Website vs Web Application: Which is Better for your Business?

Website vs web application in the digital age are frequently thrown around, sometimes seemingly interchangeably. However, understanding the crucial differences between these two types of online platforms is essential to establishing a successful presence on the web.
Throughout this guide, we’ll explore the functionalities, purposes, and key characteristics that set websites apart from web applications. By the end, you’ll be able to confidently distinguish a website from a web application, ensuring you choose the right platform to achieve your online goals.
What is a Website?
A website is a collection of interconnected web pages accessible through a single domain name or URL. Websites serve as digital storefronts, information hubs, or content repositories, primarily focusing on presenting information to visitors.
Websites are typically static or semi-dynamic digital platforms designed to showcase content, provide information, or represent an entity online. They are built using HTML, CSS, and sometimes basic JavaScript to enhance user experience.

1. Key Features of Websites
- Content-Centric Design: Websites prioritize presenting information in a clear and organized manner. Text, images, and videos are the cornerstones of website content, often structured with a consistent layout for easy navigation.
- Limited Interactivity: Unlike web applications, websites primarily offer static content with minimal interactive elements. Basic forms for contact or feedback, along with simple search functionalities, are common website features. However, user input is generally limited.
- Public Accessibility: Most, if not all, website content is publicly accessible. Users can browse freely without needing a user account or login credentials. This open access makes websites ideal for showcasing information to a broad audience.
2. Advantages of Developing Websites
- Cost-Effective Development: Websites are generally less expensive to create and maintain compared to web applications. This makes them an attractive option for businesses on a budget or those starting their online journey.
- Rapid Development and Deployment: Developing a website can be a relatively quick process, allowing you to launch your online presence faster. This is especially beneficial for businesses that need to establish an online footprint promptly.
- Broad Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection and a web browser can access your website. This removes geographical barriers and opens your content to a global audience.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Friendliness: Websites can be optimized to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). This organic visibility can significantly increase website traffic and brand awareness.
- Low Technical Barrier for Users: Accessing a website requires no special software or technical expertise. Users simply need a web browser and an internet connection, making websites user-friendly for everyone.
3. Limitations of Developing Websites
- Limited Functionality: Websites are not ideal for complex user interactions or data processing. They primarily focus on presenting static information, which can limit their ability to cater to dynamic user needs.
- Static Content Updates: Updating website content often requires intervention from a developer or someone with technical knowledge. This can lead to delays in reflecting changes or adding new information.
- Challenges with Personalization: Websites typically offer limited personalization capabilities. Tailoring content to individual user preferences or past interactions can be difficult with a basic website structure.
- Security Concerns: While security measures can be implemented, websites can be more vulnerable to certain cyberattacks compared to robust web applications with built-in security features.
4. Main Types of Websites
There’s a website format to suit almost any purpose. Here are some popular website categories:
- Business Website: A website designed to present a company’s profile, services, and contact information to customers, helping build brand credibility and generate inquiries.
- Blog Website: A website primarily focused on regularly updated content such as articles, insights, or commentary, used by individuals or organisations to engage audiences and drive traffic.
- Portfolio Website: A website showcasing a person’s or agency’s past work, skills, and achievements, thereby supporting personal branding or client acquisition.
- e-Commerce Website: A website that enables users to browse products or services, add items to a cart, and complete purchases online, thereby facilitating direct sales.
- News or Magazine Website: A website delivering current events, articles, multimedia content, and updates in a structured format, aiming to inform and retain an audience.
By carefully considering these website advantages and limitations, businesses can make an informed decision about whether a traditional website aligns with their goals and target audience. The simple development process, broad reach, and SEO potential make websites an excellent choice for establishing an online presence, showcasing information, or building brand awareness.
However, if your vision involves a more interactive and dynamic online experience with user-driven functionalities, then a web application might be the better solution. In the next section, we’ll find out what a website application is and delve deeper into the world of web applications, and explore their unique capabilities.
What is a Web Application?
To answer in short about what is a web app, it is a software program that runs on web servers and is accessed through web browsers. Web applications are designed to perform specific functions, process data, and provide interactive experiences for users.
Unlike traditional websites, web applications offer more complex functionality and user engagement, often resembling desktop applications in their capabilities.
1. Key Features of Web Applications
- Dynamic Functionality: Web applications are packed with dynamic features that allow users to interact and complete tasks. This could involve filling out forms, submitting data, receiving real-time updates, or interacting with various elements on the screen.
- Task-Oriented Design: Web applications are designed with specific tasks in mind. These tasks could range from managing finances and investments (online banking) to connecting with friends and family (social media) or purchasing products online (e-commerce stores).
- Active User Engagement: Web applications encourage active user engagement. Users actively interact with the application, providing input, receiving feedback, and manipulating data in real time. Think of editing a document, uploading photos, or participating in a live chat – these are all examples of active user engagement within a web application.
2. Advantages of developing Web Applications
- Enhanced Functionality: Unlike a website, a web application goes beyond simply displaying information. Web apps can perform complex tasks and data processing, like managing finances, editing documents, or creating online stores. This interactivity allows users to achieve specific goals through the web app.
- Scalability: Web applications can easily adapt to accommodate a growing user base. As your project gains traction, a web app can handle increasing amounts of data and users without requiring significant changes to the underlying infrastructure. This makes them ideal for businesses with the potential for rapid growth.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Unlike native apps that require installation on specific devices, web applications can be accessed from any device with a web browser, regardless of operating system. This flexibility provides wider accessibility for your users.
- Centralized Updates: Updates and improvements to a web application can be deployed instantly to all users simultaneously. This ensures everyone has access to the latest features and bug fixes, eliminating the need for individual users to download and install updates.
- Data Management: Web applications excel at storing, retrieving, and manipulating large datasets. This makes them perfect for tasks like managing customer information, processing online transactions, or analyzing website traffic data.
3. Limitations of Developing Web Applications
- Development Complexity: Building a web application typically requires more time, resources, and technical expertise compared to creating a simple website. This can be a hurdle for smaller businesses or individuals with limited budgets.
- Internet Dependency: Most web applications rely on a stable internet connection to function properly. This can be a disadvantage in areas with limited or unreliable internet access.
- Performance Considerations: While web applications can be very performant, for certain tasks that require intensive processing or low-latency interaction, native applications downloaded directly to a device might offer a faster and smoother user experience.
- Security Challenges: Because web applications operate online, they require robust security measures to protect user data from breaches and unauthorized access. Implementing and maintaining these security features is an ongoing responsibility for web app developers.
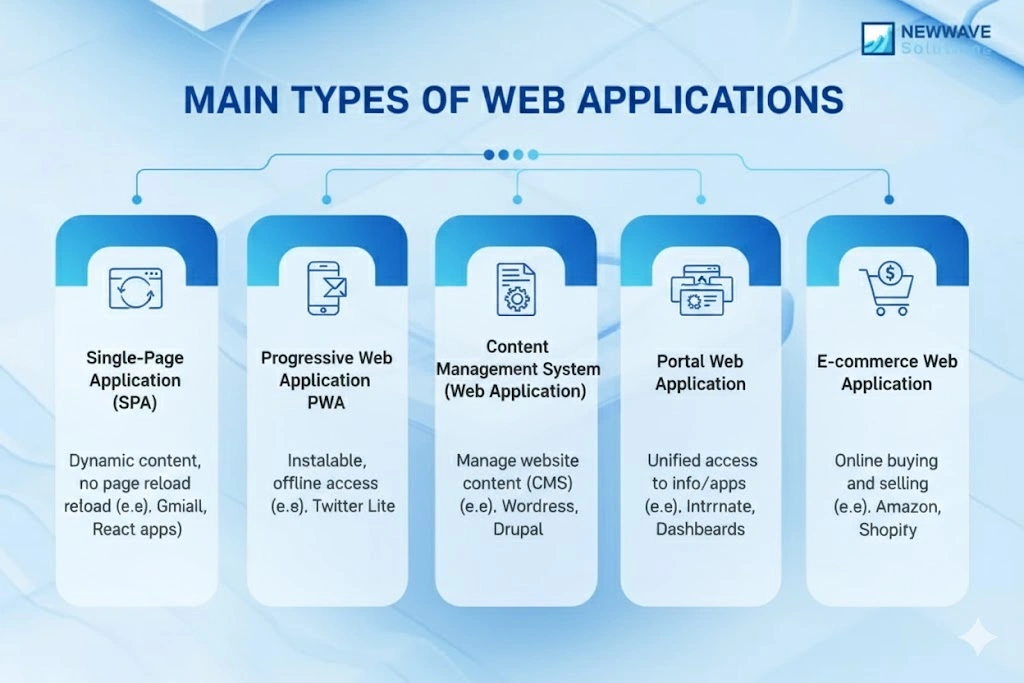
4. Main Types of Web Applications
- Single-Page Application (SPA): A web application that loads a single HTML page and dynamically updates content as the user interacts, delivering a fast, app-like experience within the browser.
- Progressive Web Application (PWA): A web application that uses modern web technologies to provide offline capability, installability, and native-like performance on web browsers across devices.
- Content Management System (CMS) Web Application: A web application that allows non-technical users to create, edit, and manage digital content via a user-friendly interface, often layered on top of a web server and database.
- Portal Web Application: A web application that aggregates services, applications, and information (such as dashboards, email, forums) into one unified interface, often used by enterprises or institutions.
- E-commerce Web Application: A web application built to handle dynamic workflows such as product management, shopping carts, secure payment processing, and user account management, supporting full transactional systems online.
Website vs Web Application: Key Differences
While both websites vs web applications (or web apps) exist on the internet and are accessible through web browsers, they offer distinct experiences. Here’s a breakdown of the main differences between a website and a web app, presented in a table for easy understanding:
| Criteria | Website | Web Application |
| Primary Goal | Build presence, inform, showcase services or products | Enable users to perform tasks, facilitate transactions, and interact with data |
| User Interactivity | Low – mostly reading content, clicking simple links or forms | High – data manipulation, real-time updates, two-way interaction |
| Authentication | Optional or none | Generally required – user accounts, personalised dashboards |
| Content Type | Static or semi-dynamic content pages | Highly dynamic content, user-generated data, personalized views |
| System Complexity | Lower complexity, simpler front-end focus | Higher complexity with back-end logic, APIs, and database interactions |
| Deployment Process | Simpler deployment (e.g., FTP upload, minimal environments) | More complex deployment (CI/CD pipelines, multiple environments, integrations) |
| Scalability | Lower scale targeted – primarily content delivery | Designed for higher scalability (users, data volume, transactions) |
| SEO Focus | High priority for organic traffic and indexing | Functionality and user experience take precedence over pure SEO |
| Technology Stack | HTML/CSS/JavaScript layers mainly for presentation | Combined front-end + back-end stacks, databases, APIs, server-side logic |
| Maintenance & Evolution | Easier to maintain, fewer dependencies, predictable updates | More demanding upkeep, ongoing feature development, and handling complex workflows |
>>> Quick Verdict:
- What makes Website a better choice:
A website excels at building brand presence, delivering content to a wide audience, and driving organic traffic thanks to its simpler structure and high SEO focus. Because deployment and maintenance require fewer dependencies and back-end systems, companies can roll out updates quickly and keep costs lower. Therefore, for businesses primarily focused on information delivery, marketing or brochure-style engagement, a website often presents a more efficient and scalable option.
- What makes Web Application a better choice:
A web application is superior when user interaction, data processing, and dynamic functionality are critical, as it supports high interactivity, scalable back-end logic, and personalized user experiences. Because it typically includes user authentication, real-time updates and complex workflows, the web application better serves transaction-driven or data-intensive business needs. Consequently, for enterprises aiming to enable tasks, business transactions, or service delivery (rather than just content consumption), a web application provides the depth and flexibility required.
Website vs Web Application: When to use what?
After exploring the key differences between these two approaches, let’s find out when to use what to help you know the optimal choice for your business:
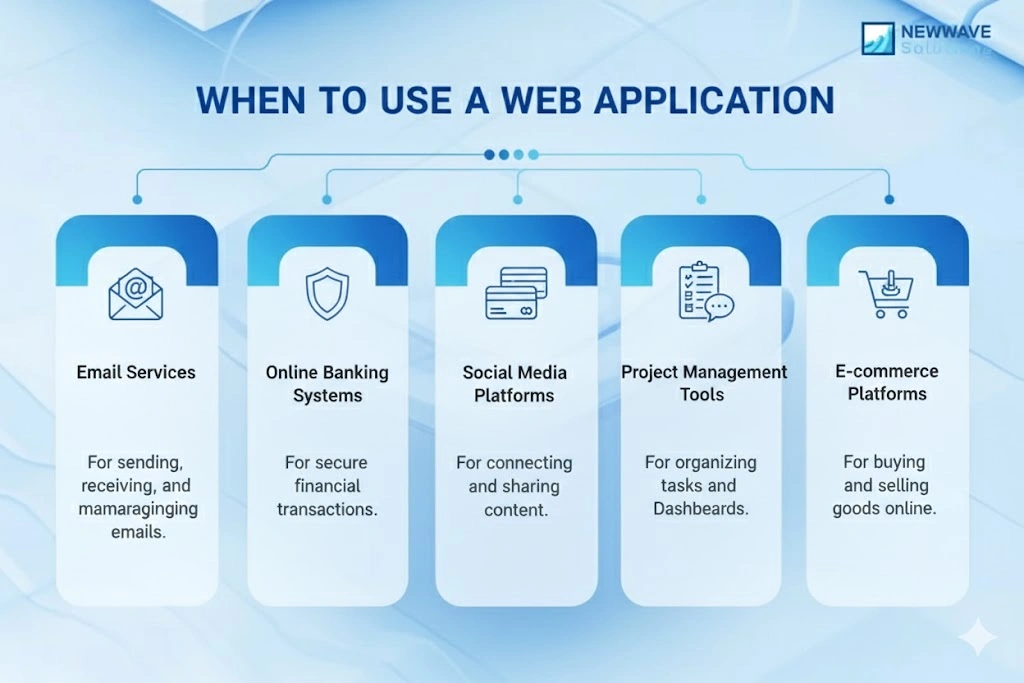
When to Use a Web Application
- Email services (e.g., Gmail): A user needs to manage, send, and receive messages in real-time with authentication and a personalised interface, so a web application is the best fit.
- Online banking systems: Customers require secure login, data manipulation (transfers, balances), and dynamic dashboards, which makes a web application appropriate.
- Social media platforms (e.g., Facebook, Twitter): These services depend on real-time interactions, user-generated content, and personalised feeds, so the interactivity of a web application is essential.
- Project management tools (e.g., Asana, Trello): Users must create tasks, drag-and-drop boards, and collaborate in real-time—functionality that goes beyond what a simple website offers, favouring a web application.
- E-commerce platforms (e.g., Amazon, eBay): When customers log in, browse products, check out, view order history, and interact dynamically, a web application handles the complexity better than a static website.
If you decide to choose to develop a web application for your project, remember to view our detailed guide on web application development to understand the whole process from idea to execution!
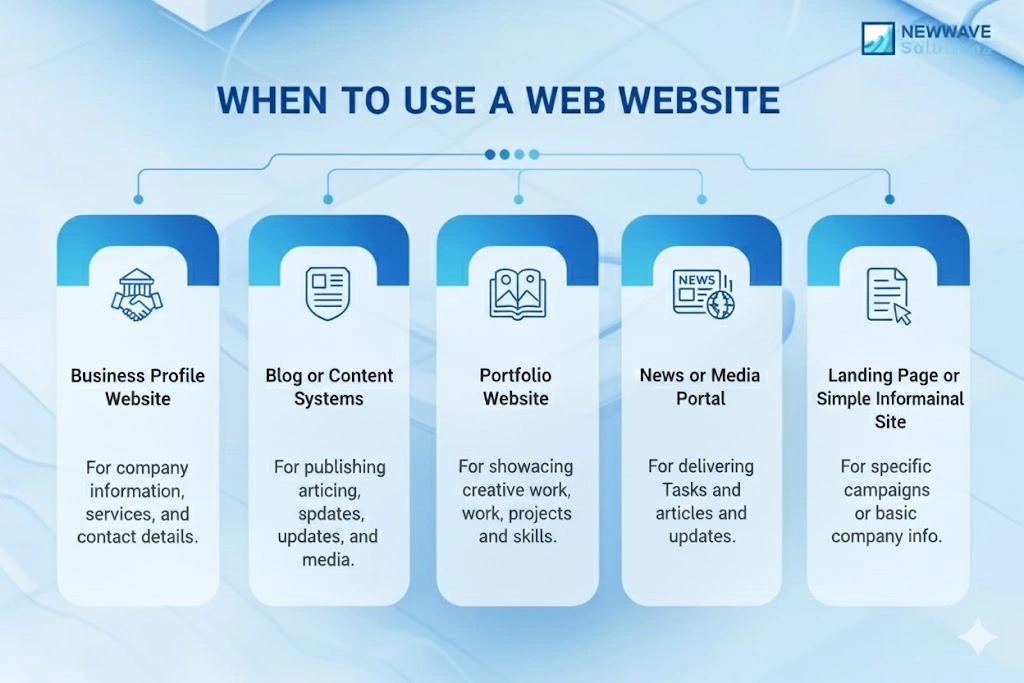
When to Use a Website
- Business profile website: When a company needs an online presence with service descriptions, contact details, and brand information, a website suffices and keeps cost and complexity low.
- Blog or content hub: For organisations publishing articles, news, or thought-leadership, a website delivers easy navigation, content management, and SEO optimisation without heavy interactive features.
- Portfolio website: Individual professionals or agencies showcasing past work and credentials benefit from a website structure that emphasises visuals and simple navigation rather than interactive features.
- News or media portal: When the goal is to distribute frequent updates, headlines, and multimedia content, a website is optimised for content delivery and SEO rather than complex user workflows.
- Landing page or simple informational site: When time-to-market and cost are priorities and users primarily need to consume information rather than perform tasks, building a website is the most efficient path.
What To Keep In Mind When Choosing a Web Application vs a Website
While both are accessed through web browsers, understanding the difference between a web app and a website is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your business goals. Read on to explore some key criteria that can help you pick the appropriate option for your business:
1. Business Goals and Objectives
- Long-term Vision: When considering your company’s website vs web app development, think about your plans. How will your online presence support your long-term growth strategy?
- Target Audience: Who are you trying to reach? Understanding your audience’s technical expertise and preferred methods of online interaction is vital.
- Core Functionality: What is the primary purpose of your online presence? Identify the essential features needed to achieve your business objectives.
2. User Experience and Engagement
- Interactivity Needs: Does your audience need to actively engage with your platform? Will they be manipulating data or performing complex tasks (common in web applications)?
- Content Update Frequency: How often will your content change? Websites can be static, while web applications often require real-time data and dynamic content updates.
- Personalization Requirements: Do you need to tailor the user experience? Consider if user accounts and personalized data are necessary for your website vs web app development.
3. Technical Considerations
- Scalability: Project your future growth in terms of users and data volume. Will you need to expand features and functionalities over time (a common requirement for web applications)?
- Integration Requirements: Does your project require seamless connections with other systems or APIs? Consider compatibility with your existing technology infrastructure.
- Security Needs: Evaluate the sensitivity of the data you’ll be handling. Determine compliance requirements specific to your industry.
4. Resource Allocation
- Budget Constraints: Compare development and maintenance costs for both website vs web application. Consider the long-term financial implications of your choice.
- Development Timeline: How quickly do you need to launch your online presence? Complex features in web applications may require longer development times compared to a basic website.
- In-house Expertise: Evaluate your team’s technical skills. Will you need to outsource development or maintenance for your chosen website vs web app development project?
5. Market Positioning and Competitive Advantage
- Industry Standards: Research what your competitors are using (website vs web app) to understand industry trends. Identify opportunities to differentiate yourself through technology.
- User Expectations: What kind of online experience does your target audience expect? Consider how your website vs. web app development choice aligns with or exceeds these expectations.
6. Future-proofing and Flexibility
- Adaptability to Change: Consider how easily your chosen platform can adapt to future technological advancements. Will it allow you to add new features or pivot your business model if needed?
- Mobile Compatibility: Is it important for your audience to access your platform from mobile devices? Evaluate the need for responsive design (common for websites) versus a native mobile app development approach.
7. Maintenance and Support
- Ongoing Management: Assess the resources required for regular updates and maintenance for your website vs web application. Consider the complexity of troubleshooting and support needs.
- Content Management: Evaluate the ease of updating and managing your content. Consider the need for a content management system (CMS) to simplify website content updates.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision between developing a website vs a web application. Remember, the best choice aligns with your specific business goals, target audience, and desired user experience.
Develop Website and Web Applications With Newwave Solutions
When your enterprise lacks the internal experience or resources to build a website or web application from scratch, engaging an external IT outsourcing partner becomes not just helpful but essential. Among the trusted providers in the market, Newwave Solutions stands out with over 14 years of experience delivering full-cycle development services — from website development services and web app development services to comprehensive software solutions and technology consulting.
With proven expertise and a mature delivery process, Newwave Solutions offers a reliable path for businesses to realize their digital ambitions without overburdening internal teams.
Why Choose Newwave Solutions for Website & Web App Development?
- Comprehensive full-stack expertise across multiple technologies: Newwave Solutions delivers website and web-app development using a wide array of technologies (Java, Python, PHP, Ruby, C#, etc.), which ensures that regardless of your tech stack preferences or legacy systems you have, they can provide a compatible and robust solution.
- Proven track record with larger enterprises and scalable platforms: The company specialises in building secure, scalable, enterprise-grade web applications, indicating strong capacity to handle high-load, high-complexity projects that demand stability and long-term maintainability.
- Flexible engagement models tailored to your needs: Whether you need a fixed-price project, time-and-material, milestone-based delivery, or staff augmentation, Newwave Solutions offers multiple contract and team models enabling you to choose the right level of control and flexibility for your business.
- Speed to market & efficient delivery with agile methodology: For web app development, the company emphasises fast delivery, MVP (Minimum Viable Product) development, and smooth integration with third-party systems (ERP, CRM, cloud), which helps businesses launch faster and adapt as they grow.
- Post-launch support, maintenance, and long-term scalability: Beyond initial build, Newwave Solutions offers maintenance and support services, ensuring that your website/web-app remains stable, secure, and evolves with your business needs over time.
- Deep outsourcing & offshore development capabilities for cost-effective scaling: With a large pool of certified developers and global delivery capacity, the firm enables businesses to scale development resources up or down without the overhead of hiring in-house, which is ideal for companies seeking to optimise costs and access global talent.

Don’t hesitate to approach Newwave Solutions if you are planning to build or upgrade your current website/ web application!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is a website the same as software?
Not exactly. A website itself isn’t software you can download and install. It’s a collection of web pages stored on a server and accessed through a web browser. Think of it as an online brochure or a digital storefront.
2. What separates a website from a web application?
Here’s where things get interesting. Both websites vs web apps live on the internet and are accessible through your browser. But their core purposes differ:
- Websites: Primarily act as informational hubs. They showcase content like text, images, and videos, often representing a company, organization, or individual. Think of company websites, news portals, or blogs. Websites are typically static, meaning their content doesn’t change much unless manually updated. You, as the user, mainly consume information on a website.
- Web Applications (web apps): Offer a more dynamic experience. They’re essentially software programs that run within your web browser, providing interactive features. Web apps often involve user accounts, data storage, and real-time updates. Think online banking, social media platforms, or e-commerce stores. Web apps are designed for you to actively engage with them, providing input and interacting with dynamic elements.
3. Website vs Web App: Which one does my business need?
This depends on your goals! If you primarily want to showcase information and build brand awareness, a website might suffice. But if you need users to perform specific tasks, like managing accounts or making purchases, then a web application is the way to go.
By understanding the core difference between a web app and a website, you can make an informed decision about which one best serves your business needs and your target audience.
Conclusion
The choice between a website and vs web application is crucial for the success of your online presence. By understanding the difference between a website vs web application, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your business goals and target audience.
In case you are in need of a professional IT outsourcing team to help you brainstorm and build a website or web application from scratch, Newwave Solutions is always available for help. Contact us today and discuss the collaboration together!
Contact Information:
- Head Office (Hanoi): 1F, 4F, 10F, Mitec Building, Cau Giay Ward, Hanoi City, Vietnam
- Branch Office (Tokyo): 1chōme118 Yushima, Bunkyo City, Tokyo 1130034, Japan
- Hotline: +84 985310203
- Website: https://newwavesolution.com
- Email: [email protected]
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply