A Practical Guide to Blockchain in Supply Chain Management

Blockchain in supply chain is turning this transparency into a tangible reality, enabling a level of traceability and security that was previously impossible. This isn’t a distant promise; it’s actively solving critical challenges in logistics, pharmaceuticals, and retail today. For forward-thinking leaders and innovators, understanding this convergence is no longer optional, it’s essential for building more efficient, trustworthy, and resilient operations. This guide cuts through the complexity to show you how.
What is Blockchain in Supply Chain?
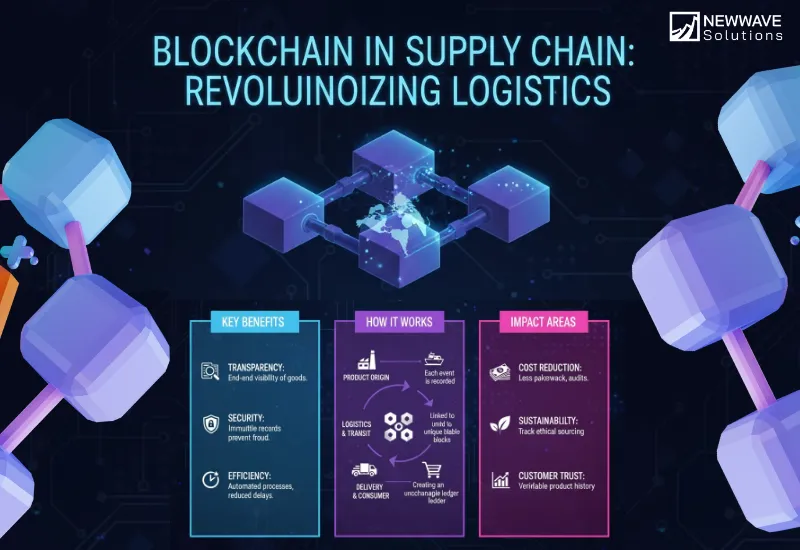
At its core, blockchain in supply chain is a strategic application of a decentralized digital ledger to track assets and record transactions as they move through a complex network of suppliers, manufacturers, shippers, and retailers. Think of it not as a mere database, but as a single, unchangeable source of truth that every participant in the supply chain can trust without needing a central authority to manage it.
Traditional supply chains run on siloed data—each company keeps its own records in its own system, leading to discrepancies, delays, and disputes. Blockchain technology supply chain solutions shatter these silos. Every time an asset changes hands or its status updates (e.g., a shipment’s temperature changes), the transaction is recorded to the ledger, cryptographically sealed, and shared across the network. This creates a complete, verifiable, and tamper-proof history of an asset’s journey from origin to end-user.
So what type of blockchain is often used in supply chain?
Not all blockchains are created equal. The supply chain industry primarily leverages two types:
- Permissioned (Private) Blockchains: This is the most common model for enterprise blockchain technology for supply chain management. Participation is by invitation only, controlled by a consortium of businesses or a single governing entity. This model offers greater privacy, faster transaction speeds, and regulatory compliance, which is essential for business-to-business operations where data must be shared selectively but verifiably. Examples include Hyperledger Fabric and Corda.
- Consortium Blockchains: A hybrid model where a group of organizations, rather than a single company, governs the blockchain. This is ideal for supply chains where multiple competitors need to collaborate on a shared platform for mutual benefit (e.g., all major shipping lines using one system for port logistics). It balances decentralization with control and is the foundation for networks like TradeLens.
How Blockchain is Used in Supply Chain?
The power of blockchain and the supply chain lies in its core architectural principles. These are not just features; they are fundamental capabilities that address specific supply chain pain points.
1. Digital Twins & Immutable Record-Keeping
This is the foundational use. A “digital twin” is a digital representation of a physical asset (a pallet, a container, a single product). Each twin is assigned a unique identifier (via QR code, RFID, or NFC). Every event in the asset’s life—manufacturing, shipping, customs clearance—is recorded as a permanent, unchangeable transaction on the blockchain. This creates a cradle-to-grave history that is cryptographically secured against tampering, eliminating fraud and erroneous data.
2. Enhanced Transparency & Traceability
Blockchain technology in supply chain management provides authorized participants with real-time, end-to-end visibility. Instead of waiting for emails and faxes, a manufacturer, logistics provider, and retailer can all view the same immutable ledger simultaneously. This allows for instant traceability; pinpointing the location and condition of any asset in seconds, a process that traditionally took days. This transparency is crucial for verifying authenticity and responding swiftly to disruptions.
3. Process Automation with Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written directly into code. They automate workflows by triggering actions automatically when pre-set conditions are met. For example, a smart contract could:
- Automate payments: Release payment to a supplier instantly upon GPS-verified delivery of goods.
- Manage compliance: Trigger an alert if a shipment of vaccines is exposed to temperatures outside a predefined range.
This eliminates manual processes, reduces administrative costs, and guarantees execution based on verified data, not promises. Developing such automated workflows is a key focus of our enterprise software development services.
4. Decentralized Consensus & Trust
Unlike a traditional database owned by one entity, a blockchain ledger is distributed across a network of computers. Transactions are validated by a consensus mechanism agreed upon by all participants. This means no single party can alter the data unilaterally. It replaces the need to trust a business partner with the ability to trust the data itself, creating a new model of verifiable trust among all supply chain participants.
What is Application of Blockchain in Supply Chain?
The theoretical promise of blockchain becomes undeniable when applied to the concrete challenges of modern logistics. Across industries, blockchain technology for supply chain management is moving from pilot projects to production systems, delivering unprecedented levels of verifiable trust, automation, and efficiency. These applications are not merely incremental improvements; they are foundational shifts in how goods and information move around the globe.
1. Food Traceability and Safety
The journey from farm to fork is notoriously complex and opaque. Blockchain technology in supply chain introduces a new paradigm of radical transparency. Each item, whether a batch of produce or a cut of meat, is assigned a unique digital identity. As it moves through each step—harvesting, processing, distribution, retail—its key data (origin, timestamps, temperature, certifications) is immutably recorded. This creates an unforgeable digital narrative of the physical product’s life story. This capability transforms food safety protocols, allowing stakeholders to move from reactive recalls to proactive risk management.
Core Benefits:
- Near-Instantaneous Traceability: Reduces the time to trace contamination sources from weeks to mere seconds, dramatically limiting the scope and financial impact of recalls while protecting public health.
- Verifiable Provenance & Quality Claims: Empowers consumers to scan a QR code and access immutable proof of organic, fair-trade, or locally-sourced claims, building brand trust and enabling informed purchasing decisions.
- Optimized Supply Chain Efficiency: Provides all authorized parties with real-time visibility into inventory location and condition, reducing spoilage and improving demand forecasting.
Real-World Example: Walmart’s implementation of IBM Food Trust famously traced the origin of mangoes in 2.2 seconds, a process that previously took seven days, showcasing a monumental leap in operational responsiveness and consumer safety.
2. Pharmaceutical Authentication in Medical
The pharmaceutical supply chain in medical software development solutions is a high-stakes environment where counterfeiting and temperature excursions can have dire human consequences. Blockchain and supply chain management converge here to create an immutable chain of custody for every drug package. Each unit is serialized and logged onto the blockchain at its point of origin. Every subsequent handoff—from manufacturer to wholesaler, to pharmacy, to patient—is recorded as a tamper-proof event. This system effectively creates a digital fortress around legitimate medicines, making it economically and technically infeasible for counterfeit products to enter the stream.
Core Benefits:
- Eradication of Counterfeits: Provides a secure, verifiable method for pharmacists and patients to authenticate medications, directly combating a global problem that costs lives and billions in lost revenue.
- Regulatory Compliance Automation: Delivers an automated, immutable audit trail that simplifies compliance with stringent regulations like the U.S. Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA), reducing administrative overhead and audit preparation time.
- Integrity Assurance for Sensitive Cargo: IoT sensors can record temperature and humidity data directly to the blockchain, providing undeniable proof that vital drugs like vaccines were maintained within required conditions throughout their journey.
Real-World Example: Leading pharmaceutical manufacturers are leveraging platforms like MediLedger to create an interoperable, decentralized network for verifying prescription drug returns and ensuring the integrity of the pharmaceutical supply chain.
3. Luxury Goods and High-Value Asset Authentication
For luxury brands, authenticity is the cornerstone of value. Counterfeiting erodes profits, dilutes brand equity, and betrays consumer trust. Blockchain technology supply chain solutions directly combat this by providing a digital certificate of authenticity that is as unique and secure as the physical product itself. At the point of creation, a luxury handbag, watch, or piece of jewelry is paired with a digital token on the blockchain. This token, accessible via NFC or a QR code, records the item’s provenance, ownership history, and service records, creating a valuable and un-hackable asset passport.
Core Benefits:
- Irrefutable Proof of Authenticity: Empowers consumers and retailers to instantly verify a product’s legitimacy, effectively shutting down the secondary market for high-quality fakes.
- Enhanced Brand Storytelling & Value: Transforms the ownership experience by providing a rich, verifiable history of the product, from its raw materials to its craftmanship, strengthening emotional connection and residual value.
- Streamlined After-Sales & Warranty Services: Provides a clear history of ownership and service, automating warranty validation and preventing fraud in repair and maintenance claims.
Real-World Example: LVMH, the world’s largest luxury group, launched the Aura Blockchain Consortium to provide a universal solution for tracing luxury products across its prestigious brands, including Louis Vuitton and Dior, ensuring authenticity and proving product origin to discerning customers.
4. Cross-Border Trade and Logistics
International shipping is a testament to complexity, involving dozens of actors and a mountain of paper-based documentation. Blockchain technology for supply chain management streamlines this chaos by digitizing and synchronizing the entire documentation flow. Bills of lading, letters of credit, customs declarations, and certificates of origin are converted into digital assets on a shared ledger. This creates a single, synchronized version of the truth visible to all permitted parties—shippers, carriers, ports, customs agencies, and banks—dramatically reducing the delays and errors inherent in manual, siloed processes.
Core Benefits:
- Accelerated Document Processing: Reduces the processing time for critical trade documents from days to hours, shortening overall shipping times and improving vessel and port turnaround times.
- Significant Cost Reduction: Eliminates massive administrative overhead associated with document preparation, courier services, and manual data re-entry, directly improving the bottom line.
- Enhanced Visibility & Predictability: Provides all stakeholders with real-time, permissioned visibility into the status of shipments and documentation, enabling better planning and reducing uncertainty.
Real-World Example: TradeLens, a platform co-developed by Maersk and IBM, digitizes the supply chain by bringing together a ecosystem of ports, carriers, and logistics providers onto a neutral, open platform, demonstrating how blockchain and the supply chain can drive industry-wide collaboration.
5. Sustainable and Ethical Sourcing
Modern consumers and regulators increasingly demand proof of ethical and sustainable practices. Blockchain and supply chain management provides the missing link between claims and verifiable evidence. By tracking raw materials like conflict-free minerals, organic cotton, or sustainably harvested wood from their very origin, blockchain creates an immutable audit trail. This trail verifies that environmental standards and fair labor practices were upheld at every single step, moving sustainability from a marketing slogan to a demonstrable fact.
Core Benefits:
- Verifiable ESG Compliance: Provides auditors and consumers with cryptographically secured proof that products meet Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria, which is increasingly mandated by regulations like the EU’s Digital Product Passport.
- Risk Mitigation in Sourcing: Allows companies to pinpoint and eliminate suppliers that engage in unethical practices, protecting the brand from reputational damage and associated financial losses.
- Empowers Conscious Consumerism: Builds deep brand loyalty by allowing consumers to make purchasing decisions that align with their values, supported by transparent and tamper-proof data.
Real-World Example: The diamond industry, led by De Beers’ Tracr platform, uses blockchain to provide consumers with a guarantee that their diamonds are conflict-free, tracing each stone from the mine through cutting and polishing to the final jewelry setting.
6. Automated Supply Chain Finance
Traditional trade finance is hampered by paper-intensive processes, a lack of transparency, and significant delays that strain the cash flow of small and medium-sized suppliers. Blockchain technology in supply chain unlocks working capital by providing financiers with a real-time, transparent, and verifiable view of transactions and inventory levels. Smart contracts can then automate financing agreements, releasing payments instantly upon the digital fulfillment of pre-coded conditions, such as the verified receipt of goods.
Core Benefits:
- Improved Cash Flow & Liquidity: Enables suppliers, especially SMEs, to access capital faster based on verified transactions, reducing the cash conversion cycle and improving financial stability.
- Reduced Risk & Lower Costs: Provides banks and insurers with an immutable view of supply chain activity, reducing the risk of fraud and enabling them to offer more competitive financing rates.
- Frictionless Automation: Smart contracts automate letters of credit and invoice financing, eliminating manual processing, reducing errors, and ensuring timely payments for all parties.
Real-World Example: Various fintech initiatives are emerging that integrate with enterprise ERP systems via blockchain to offer dynamic discounting and supply chain finance solutions, where payments are triggered automatically by shipment confirmations recorded on the ledger.
Benefits and Challenges
Implementing blockchain and supply chain management is a strategic decision with profound upside, but it requires navigating real-world complexities.
Benefits
The advantages are transformative and drive measurable ROI.
- Unprecedented Transparency & Traceability: All authorized participants see the same information in real-time, creating a single source of truth and enabling instant traceability from origin to destination.
- Enhanced Security & Trust: The decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain makes it extremely resistant to fraud, data tampering, and cyber-attacks, building trust on a systemic level.
- Radical Efficiency & Cost Reduction: By automating manual, paper-based processes with smart contracts, blockchain technology in supply chain slashes administrative overhead, reduces delays, and minimizes human error.
- Greater Resilience & Compliance: Provides a clear audit trail for regulators, simplifies compliance reporting, and allows companies to quickly identify and respond to disruptions.
Challenges
Navigating these hurdles is critical for a successful implementation.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Connecting new blockchain platforms to existing ERP, WMS, and other legacy IT systems is a significant technical and financial challenge.
- Industry-Wide Collaboration: Success often depends on getting an entire ecosystem of suppliers, partners, and competitors to adopt the same standards and platform, which requires strong governance and leadership.
- Scalability & Performance: Some blockchain networks can face limitations in processing a very high volume of transactions quickly and cheaply, though technology is continually improving.
- Skill Gap & Knowledge: There is a shortage of professionals with expertise in both blockchain technology and supply chain logistics, making staff augmentation a valuable strategy for many businesses.
Famous Case Studies Using Blockchain Technology in Supply Chain
While the theoretical promise of blockchain is compelling, its true measure lies in tangible, operational results. Beyond the concepts of decentralization and immutability, real-world implementations are now delivering irrefutable ROI, proving the profound value proposition of blockchain technology supply chain:
- Walmart & IBM Food Trust: As mentioned, Walmart’s use of blockchain to trace food products has set a new industry standard for speed and safety, reducing traceability times from days to seconds and dramatically improving recall efficiency.
- Maersk & TradeLens: This shipping giant co-developed TradeLens to digitize the global trade ecosystem. The platform brings together dozens of ports, carriers, and customs authorities onto a shared ledger, reducing paperwork and streamlining the entire journey of a shipping container.
- De Beers & Tracr: This is one of the most successful examples of blockchain technology for supply chain management in luxury goods. Tracr provides a diamond’s immutable record from mine to retail, assuring consumers of its authenticity and ethical origin, thereby protecting the brand’s value and consumer trust.
The Future of Blockchain Technology and Supply Chain
The future of blockchain and the supply chain is not about blockchain alone. Its true potential is unlocked when fused with other emerging technologies solutions.
Blockchain with IoT sensors
The integration of IoT sensors with blockchain is a game-changer. Sensors on shipping containers, pallets, or individual products automatically collect and record data (like location, temperature, humidity, shock) directly onto the blockchain. This creates a stream of trustworthy, tamper-proof data about the condition of goods in transit, enabling:
- Condition-based smart contracts: Automatic actions triggered by real-world events (e.g., a insurance payout if temperatures exceed a threshold).
- Unprecedented quality control: Verifiable proof that sensitive goods (pharmaceuticals, food) were kept within specified conditions throughout their journey.
>> View more what can we offer in IoT software development services
Is Your Supply Chain Ready for a Transformation?
Understanding the potential of blockchain in supply chain is the first step. The next—and most critical—step is execution. This is where choosing the right technology partner defines your success.
At Newwave Solutions, we don’t just build software; we build solutions that solve complex business problems. Our expertise in blockchain technology for supply chain management is matched by our deep experience in cross-platform development and systems integration. We understand that a blockchain development solution is only as strong as its ability to connect seamlessly with your existing operations.
What can you expect when you work with us?
- End-to-End Expertise: From initial technology consulting and strategy to full-scale custom software development services and integration, we guide you through every stage of your project.
- Proven Methodologies: We leverage agile development and robust project management to deliver solutions on time and within budget, whether you need a dedicated team or a fixed-scope project.
- Flexible Engagement Models: We offer tailored staff augmentation services to fill your skill gaps and flexible hiring models to suit your specific business needs and scale.
The future of supply chain is transparent, efficient, and resilient. Let’s build it together. Contact us for a detail consultation to explore how we can transform your supply chain operations.
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply