What is .NET Core? Features, Benefits & Use Cases for Businesses

Many enterprises faced limitations with the old .NET Framework, which was tied to Windows and lacked flexibility for cloud-native, microservices, and cross-platform development. To solve this challenge, Microsoft introduced .NET Core, an open-source, cross-platform framework built to streamline enterprise application development with speed, security, and scalability. This Newwave Solutions’ blog is designed for IT leaders, developers, and business decision-makers who want to explore what is .NET Core, its features, advantages, use cases, and how it can transform enterprise software strategies.
What Is .NET Core?
.NET Core is Microsoft’s open-source, cross-platform framework designed for building scalable web, cloud, desktop, and mobile applications. It plays a crucial role in helping enterprises adopt modern architectures such as microservices and cloud-native solutions, while ensuring high performance and flexibility. Its modular design and wide ecosystem make it a preferred choice for businesses modernizing their digital infrastructure.
Example: UPS migrated parts of its logistics and tracking systems to .NET Core, which enabled faster development cycles, improved scalability, and significant performance improvements for handling millions of daily transactions.
How .NET Core Works
.NET Core works by combining a modular runtime, libraries, tools, and language support to deliver a unified development experience across platforms. Its architecture ensures flexibility, performance, and consistency, whether running web, cloud, or desktop applications.
- Runtime – CoreCLR executes applications, managing memory, garbage collection, and Just-In-Time compilation.
- Libraries – The Base Class Library (BCL) provides reusable functionality for tasks such as file access, networking, and security.
- Tools – The Command Line Interface (CLI) enables project creation, building, testing, and deployment through simple commands.
- Language support – Developers can write applications using, F#, or VB.NET, C# web development services depending on team expertise and project needs.
- Modular NuGet packages – Applications can include only the necessary components, making them lightweight and easier to maintain.
What is .NET Core used for?
To answer what is asp.NET Core used for, we will focus on some of its core usage purposes below:
- Web application development – .NET Core provides a powerful runtime for building secure, scalable web applications, supporting both MVC and API-driven architectures.
- Cloud-based services – Enterprises use .NET Core to build microservices and deploy them seamlessly on cloud platforms like Microsoft Azure, improving flexibility and cost-efficiency.
- Cross-platform applications – Businesses can develop apps that run consistently across Windows, Linux, and macOS, reducing infrastructure and licensing costs.
- IoT solutions – With its lightweight runtime, .NET Core supports IoT device communication and real-time data processing, enabling smart systems in manufacturing or logistics.
- Enterprise integration systems – .NET Core connects with databases, APIs, and third-party platforms to streamline workflows and unify business operations.
- Mobile backends – Companies use .NET Core to power mobile apps with secure APIs and real-time data sync, ensuring reliable user experiences.
7 Key Features of .NET Core
- Cross-platform development – .NET Core allows businesses to build and run applications seamlessly on Windows, Linux, and macOS, ensuring flexibility across environments.
- High performance and scalability – The framework delivers optimized runtime performance that can handle demanding enterprise workloads with millions of requests.
- Support for modern architectures – Companies can implement microservices and container-based deployments, making systems more resilient and adaptable to change.
- Unified programming model – Developers can use ASP.NET Core, Entity Framework Core, and Blazor together under one platform to accelerate enterprise app development.
- Built-in dependency injection – Applications gain cleaner, more maintainable codebases by leveraging dependency injection as a core part of the framework.
- Cloud-native readiness – Deep integration with Microsoft Azure enables smooth deployment, monitoring, and scaling of cloud-based applications.
- Open-source ecosystem – A large, active community contributes tools, libraries, and support, helping businesses innovate faster and reduce vendor lock-in.
Pros & Cons of using .NET Core
By exploring the advantages and limitations of .NET Core, businesses can determine whether this framework aligns with their technical needs and long-term goals. Let’s view the details below:
Advantages of .NET Core
- Enterprise-grade performance:.NET Core delivers high-speed execution and optimized memory usage, making it suitable for mission-critical applications that demand performance at scale.
- Cross-platform flexibility: Developers can build and run applications on Windows, Linux, and macOS, which provides businesses with greater deployment freedom.
- Modular lightweight deployment: Applications can include only the required libraries, reducing overhead and simplifying maintenance for diverse environments.
- Cloud-native integration: With seamless support for Docker, Kubernetes, and Azure, .NET Core enables enterprises to adopt microservices and modern DevOps practices effectively.
- Strong security features: Built-in authentication, encryption, and Microsoft’s regular patch updates ensure compliance with enterprise security standards.
- Vibrant open-source community: Active developer support and contributions guarantee ongoing innovation, quick fixes, and a rich ecosystem of libraries and tools.
Limitations of .NET Core
- Learning curve for legacy developers: The .NET developers who are only familiar with the traditional .NET Framework may face challenges adapting to the modular, cross-platform structure of .NET Core.
- Limited support for older libraries: Some Windows-only frameworks and APIs are not compatible, which may complicate migration for legacy applications.
- Migration complexity: Moving from .NET Framework to .NET Core often requires code refactoring and system adjustments, adding time and cost to large enterprise projects.
5 Common Use Cases of .NET Core
In real-world scenarios, .NET Core has been applied across diverse industries to support mission-critical systems and enhance business productivity. Below are the most common fields where enterprises leverage their scalability, security, and flexibility.
1. Banking & Finance
Banks and financial institutions use .NET Core to build secure transaction platforms, compliance dashboards, and fraud detection systems that can process millions of operations daily. Its performance and enterprise-grade security features help reduce risks while meeting strict compliance requirements.
Example: A large retail bank migrated its core banking systems to .NET Core and microservices on Azure, which cut transaction latency (from 8-10 seconds to <2 seconds) and improved customer onboarding speed by 40 % during peak load periods.
2. Healthcare
Healthcare providers leverage .NET Core to build patient data management systems, electronic health records (EHRs), and telemedicine platforms. The framework ensures HIPAA-compliant security and provides scalability for handling sensitive data across multiple facilities.
Example: A hospital network adopted .NET Core for its telemedicine and healthcare software development services, resulting in faster appointment scheduling and improved accessibility for patients across regions.
3. Retail & E-commerce
Retailers use .NET Core to power inventory management, point-of-sale (POS) systems, ecommerce development services, and e-commerce platforms with seamless cloud synchronization. Its ability to handle real-time transactions ensures smooth customer experiences even during peak sales.
Example: The e-commerce platform GoDaddy is cited among companies using .NET (including .NET Core) for scalability and handling high traffic loads.
4. Logistics & Supply Chain
In logistics, .NET Core is used for building real-time fleet tracking dashboards, supply chain management systems, and microservices to optimize delivery routes. The modular nature of the framework makes it easy to update or expand functionalities as needed.
Example: UPS is mentioned in .NET customer showcases and is known for using .NET technologies for its logistics, routing, and tracking systems.
5. SaaS Platforms
SaaS providers rely on .NET Core to build scalable APIs, subscription management systems, and multi-tenant applications. Its cross-platform support and microservices architecture make it an ideal choice for cloud-first business models.
Example: A SaaS startup scaled its subscription platform using .NET Core, enabling 5x growth in user base without compromising performance or uptime.
How to Setup & Use .NET Core
Setting up .NET Core for the first time may seem daunting, but by following a structured process, you can quickly build and deploy your first application. Here is a step-by-step guide that covers how to set up .NET Core and how to use .NET Core effectively.
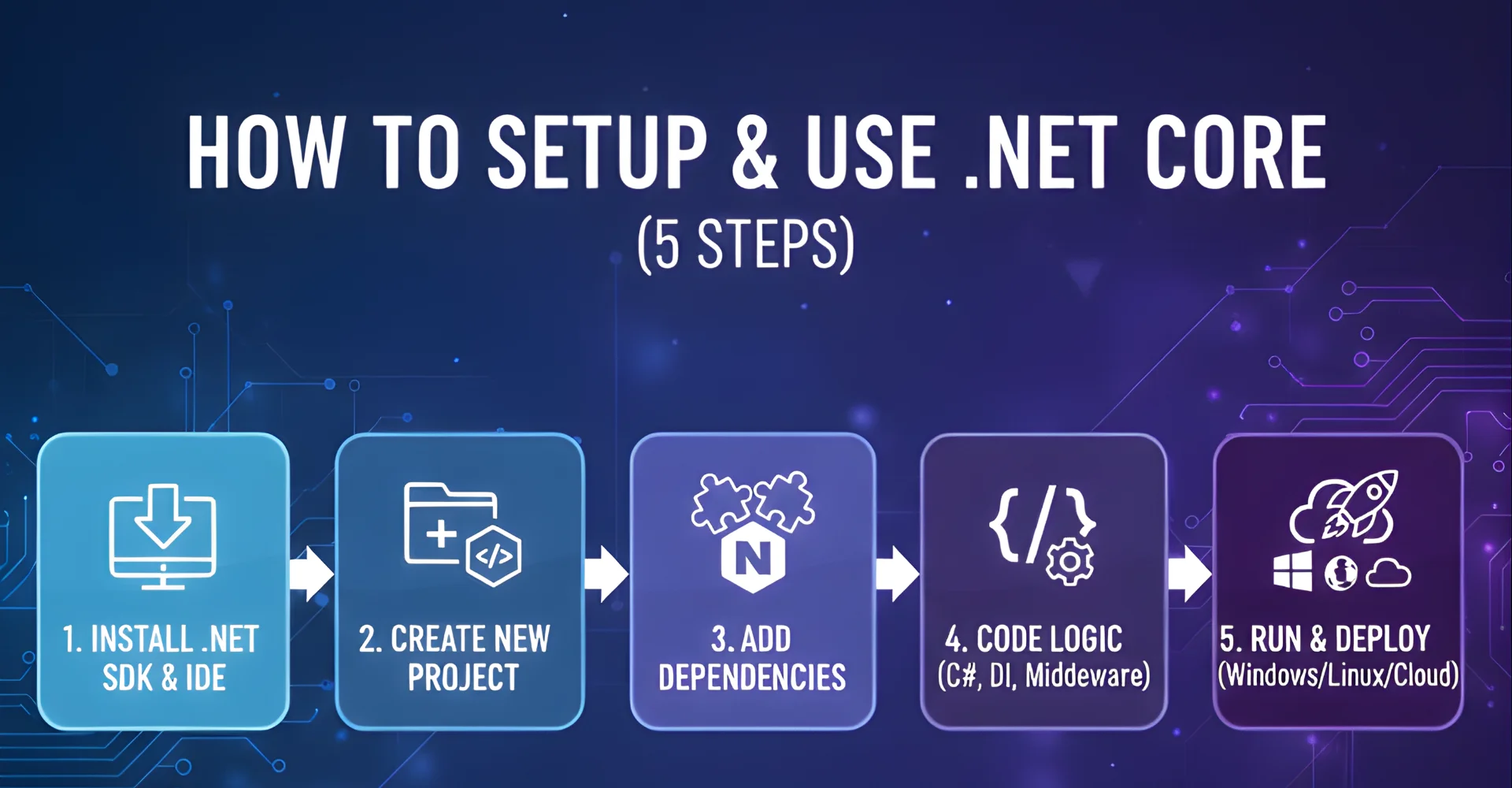
- Step 1: Install the .NET SDK and Visual Studio/VS Code: You need the .NET SDK package to compile and run applications, and Visual Studio or VS Code provides the development environment with debugging and IntelliSense features.
- Step 2: Create a new .NET Core project via CLI or IDE template: You can use the dotnet new command or project templates in Visual Studio to scaffold applications quickly, such as a web API, console app, or MVC project.
- Step 3: Add dependencies through NuGet: Required libraries and frameworks can be installed from NuGet, ensuring your application has modular and up-to-date components for tasks like authentication or data access.
- Step 4: Write application logic in C# with DI and middleware: Dependency Injection (DI) and middleware pipelines make your code cleaner, more testable, and easier to extend as your project grows.
- Step 5: Run and deploy to a chosen platform (Windows/Linux/Cloud): After testing locally, you can publish the app to servers or cloud platforms like Azure and AWS, ensuring it runs reliably across environments.
.NET Core vs .NET Framework vs .NET 5+
Over the years, Microsoft has transitioned from the traditional .NET Framework to the modern, cross-platform .NET Core, and further into the unified .NET 5+ platform. This comparison helps enterprises understand the evolution, limitations, and future-proofing of each option.
| Criteria | .NET Framework | .NET Core |
.NET 5+ |
| Cross-platform support | Windows-only, limiting reach | Runs on Windows, Linux, and macOS | Fully unified with broad cross-platform capabilities |
| Performance optimization | Good, but limited by older runtime | High performance with lightweight runtime | Optimized runtime with even better benchmarks for enterprise workloads |
| Ecosystem & Libraries | Mature but Windows-focused | Open-source ecosystem, growing community contributions | Unified ecosystem with support for both old and new libraries |
| Enterprise adoption | Legacy apps still rely on it | Widely adopted for modern apps | Recommended by Microsoft as the long-term standard |
| Cloud-native readiness | Requires extra tools for cloud deployment | Built with containers and microservices in mind | Full integration with Azure and cloud-native workflows |
Verdict: While .NET Framework remains useful for legacy systems, .NET Core and especially .NET 5/6+ represent the future of enterprise software development. For businesses seeking scalability, performance, and cloud-native support, .NET 6+ is the most future-proof choice.
.NET Core in Cloud & Microservices
One of the most powerful aspects of .NET Core is its seamless integration with cloud-native and microservices architectures, making it a go-to choice for enterprises modernizing their systems. Companies can build applications that scale on demand while maintaining reliability and security.
- Integration with Azure and AWS: .NET Core offers first-class integration with Azure services such as App Service, Functions, and Cosmos DB, and it also runs efficiently on AWS EC2 and Lambda.
- Containerization with Docker and Kubernetes: Applications built with .NET Core can be packaged into Docker containers and orchestrated with Kubernetes, enabling enterprises to scale microservices-based systems across hybrid or multi-cloud environments.
- Enterprise example: Companies such as Siemens Healthineers use .NET Core to build containerized microservices for medical imaging solutions, which improves deployment speed and reliability across global healthcare facilities.
Future of .NET Core in the .NET Ecosystem
The future of .NET Core lies in its unification under the broader .NET software development, ecosystem, with Microsoft continuing its roadmap through .NET 8 and beyond. This evolution provides a single, consistent platform for building cloud-native, desktop, mobile, and IoT applications.
For enterprises, this means that investing in .NET Core today ensures long-term viability and compatibility with future frameworks. While WPF, Xamarin, and ASP.NET remain part of the larger family, .NET 8+ positions itself as the backbone of enterprise development. Microsoft’s ongoing improvements in performance, AI integration, and cross-platform tooling guarantee that .NET Core will remain a reliable and future-proof solution.
FAQs
1. What is a.NET Core?
.NET Core is Microsoft’s open-source, cross-platform framework used to build modern web, cloud, desktop, and mobile applications. It is designed for scalability, performance, and flexibility across Windows, Linux, and macOS.
2. What are the benefits of .NET Core?
The main benefits include cross-platform support, modular lightweight deployment, enterprise-grade performance, strong security features, and seamless integration with cloud and containerized environments.
3. Is .NET Core free?
Yes, .NET Core is completely free and open source under the MIT license. This makes it cost-effective for enterprises and developers of all sizes.
4. Can .NET Core be used for enterprise projects?
Yes, .NET Core is widely adopted in enterprises for building high-performance, cloud-native, and scalable applications. Many global companies use it for banking platforms, SaaS applications, and large-scale enterprise systems.
5. What is the difference between .NET Core and .NET Framework?
The .NET Framework is Windows-only and best for legacy applications, while .NET Core is cross-platform, modular, and designed for modern cloud and microservice architectures.
6. How does .NET Core handle microservices?
.NET Core supports microservices through lightweight APIs, containerization with Docker, and orchestration with Kubernetes. It integrates seamlessly with Azure Service Fabric and other cloud-native tools.
7. Is .NET Core secure?
Yes, it includes built-in authentication, data protection APIs, HTTPS enforcement, and regular security patches from Microsoft, making it enterprise-ready.
8. How does .NET Core compare with Java for enterprise development?
Both are strong enterprise platforms, but .NET Core excels in cloud-native development, Windows ecosystem integration, and performance benchmarks. Java offers a larger ecosystem and portability across enterprise-grade systems. The choice often depends on existing infrastructure and developer expertise.
Conclusion
To sum up, what is .NET Core can be defined as Microsoft’s modern, cross-platform framework that simplifies enterprise application development with robust performance, modular design, and long-term scalability. It empowers businesses to build secure, cloud-ready, and future-proof applications while reducing overhead and improving developer efficiency.
In case your business does not have the experience to apply .NET CORE to the business model, partnering with professional .NET Core developers ensures smooth adoption and optimized outcomes.
With over 14 years of delivering enterprise-grade solutions, Newwave Solutions allows you to hire ASP.NET developers skilled in ASP.NET Core, MVC, Web API, Entity Framework, and Azure, ensuring secure and performance-driven applications. Whether you need a single expert or a full offshore team, our flexible hiring models align seamlessly with your workflows, timelines, and business objectives.
Approach us today to simplify your .NET Core application!
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply