already know what is HTML5 and its core functions, setting it up without technical knowledge can be confusing. From years of applying this model in enterprise projects and supporting numerous clients, we have prepared a quick setup guide to help you get started effectively.
Step 1: Start with a DOCTYPE declaration <!DOCTYPE html>
This line tells browsers that the document uses HTML5, ensuring consistent rendering across devices.
Step 2: Use semantic tags to structure content (e.g., <header>, <footer>)
Semantic tags make your code cleaner, easier to maintain, and more SEO-friendly, helping businesses improve accessibility and visibility.
Step 3: Embed media using <video> and <audio> tags
This allows you to integrate multimedia directly into your site without relying on plugins, which boosts performance and security.
Step 4: Add offline storage or geolocation features if needed
Use tools like localStorage, IndexedDB, or the Geolocation API to improve user experience in mobile-first environments.
By following these steps, businesses can better understand how to use HTML5 and simplify how to set up HTML5 for practical, real-world applications.
HTML5 vs Other Web Technologies
While HTML5 is a widely adopted standard, businesses often compare it with legacy technologies like Flash or alternatives like native mobile applications. The table below highlights the key differences of HTML5 vs other competitors so you can compare and consider the appropriate option for your web development.
|
Criteria |
HTML5 | Flash | Native Mobile Apps |
Best Choice |
| Performance | Lightweight, fast loading across devices. | Slower, requires plugins. | High-performance optimized for specific devices. | Native Apps for performance-heavy tasks. |
| Security | More secure than plugins, though APIs require careful implementation. | Frequent vulnerabilities and plugin exploits. | Secure when following OS-level standards. | Native Apps lead in robust security. |
| Ecosystem | Backed by W3C and supported globally across browsers. | Deprecated, no longer updated or supported. | Strong app store ecosystems (Apple, Google). | Tie: HTML5 for web, Native Apps for mobile ecosystems. |
| Cost | Free, open standard with no licensing fees. | Costly to maintain due to obsolescence. | Higher cost for separate iOS/Android development. | HTML5 is the most cost-effective. |
| Device Support | Cross-platform, works on all modern browsers and devices. | Limited, outdated, and no mobile compatibility. | Fully optimized for specific devices. | HTML5 for cross-platform, Native Apps for device-specific features. |
Who Should Use HTML5?
- Startups building responsive websites: HTML5 provides an affordable, open-source standard that allows startups to quickly create responsive sites that look and function well across devices.
- Enterprises needing cross-platform apps: HTML5 enables businesses to deploy applications that work seamlessly on desktops, tablets, and smartphones, reducing the cost of maintaining multiple versions.
- E-learning platforms requiring accessibility: With built-in semantic tags and ARIA support, HTML5 helps educational platforms meet accessibility standards and deliver inclusive learning experiences.
- Media companies streaming rich content: HTML5’s native support for video and audio allows media businesses to stream content without third-party plugins, improving performance and reliability.
- Governments and regulated industries ensuring compliance: HTML5 supports secure, structured, and standards-based development, making it easier for organizations in regulated sectors to meet compliance requirements.
FAQs
1. Is HTML5 free?
Yes, HTML5 is completely free and open-source. Any business or developer can use it without paying licensing fees.
2. Is HTML5 a frontend or backend?
HTML5 is a frontend technology. It structures and displays content in browsers, while backend languages like PHP or Node.js handle server-side logic.
3. Can HTML5 build mobile apps?
Yes, HTML5 can be used with hybrid frameworks like Ionic or Apache Cordova to build cross-platform mobile apps, though native apps may still perform better for device-heavy features.
4. What browsers support HTML5?
All modern browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge, support HTML5, making it widely accessible for users worldwide.
5. How secure is HTML5?
HTML5 is secure when implemented properly, but developers must manage vulnerabilities in APIs like local storage or geolocation to protect user data.
Conclusion
In summary, what is HTML5 can be understood as the foundational language that structures and presents all modern web content, integrating native support for multimedia and interactivity that previous standards lacked. Make sure you understand its core functions and usage guide carefully to implement this language model effectively into your contemporary web development process.
In case your organization is lacking the technical depth or internal resources for HTML5 project implementation, you should consider collaborating with professional web development services like Newwave Solutions to optimize this markup language for their specific project needs. We utilize over 14 years of proven expertise in web & mobile app development services, IT outsourcing, software development/ maintenance, and emerging technology services to provide a full cycle support, ensuring that modern tech like HTML5 can be integrated into your core products/ services with high efficiency and reliability.
Partner with Newwave Solutions to boost your next-generation web application project effectively with strategic, expert implementation of HTML5 standards.
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply