Blockchain in Fintech: Use Cases, Benefits, Challenges & Potentials

The future of finance is being rebuilt on blockchain, a world of instant settlements, self-executing smart contracts, and sovereign digital identity. This convergence of blockchain and fintech is dismantling archaic systems, replacing them with transparent, efficient, and secure protocols. For forward-thinking leaders, grasping this shift is critical. This guide cuts through the complexity to provide the strategic insights you need to leverage blockchain in fintech and turn its disruptive potential into your next competitive advantage.
Get to Know Common Definitions for Blockchain in Fintech
At its heart, blockchain in fintech is a revolutionary way of recording and sharing data. Think of it not as a single technology, but as a new protocol for trust. Traditionally, we rely on central authorities like banks or governments to maintain ledgers and validate transactions. A blockchain technology replaces this need for a middleman by distributing an identical copy of the ledger across a vast network of computers.
Every transaction is grouped into a “block,” cryptographically sealed, and chained to the previous one. This creates a permanent, unchangeable history that is transparent to everyone in the network and incredibly difficult to corrupt. This simple yet powerful concept is the engine behind most modern fintech and blockchain technology innovations.
This brings us to common terms you’ll hear:
- Cryptocurrency: This is the most famous application. It’s a digital currency that uses cryptography for security and operates on a blockchain. It enables peer-to-peer value transfer without a central bank.
- Bitcoin: The first and most well-known cryptocurrency, created to be a decentralized digital cash system.
- Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts. The terms of the agreement are written directly into code, which automatically executes when conditions are met, eliminating the need for an intermediary.
So what type of blockchain is often used in fintech?
Not all blockchains are the same. The choice depends on the specific use case and required balance between control, privacy, and decentralization.
- Permissioned (Private) Blockchains: These are common in enterprise fintech and blockchain projects. Participation is invite-only, controlled by a single organization or a consortium. They offer greater privacy, efficiency, and regulatory compliance, making them ideal for business-to-business applications like trade finance or KYC checks. Hyperledger Fabric is a leading example.
- Permissionless (Public) Blockchains: These are open for anyone to join, read, and participate in (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum). They are fully decentralized and secure but can be slower and more transparent than some businesses prefer. They are the foundation for Decentralized Finance (DeFi).
- Consortium Blockchains: A hybrid model where a group of organizations, rather than a single entity, governs the blockchain. This is perfect for industries like banking where multiple players need to collaborate on a shared ledger while maintaining a degree of control. RippleNet is a good example in cross-border payments.
How Blockchain is Used in Fintech?
Blockchain in fintech is not merely a new database, it is a foundational shift in how we structure economic interactions. It provides a new protocol for trust, moving from a model reliant on centralized institutions to one powered by decentralized, cryptographic, and algorithmic certainty. This engineering is what enables the revolutionary applications we see today. The strategic implementation of these mechanics is a core focus of our emerging technology services, ensuring they align with specific business objectives:
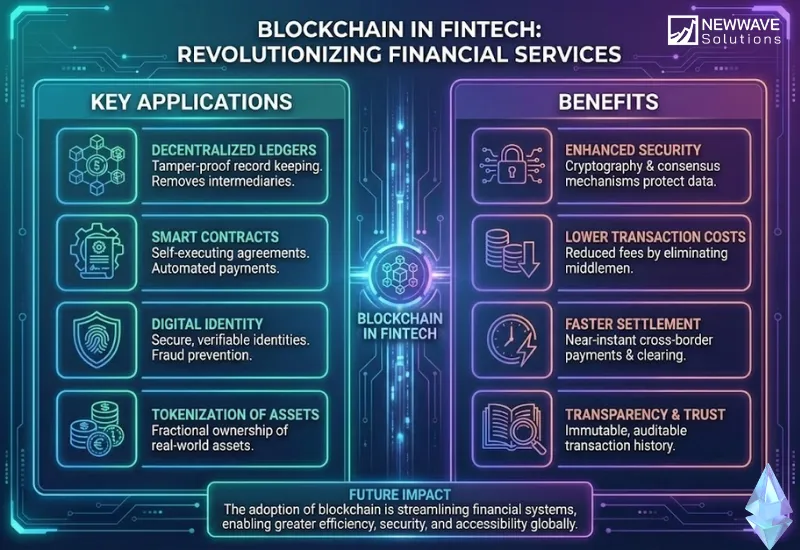
1. Decentralization & Disintermediation
Blockchain’s core innovation is its ability to facilitate trust without a central authority. It replaces intermediaries like banks and clearinghouses with a peer-to-peer network where each participant (node) maintains an identical ledger. Through a consensus mechanism, a set of mathematical rules, the network collectively agrees on the validity of transactions. This disintermediation does more than cut fees; it eliminates single points of failure, reduces systemic latency, and censors-proof financial interactions, allowing value to move as seamlessly as information online.
2. Immutable & Transparent Ledger
Once a transaction is validated by consensus and added to the chain, it is cryptographically sealed to the previous block, creating a permanent, unchangeable record. Attempting to alter this data would require an attacker to overpower the entire network’s computing power and rewrite its entire history—a feat that is computationally prohibitive and instantly detectable. This immutability, combined with controlled transparency, forges an unprecedented and verifiable audit trail that drastically reduces fraud and simplifies compliance.
3. Smart Contract Automation
Smart contracts are autonomous, tamper-proof scripts that execute business logic automatically. They transform the blockchain from a passive database into an active participant. When pre-defined conditions are met (e.g., a confirmed delivery), the contract self-executes the corresponding terms (e.g., releasing a payment). This eliminates manual processing, guarantees outcomes without intermediaries, and enables complex, multi-party agreements—from derivatives to insurance—that are both transparent and trustless.
4. Enhanced Security & Identity Management
Security is inherent in blockchain’s decentralized and cryptographic design, which removes central points of attack. This is powerfully applied to identity through Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI), which allows individuals to own and control their verified credentials (e.g., passports, licenses) in a secure digital wallet.
Users can cryptographically prove their identity or eligibility to institutions without exposing the underlying data, streamlining KYC/AML processes into a one-time verification that enhances privacy and security. Building such user-centric systems is a hallmark of our enterprise software development expertise.
Common Use Cases of Blockchain in Fintech
From reinventing global payment rails to creating new asset classes, fintech and blockchain technology is solving long-standing problems of inefficiency, opacity, and exclusion. The following examples illustrate how this powerful convergence is already delivering value across the industry.
1. Cross-Border Payments and Remittances
The traditional correspondent banking network is a labyrinth of intermediaries, each adding cost, delay, and potential error to international transactions. Blockchain in fintech development solutions elegantly dismantle this model by establishing direct, peer-to-peer payment channels between financial institutions. Value is transferred across a shared ledger—often using stablecoins to mitigate volatility—settling in minutes instead of days. This creates a seamless experience akin to sending an email, but for value, fundamentally altering the economics and speed of global money movement.
Core Benefits:
- Radical Cost Reduction: Slashes fees by up to 80% by eliminating multiple intermediary banks.
- Instant Settlement: Finalizes transactions in minutes, 24/7, improving cash flow and operational efficiency.
- Unprecedented Transparency: Provides real-time tracking and a clear, immutable audit trail for every payment.
Real-World Example: RippleNet is leveraged by companies like MoneyGram to facilitate real-time, low-cost international transfers, demonstrating the scalable enterprise application of this technology.
2. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi is the most ambitious expression of blockchain for fintech, aiming to reconstruct the entire traditional financial stack—lending, borrowing, trading—on open and programmable networks. It replaces centralized institutions with autonomous, transparent smart contracts, creating a global, permissionless financial system. Users interact directly with these protocols to earn yield on assets, access leverage, or trade tokens, all while maintaining custody of their funds. This represents a paradigm shift from “trust in an institution” to “trust in code.”
Core Benefits:
- Permissionless Access: Offers financial services to anyone with an internet connection, 24/7.
- Transparency & Composability: All transactions are public and protocols can interoperate like “money Legos,” fostering innovation.
- User Sovereignty: Individuals maintain control of their assets (self-custody) at all times.
Real-World Example: Aave is a leading decentralized lending protocol where users can lend and borrow a wide variety of crypto assets without a centralized intermediary, governed entirely by its community.
3. Trade Finance
International trade remains crippled by a paper-based system fraught with inefficiency and fraud risk. Letters of credit and bills of lading are slow to process and easy to forge. Blockchain for fintech injects trust and automation by providing all parties—exporters, importers, banks, logistics providers—with a single, immutable source of truth. Smart contracts automate the entire workflow, triggering payments and transferring ownership titles automatically upon the digital verification of pre-defined conditions, such as a container’s arrival at port.
Core Benefits:
- Fraud Mitigation: Immutable ledger ensures documents cannot be altered or duplicated.
- Operational Efficiency: Reduces processing time from weeks to days, freeing up working capital.
- Enhanced Transparency: All authorized participants view the same data in real-time, reducing disputes.
Real-World Example: The we.trade platform, backed by a consortium of major banks like HSBC and UBS, uses blockchain to digitize and automate trade finance processes for European businesses.
4. Tokenization of Real-World Assets (RWA)
Tokenization is the process of converting ownership rights of a physical or financial asset into a digital token on a blockchain. This powerful application of fintech and blockchain technology is unlocking trillions of dollars in previously illiquid capital. By fractionalizing high-value assets like real estate, fine art, or private equity, blockchain enables broader investor access and creates vibrant, 24/7 secondary markets for assets that were once difficult to divide and sell.
Core Benefits:
- Increased Liquidity: Unlocks value in illiquid assets by enabling fractional ownership and easier transfer.
- Democratized Access: Lowers the minimum investment threshold, opening new asset classes to retail investors.
- Automated Compliance: Programmable tokens can embed regulatory rules, streamlining ownership transfer and compliance.
Real-World Example: Major institutions like UBS and BlackRock have launched tokenized money market funds on blockchain networks, signaling strong institutional belief in this future.
5. Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
The current KYC process is a study in redundancy and risk. Customers repeatedly submit sensitive documents to every new financial institution, creating friction and multiplying the risk of data breaches. Blockchain and fintech offer a superior model through Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI). Users undergo verification once by a trusted provider, obtaining cryptographically secure credentials. They then control and share these verified attestations with institutions in a privacy-preserving manner, proving their eligibility without revealing underlying data.
Core Benefits:
- Enhanced Security & Privacy: Users share minimal, verified data, reducing exposure to breaches.
- Dramatic Cost Reduction: Banks save significantly on repetitive compliance checks and manual reviews.
- Streamlined Onboarding: Cuts customer onboarding time from days to minutes, improving user experience.
Real-World Example: Banks like PKO Bank Polski are implementing blockchain-based systems to create a digital identity standard, allowing customers to reuse their KYC verification across multiple services.
>> See more what we can offer in our Custom Banking Software Development Services
6. Smart Contracts for Automated Financial Workflows
The automation potential of smart contracts extends far beyond DeFi into core enterprise operations. These tamper-proof scripts can automate complex, multi-party financial agreements with guaranteed execution. In insurance, a parametric policy can automatically pay out claims when an oracle verifies a flight delay or natural disaster. In capital markets, they can automate dividend distributions, bond coupon payments, and even complex derivative settlements, removing manual intervention and counterparty risk.
Core Benefits:
- Unparalleled Efficiency: Eliminates manual processing, reduces errors, and operates 24/7.
- Guaranteed Execution: Transactions occur exactly as coded, removing uncertainty and disputes.
- Cost Savings: Significantly reduces administrative and operational overhead.
Real-World Example: Etherisc is developing decentralized insurance protocols that use smart contracts to automate flight delay insurance, providing instant payouts to policyholders.
7. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
CBDCs represent the sovereign entry into the digital currency landscape. A CBDC is a digital form of a nation’s fiat currency, issued and backed by the central bank, potentially leveraging blockchain or DLT for distribution. Unlike volatile cryptocurrencies, a CBDC offers the digital convenience of crypto with the stability and trust of government-backed money. It promises to make monetary policy more efficient, reduce the costs of cash management, enhance financial inclusion, and provide a secure foundation for the future digital economy.
Core Benefits:
- Monetary Policy Efficiency: Enables more precise and direct implementation of monetary tools.
- Financial Inclusion: Provides a safe digital payment option for the unbanked population.
- Innovation Foundation: Creates a programmable platform for future financial innovation.
Real-World Example: The digital Chinese yuan (e-CNY) is one of the most advanced large-scale CBDC pilots, with millions of users and a growing ecosystem of merchants, showcasing a potential model for the future of state-backed digital cash.
Benefits and Challenges of Blockchain in Fintech
The decision to integrate blockchain in fintech is a strategic one, offering a chance to redefine a business’s fundamental operations and value proposition. However, its adoption is not a simple upgrade; it is a paradigm shift that demands a clear-eyed understanding of both its transformative potential and the significant hurdles that must be navigated for successful implementation.
Benefits
The advantages of fintech and blockchain technology extend far beyond incremental cost savings, paving the way for an entirely new operational ethos built on verifiable trust and radical automation:
- Unprecedented Transparency: Every transaction is recorded on a shared ledger, visible to all permitted parties. This builds trust and makes auditing far simpler and more reliable.
- Enhanced Security & Trust: The decentralized and cryptographic nature of blockchain makes it extremely resistant to fraud, hacking, and data tampering. Trust is established by the technology itself, not just by an institution’s reputation.
- Radical Efficiency & Cost Reduction: By automating processes with smart contracts and removing intermediaries, blockchain slashes administrative overhead, processing times, and operational costs. This is a key value proposition we deliver through our enterprise software development services.
- Increased Accessibility & Financial Inclusion: Blockchain for fintech enables decentralized financial services (DeFi) that are open to anyone with a smartphone and internet connection, potentially bringing billions of unbanked individuals into the global economy.
Challenges
For all its promise, the path to blockchain integration is fraught with technical, regulatory, and operational complexities that require careful strategic management:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The legal landscape for digital assets and smart contracts is still evolving globally. This creates a complex environment for businesses to operate in.
- Scalability Issues: Some major blockchain networks struggle to process a high volume of transactions quickly and cheaply, though new solutions are constantly emerging.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Connecting cutting-edge blockchain applications with decades-old banking IT infrastructure is a complex and costly technical challenge.
- Skill Gap & Education: There is a significant shortage of developers and business leaders with deep expertise in fintech and blockchain technology, making talent acquisition difficult.
Fintech blockchain trends and beyond
The evolution of blockchain in fintech is accelerating. The next few years will be defined by trends that move from speculation to practical, scalable integration.
We are moving into the era of Institutional DeFi (DeFi 2.0), where the infrastructure will become more regulated, secure, and integrated with traditional finance, attracting major banks and investment firms. Furthermore, blockchain and fintech will be crucial for Green Finance, providing transparent and unchangeable systems to track carbon credits, ESG metrics, and sustainable investments, ensuring authenticity and preventing “greenwashing.”
Most importantly, we will see a shift towards Embedded Finance Infrastructure. Blockchain will become an invisible backbone, powering features within everyday apps without users even realizing it—think in-app crypto wallets, tokenized loyalty points, and seamless cross-border settlement layers for e-commerce platforms. Successfully navigating this future requires a partner who understands both the technology and the market. A well-defined technology consulting strategy is essential to leverage these trends for your business advantage.
Why choose Newwave solutions for your blockchain Fintech project?
At Newwave Solutions, we don’t just code; we translate complex technological potential into tangible business outcomes. Our expertise in fintech and blockchain technology is matched by our mastery of cross-platform development frameworks, ensuring the solutions we build are not only innovative but also scalable, secure, and seamlessly integrated into your existing ecosystem.
What can you expect when you work with us?
- End-to-End Development: From initial concept and strategy to deployment and maintenance, we guide you through every stage of your blockchain for fintech project.
- Flexible Engagement Models: Whether you need a dedicated development team, a fixed-scope project, or specialized staff augmentation to fill skill gaps, we have a model that suits your needs.
- Deep Technical & Industry Expertise: Our team combines blockchain proficiency with a firm understanding of financial regulations and user experience design.
Your vision for a more efficient, transparent, and innovative financial product is achievable. Discuss your project idea and explore how we can bring it to life together.
What are you waiting for? Let’s contact Newwave Solutions today!
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.



Leave a Reply