What is Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)? Everything you need to know about SDLC

The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is the foundation of every software project. It is a series of phases that a software project goes through, from planning and design to development, testing, and deployment, ensuring an efficient and structured workflow. In this article, Newwave Solutions will provide a comprehensive overview of the SDLC — covering what is Software Development Life Cycle, its stages, models, and key benefits.
What is Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a systematic process that helps plan, develop, test, and maintain software efficiently. In software development services, the SDLC divides the entire process into clearly defined stages, each with its own objectives and deliverables. This approach enables development teams to manage, collaborate, and track project progress more effectively.
By applying the SDLC, businesses can build software that not only meets technical requirements but also aligns with business goals and real user needs.
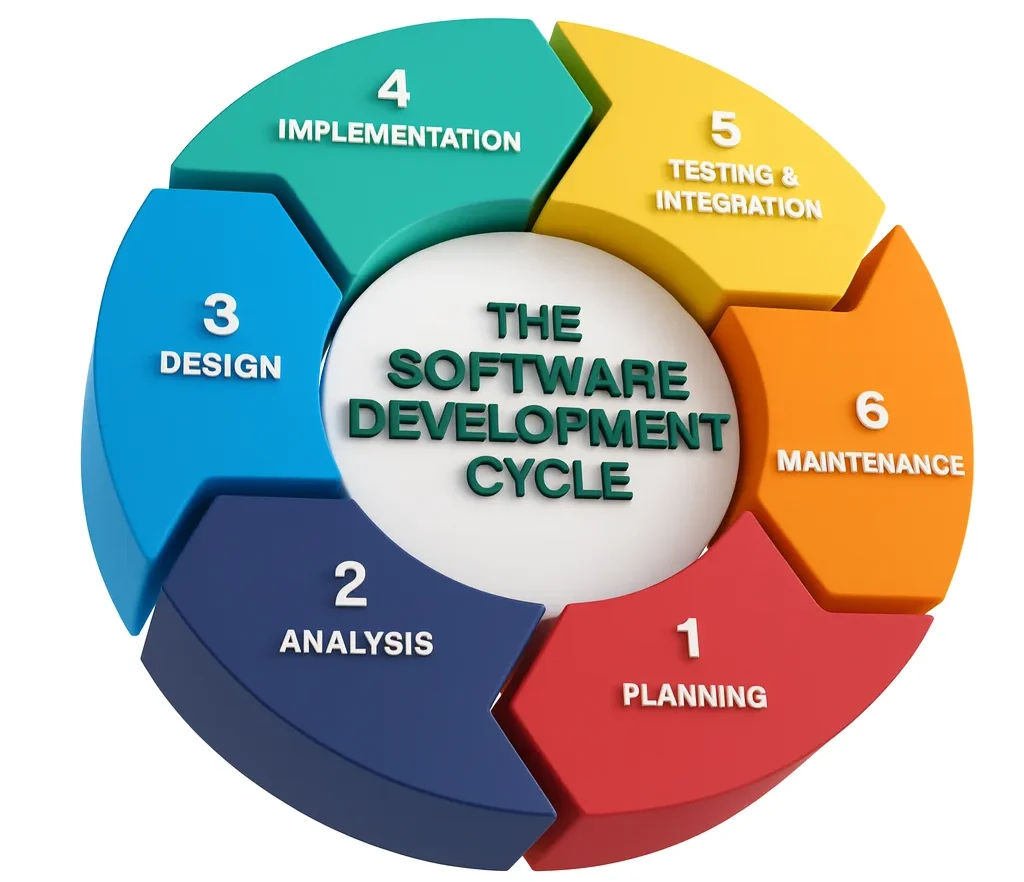
So why is it important?
- Risk Mitigation: Detects and resolves issues early, avoiding costly fixes.
- Quality Assurance: Ensures thorough testing for reliable, high-quality software.
- Cost Control: Enables accurate estimates and prevents budget overruns.
- Time Management: Sets clear timelines for predictable project delivery.
- Stakeholder Communication: Improves clarity and collaboration among teams.
- Requirement Management: Captures and implements all business and technical needs.
- Maintenance Planning: Prepares for smooth updates and future enhancements.
To better understand SDLC implementation, you could consider these below real-world applications with SDLC for easier imaging:
- Banking Software Solutions: Institutions like JPMorgan Chase use strict SDLC to ensure regulatory compliance, secure design, accurate transactions, and ongoing updates.
- E-commerce Platforms: Amazon applies SDLC for every new feature, from planning and coding to testing, deployment, and continuous optimization.
- Mobile Apps: Apps like Instagram and WhatsApp follow SDLC to achieve seamless user experience, cross-platform performance, and scalable infrastructure.
What are the 7 Phases of SDLC?
The seven phases of SDLC form a structured yet flexible framework for building software. Each phase builds on the last while allowing teams to revisit earlier steps when needed. Understanding these phases is key for effective project management and collaboration, ensuring every stage—from planning to long-term maintenance—is executed thoroughly and nothing critical is overlooked. Let’s go for details in each phase below:
| Phase | Key Activities | Details | Deliverables |
| 1. Planning |
|
Establishes project foundation by identifying goals, constraints, and success criteria. Involves stakeholder consultation and feasibility analysis |
|
| 2. Analysis |
|
Deep dive into functional and non-functional requirements, user needs analysis, and technical constraint identification |
|
| 3. Design |
|
Creates the blueprint for software construction, including system architecture, data flow, and user interaction patterns |
|
| 4. Development |
|
Actual construction of software based on design specifications using appropriate programming languages and development tools |
|
| 5. Testing |
|
Comprehensive validation of software functionality, performance, security, and user experience |
|
| 6. Deployment |
|
Transition of software from development to production environment with user onboarding and support systems |
|
| 7. Maintenance |
|
Ongoing support and evolution of software to meet changing needs and address emerging issues |
|
The most critical phase in SDLC is arguably the Requirements Analysis phase, as it forms the foundation for all subsequent development activities. Poor requirement definition leads to scope creep, budget overruns, and software that fails to meet user needs. However, the Testing phase is equally crucial, as it ensures software quality and prevents costly post-deployment issues.
How Many Models of SDLC?
There are eight primary SDLC models, each offering different approaches to managing the phases of software development. These models vary in their structure, flexibility, and suitability for different types of projects. While all models follow the basic SDLC phases, they differ in how these phases are organized, executed, and interconnected.
1. Waterfall
The Waterfall model is the most traditional and linear approach to software development. In this model, each phase must be completed entirely before moving to the next phase, creating a cascading effect similar to a waterfall. This sequential approach provides clear structure and documentation at each stage, making it easy to manage and understand.
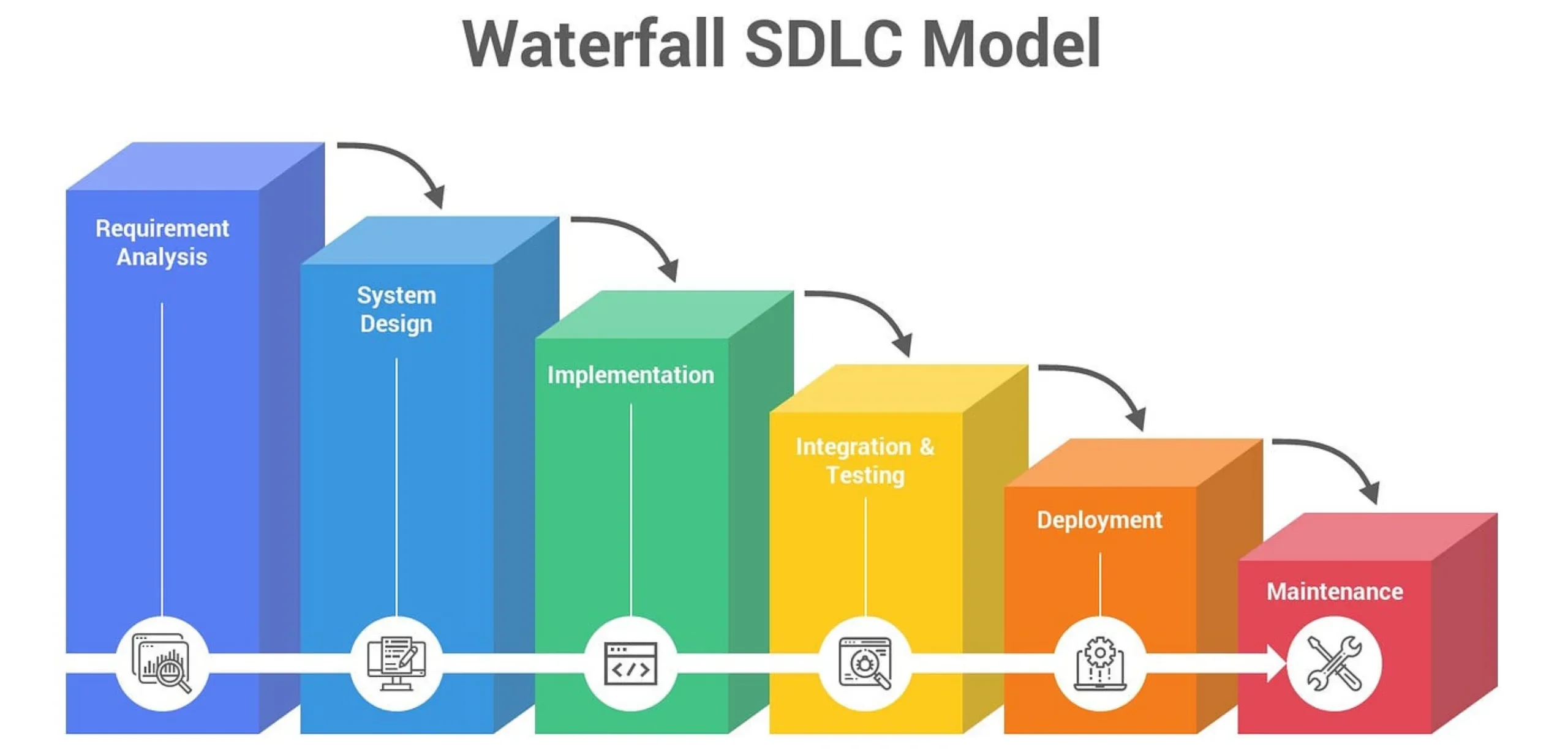
The Waterfall model works best when requirements are well-defined and unlikely to change during development. It emphasizes thorough planning and documentation, making it suitable for projects with strict regulatory requirements or where extensive documentation is necessary.
| Pros | Cons |
| Clear project structure and milestones | Inflexible to requirement changes |
| Comprehensive documentation | Late discovery of issues |
| Easy to manage and understand | No working software until late in the process |
| Well-suited for fixed-price contracts | Limited customer feedback during development |
| Clear roles and responsibilities | High risk if initial requirements are incorrect |
Suitable for:
- Projects with stable, well-defined requirements
- Government and regulatory compliance projects
- Large-scale enterprise systems with extensive documentation needs
- Projects where the technology is well-understood
- Fixed-budget, fixed-timeline contracts
2. V-Model
The V-Model, also known as the Verification and Validation model, is an extension of the Waterfall model that emphasizes testing throughout the development process. The model gets its name from the V-shape formed by the development and testing phases, where each development phase has a corresponding testing phase.
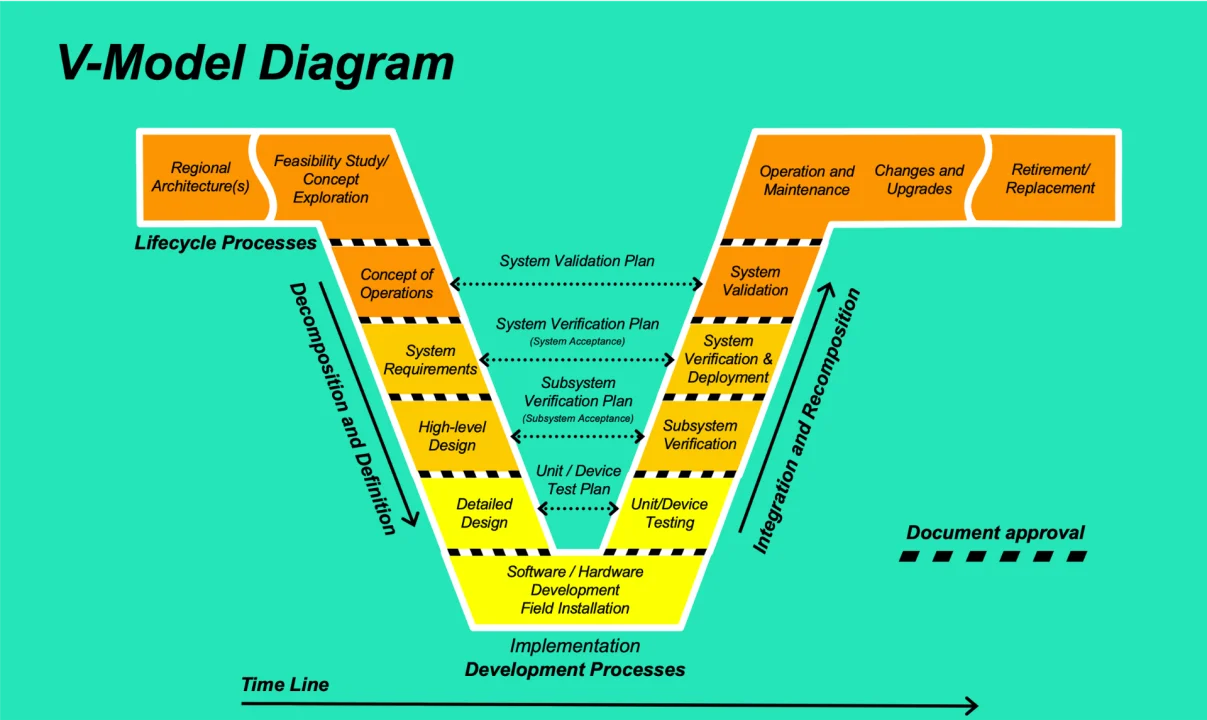
This model ensures that testing activities are planned early and executed systematically, reducing the likelihood of defects in the final product. The V-Model is particularly effective for projects requiring high reliability and extensive testing, such as safety-critical systems.
| Pros | Cons |
| Early test planning and execution | Inflexible to changing requirements |
| High-quality deliverables through rigorous testing | No working software until late stages |
| Clear testing objectives for each phase | Expensive due to extensive testing |
| Suitable for safety-critical applications | Sequential nature limits parallel activities |
| Well-defined deliverables and milestones | Limited customer involvement during development |
Suitable for:
- Safety-critical systems (medical devices, automotive, aerospace)
- Projects requiring extensive testing and validation
- Systems with strict quality and compliance requirements
- Projects where requirements are stable and well-understood
- Applications requiring formal verification processes
3. Agile
The Agile model revolutionized software development by emphasizing iterative development, customer collaboration, and adaptive planning. Instead of following a rigid sequence, Agile breaks projects into small iterations called sprints, typically lasting 1-4 weeks, with each sprint delivering working software.
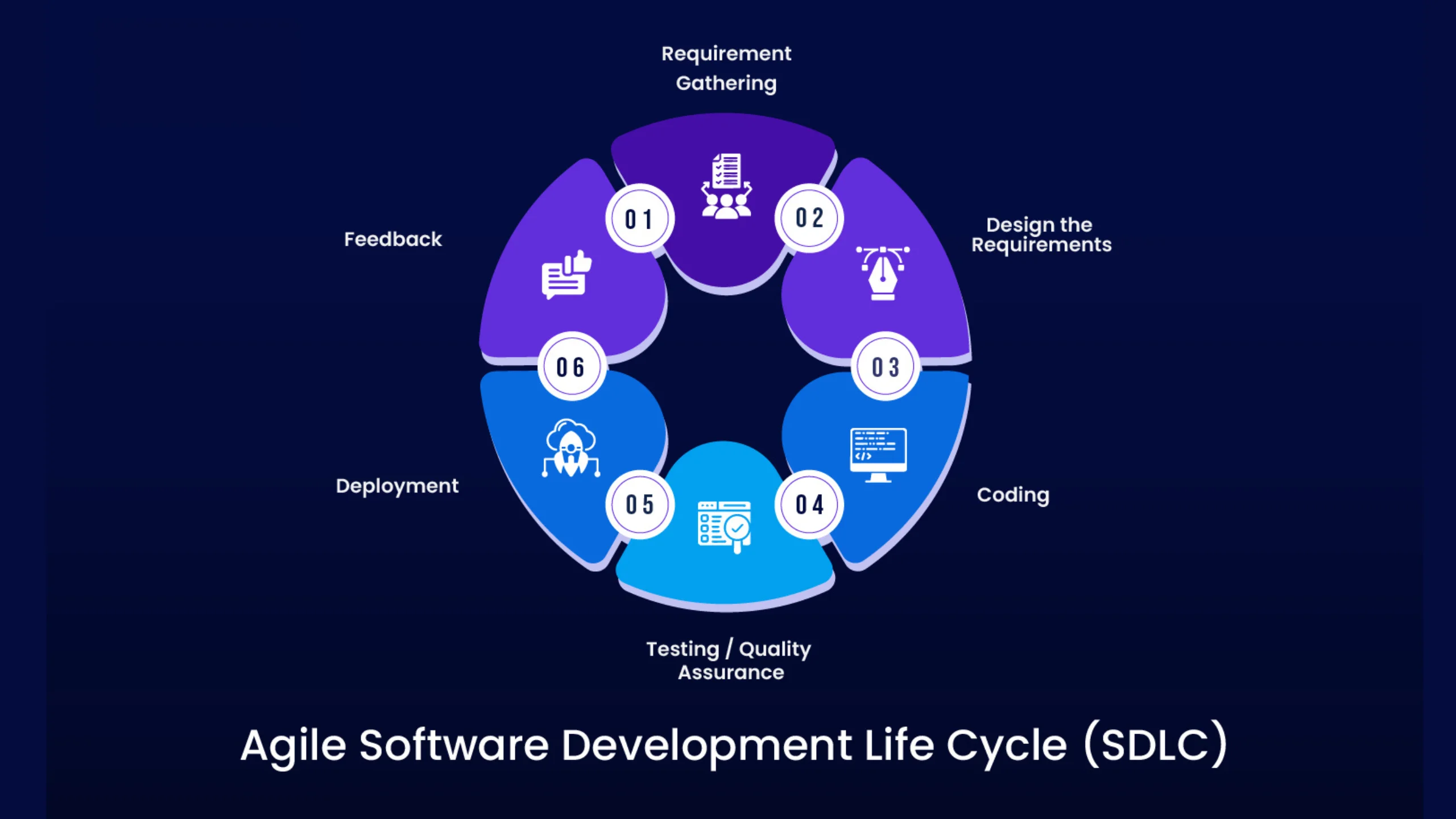
Agile promotes continuous customer feedback, team collaboration, and the ability to respond quickly to changing requirements. This approach has become increasingly popular due to its flexibility and focus on delivering value early and frequently.
| Pros | Cons |
| Flexible and adaptive to changes | Requires experienced team members |
| Early and continuous delivery of working software | Can lack proper documentation |
| High customer satisfaction through regular feedback | Difficult to estimate timelines and costs |
| Promotes team collaboration and communication | Requires active customer involvement |
| Reduces risk through iterative development | May lead to scope creep without proper control |
Suitable for:
- Projects with evolving or unclear requirements
- Customer-facing applications requiring frequent updates
- Startups and innovative product development
- Teams with experienced developers and active product owners
- Projects where time-to-market is critical
4. Lean
The Lean model applies manufacturing principles to software development, focusing on eliminating waste and maximizing value delivery. Lean emphasizes continuous improvement, just-in-time delivery, and empowering development teams to make decisions quickly.
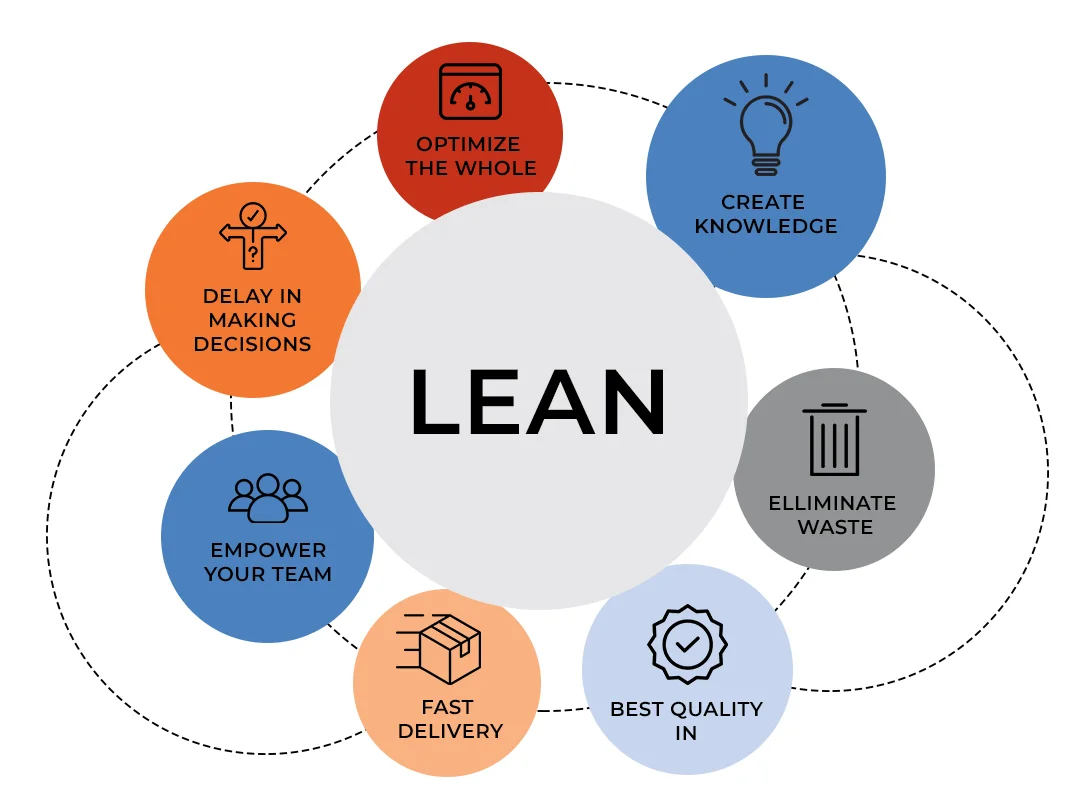
This model prioritizes efficiency and value creation while minimizing activities that don’t contribute directly to customer value. Lean principles complement other methodologies and can be integrated with Agile practices for enhanced effectiveness.
| Pros | Cons |
| Eliminates waste and improves efficiency | Requires significant cultural change |
| Focuses on customer value delivery | May sacrifice documentation for speed |
| Empowers teams and reduces bureaucracy | Difficult to implement in traditional organizations |
| Continuous improvement mindset | Requires experienced team members |
| Faster time-to-market | May lack sufficient planning for complex projects |
Suitable for:
- Organizations seeking to optimize development processes
- Projects with tight budgets and timelines
- Teams experienced in lean principles
- Continuous improvement and optimization initiatives
- Startups requiring rapid development and deployment
5. Iterative
The Iterative model develops software through repeated cycles, with each iteration building upon the previous one. Unlike Waterfall, the Iterative model allows for revisiting and refining earlier phases based on feedback and learning from each iteration.
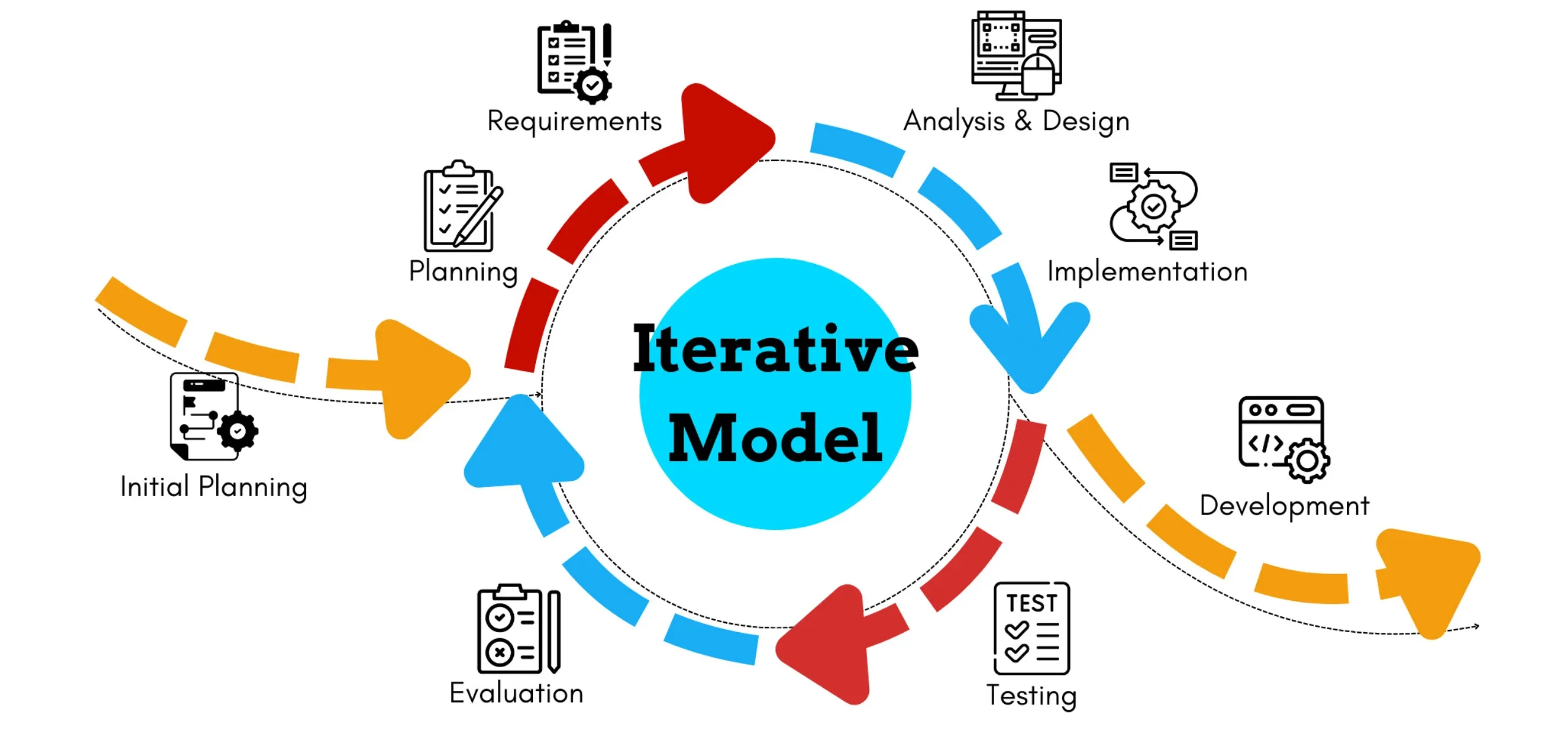
This approach enables teams to improve the software progressively, incorporating lessons learned and adapting to changing requirements. Each iteration typically includes all SDLC phases but focuses on specific features or components.
| Pros | Cons |
| Allows for refinement and improvement | Can be time-consuming with multiple iterations |
| Early identification and resolution of issues | May lead to scope creep |
| Flexibility to accommodate changes | Requires careful planning and management |
| Risk reduction through incremental development | Can be expensive due to repeated phases |
| Regular feedback and validation opportunities | May lack clear project completion criteria |
Suitable for:
- Large, complex projects that can be broken down into components
- Projects where requirements are expected to evolve
- Teams learning new technologies or domains
- Projects requiring proof-of-concept development
- Applications where user feedback drives feature development
6. Spiral
The Spiral model combines iterative development with systematic risk assessment, making it ideal for large, complex, and high-risk projects. The model follows a spiral path through four main activities: determining objectives, analyzing risks, developing and testing, and planning the next iteration.
Each spiral iteration includes risk analysis, which helps identify potential problems early and develop strategies to mitigate them. This makes the Spiral model particularly suitable for projects with significant technical or business risks.
| Pros | Cons |
| Excellent risk management and mitigation | Complex and expensive to implement |
| Flexibility to incorporate changes | Requires risk assessment expertise |
| Early identification of high-risk elements | Not suitable for small projects |
| Combines benefits of other models | Lengthy development process |
| Suitable for large, complex projects | Success depends on risk analysis accuracy |
Suitable for:
- Large-scale, complex software systems
- Projects with significant technical risks
- Research and development projects
- Systems requiring extensive risk assessment
- Projects with uncertain or evolving technology requirements
7. Big Bang
The Big Bang model is an informal approach that involves minimal planning and jumps directly into coding. This model works on the principle that software requirements are either very simple or completely unknown, making detailed planning impractical.
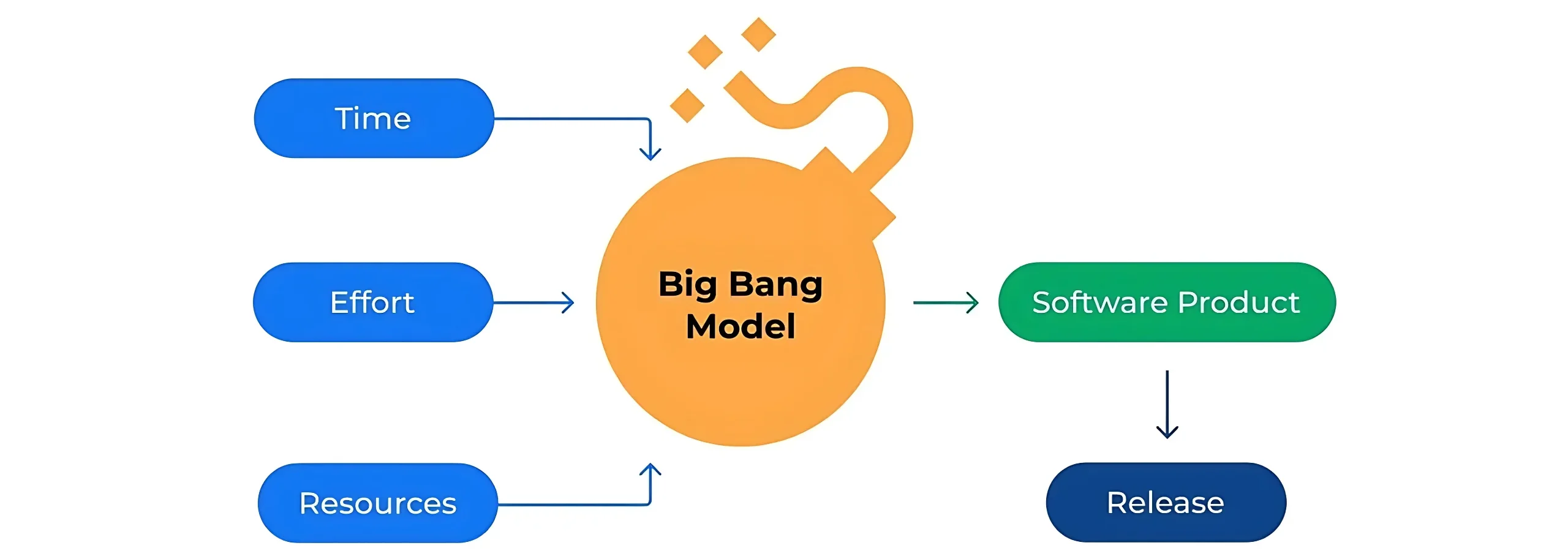
While seemingly chaotic, the Big Bang model can be effective for small projects, proof-of-concepts, or experimental development where the focus is on rapid prototyping rather than systematic development.
| Pros | Cons |
| Minimal planning and documentation required | High risk and unpredictable outcomes |
| Suitable for small, simple projects | Difficult to track progress |
| Flexible and allows for creativity | May result in poor quality software |
| Low cost for appropriate projects | Not scalable for larger projects |
| Quick start and rapid prototyping | Limited customer involvement |
Suitable for:
- Small, experimental projects
- Proof-of-concept development
- Academic or research projects
- Projects with very simple requirements
- Rapid prototyping initiatives
8. Rapid Application Development (RAD)
RAD emphasizes rapid prototyping and iterative development with heavy user involvement. This model uses pre-built components, visual development tools, and reusable code to accelerate the development process while maintaining quality.
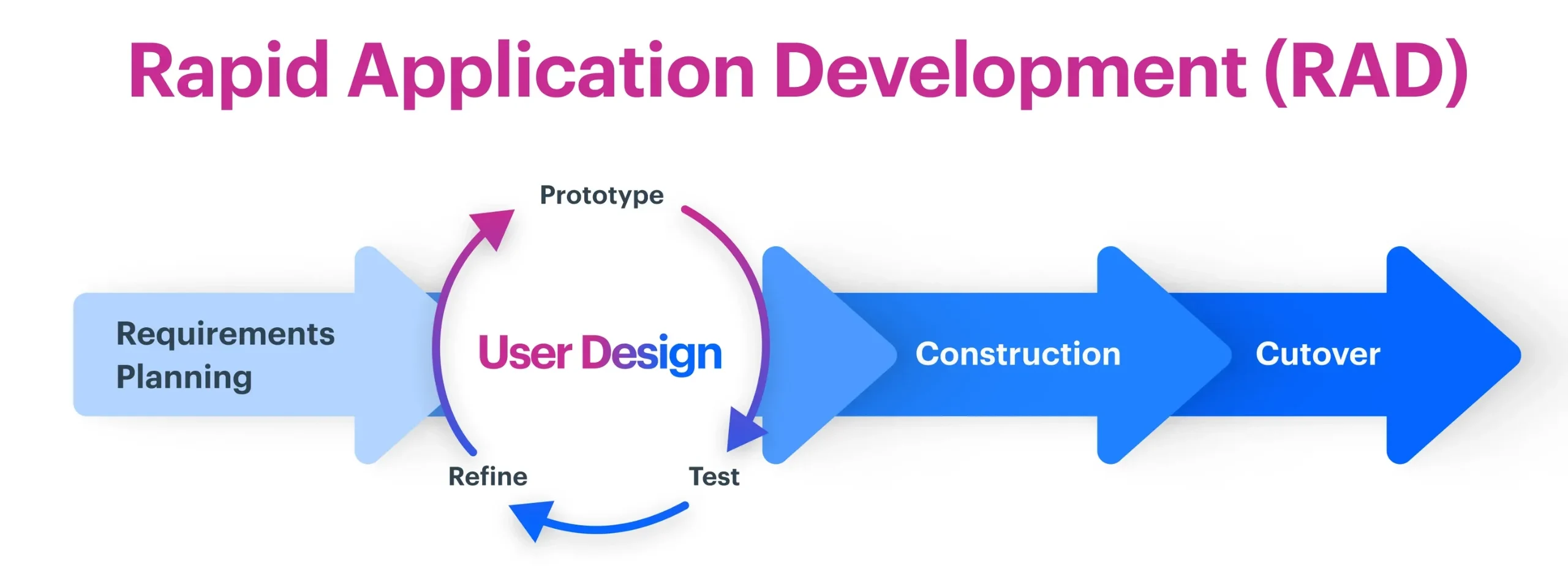
RAD is particularly effective for projects where user interface and user experience are critical, as it allows for rapid creation and testing of prototypes with actual users.
| Pros | Cons |
| Fast development and delivery | Requires skilled developers and designers |
| High user involvement and satisfaction | Not suitable for all types of projects |
| Reusable components reduce development time | May compromise system performance |
| Suitable for business applications | Requires user availability throughout development |
| Reduced development costs | Limited scalability for large systems |
Suitable for:
- Business applications with well-understood domains
- Projects requiring rapid time-to-market
- User interface-intensive applications
- Projects with available and engaged users
- Systems that can leverage existing components and frameworks
How does SDLC Address Security?
Security integration within SDLC has evolved from an afterthought to a fundamental requirement throughout the development process. Modern SDLC practices embed security considerations into every phase, creating more robust and secure software.
Security-by-Design Approach:
- Planning & Analysis: Identify security requirements, compliance needs, and conduct initial threat modeling
- Design: Implement security architecture, access controls, encryption strategies, and detailed threat assessments
- Development: Apply secure coding practices, input validation, proper error handling, and authentication mechanisms
- Testing: Execute penetration testing, security code reviews, vulnerability assessments, and compliance validation
- Deployment: Implement secure configuration management and monitoring systems
- Maintenance: Provide ongoing security updates, threat monitoring, and incident response procedures
DevSecOps Integration automates security throughout CI/CD pipelines with continuous vulnerability scanning, automated security testing, and policy enforcement. This ensures security standards are maintained consistently while enabling rapid development cycles without compromising protection.
>> Read more: What is DevOps Software Development? A Smarter Path to Speed and Reliability
Benefits & Challenges of SDLC
While SDLC provides significant benefits, successful implementation requires addressing inherent challenges through proper planning and execution:
| Benefits | Challenges |
| Improved Software Quality: Systematic testing and validation throughout development ensures higher-quality deliverables | Scope Creep: Projects may expand beyond original requirements without proper change management processes |
| Better Project Management: Clear phases, milestones, and deliverables enable effective project tracking and control | Requirement Changes: Evolving business needs may conflict with established development phases and timelines |
| Risk Reduction: Early identification and mitigation of potential issues prevents costly late-stage fixes | Resource Management: Balancing team skills, availability, and project demands across multiple phases |
| Cost Control: Accurate estimation and budget management through structured planning and monitoring | Technology Evolution: Rapid changes in technology may outpace development timelines and architectural decisions |
| Enhanced Communication: Standardized documentation and processes improve stakeholder collaboration | Team Coordination: Managing multiple team members across different phases and ensuring consistent communication |
| Quality Assurance: Built-in testing and validation processes ensure software meets requirements and standards | Time Constraints: Balancing thorough development processes with market pressures and delivery deadlines |
| Maintainability: Proper documentation and structure facilitate ongoing maintenance and future enhancements | Skill Requirements: Teams need diverse skills and experience to effectively implement SDLC practices |
The key to maximizing SDLC benefits while minimizing challenges lies in selecting the appropriate model for each project, maintaining flexibility within structured processes, and continuously improving development practices based on lessons learned and changing business needs.
How Newwave Solutions Kickstarts Your SDLC?
At Newwave Solutions, we understand the critical importance of following proven SDLC methodologies to deliver exceptional software solutions. As a leading IT outsourcing services provider, we specialize in implementing comprehensive SDLC processes tailored to your business requirements and industry standards.
Our experienced development teams are proficient in all major SDLC models, from traditional Waterfall approaches for regulatory compliance projects to Agile methodologies for rapid product development. We offer end-to-end software development services, including:
- Strategic Planning and Analysis: We work closely with your stakeholders to define clear requirements, establish project scope, and develop comprehensive project roadmaps
- Architecture and Design Services: Our expert architects create scalable, secure, and maintainable software designs that align with your business objectives
- Custom Development Solutions: From web applications to mobile platforms and enterprise systems, we deliver high-quality code following industry best practices
- Comprehensive Testing and QA: Our quality assurance teams implement rigorous testing protocols to ensure your software meets the highest standards
- DevSecOps Implementation: We integrate security throughout the development lifecycle, protecting your applications and data
- Ongoing software maintenance and support services: Our long-term partnership approach ensures your software continues to evolve with your business needs
Partner with Newwave Solutions to leverage our SDLC expertise and transform your software development initiatives. Contact us today to discuss how our proven methodologies and experienced teams can accelerate your digital transformation journey while ensuring project success and long-term value creation.
Ready to implement robust SDLC practices for your next project? Let Newwave Solutions guide you through every phase of development, from initial planning to ongoing maintenance and optimization.
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply