Top 10 Backend Frameworks for Web Development

As the demand for robust, scalable, and efficient web applications continues to rise, developers around the world are constantly seeking out the best backend frameworks to power their projects. A well-designed backend framework not only streamlines the development process but also ensures optimal performance, security, and maintainability.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll reveal the top 10 backend frameworks that are shaping the future of web development, exploring their unique features, strengths, and use cases so that you can pick the desired one for your own project. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting your journey, this article can certainly provide useful information to assist your backend development process effectively.
What is a Backend Framework?
A backend framework is a collection of pre-written code, libraries, and tools designed to simplify and accelerate the development of web applications. These frameworks handle server-side operations, such as routing, database interactions, user authentication, and API management. By leveraging a backend framework, developers can focus on building application-specific logic and functionality, rather than spending time on low-level implementation details.
Common Features of a Backend Framework:
Since a backend framework can contain a massive series of functions and roles in the backend development process, we will only focus on the important features below:
- Routing System: A routing system maps incoming requests to specific handler functions, enabling organized management of different URL endpoints within web applications. This feature simplifies navigation logic and ensures efficient request processing across complex application architectures.
- ORM/Database Integration: Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) tools provide seamless interaction between application code and databases, abstracting SQL queries into object-oriented operations. Developers benefit from reduced boilerplate code and database-agnostic solutions that enhance portability and maintainability.
- Authentication & Authorization: Built-in mechanisms for user authentication and role-based access control secure applications against unauthorized access and manage permissions effectively. These features streamline identity management while ensuring compliance with security standards and protecting sensitive data.
- Middleware Support: Middleware functions process requests and responses in a layered pipeline, allowing cross-cutting concerns like logging, compression, and error handling to operate consistently. This architecture promotes code reusability and centralized management of common functionalities across the application.
- Templating Engine: Templating engines render dynamic HTML content by combining server-side data with predefined templates, facilitating separation of concerns between logic and presentation. The feature accelerates view development and enables consistent UI generation with minimal frontend dependencies.
- Security Protections: Integrated protections against common vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, XSS, and CSRF safeguard applications from prevalent web threats. These automated defenses reduce manual security implementation efforts and maintain robust protection throughout the application’s lifecycle.
- Caching Mechanisms: Built-in caching layers store frequently accessed data in memory, significantly reducing database load and improving response times for repeated requests. This optimization enhances overall performance and scalability, particularly for high-traffic applications handling dynamic content.
Benefits of Using a Backend Framework
Adopting a backend framework offers numerous benefits that can significantly enhance the development process and the overall quality of your web applications. Here are some key advantages to consider:
- Rapid Development: Backend frameworks provide a solid foundation and a wealth of pre-built components, libraries, and tools. This accelerates the development process, allowing developers to focus on building application-specific logic rather than reinventing the wheel.
- Consistency and Maintainability: Well-designed frameworks enforce coding standards and best practices, resulting in consistent and maintainable codebases. This makes it easier for developers to collaborate, understand each other’s code, and maintain applications over time.
- Security and Reliability: Most popular backend web frameworks prioritize security and reliability, incorporating features like input validation, protection against common web vulnerabilities (such as cross-site scripting and SQL injection), and robust error-handling mechanisms.
- Scalability: Many backend frameworks are designed with scalability in mind, offering features like load balancing, caching, and support for distributed computing. This ensures that applications can handle increased traffic and resource demands as they grow.
- Community Support: Popular backend frameworks have active communities of developers who contribute to their improvement, share knowledge, and provide support. This wealth of resources can greatly aid in troubleshooting, learning, and staying up-to-date with the latest best practices and features.
- Integration and Interoperability: Backend frameworks often provide seamless integration with databases, caching systems, and other third-party services and APIs, facilitating the development of complex and interconnected applications.
- Testing and Debugging: Most frameworks include tools and utilities for testing, debugging, and monitoring, which can significantly improve the overall quality and robustness of your applications.
Top 10 Backend Frameworks for Modern Web Development
Here are the 10 best backend frameworks that are being used widely by businesses and enterprises around the globe:

1. Django (Python)
Django is a high-level Python backend framework that has been a staple in the web development community for over a decade. Known for its “batteries included” philosophy, Django provides a comprehensive set of features out of the box, including an ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) for database interactions, URL routing, a templating engine, and robust security features.
>>>Read more: Top 5 Python Backend Frameworks for Web Applications
Key Features
- Model-View-Template (MVT) Architecture: Django follows the MVT architectural pattern, which separates the application logic into three interconnected components: models (data access layer), views (business logic), and templates (presentation layer).
- Django ORM: The Django ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) provides an abstraction layer for working with databases, allowing developers to write database-agnostic code and seamlessly interact with various database management systems.
- Admin Interface: Django comes with a built-in admin interface that provides a user-friendly way to manage and interact with your application’s data.
- Form Handling: Django simplifies form handling and validation, making it easier to create and process web forms.
- Robust Security: Django includes numerous security features out of the box, such as protection against cross-site scripting (XSS), cross-site request forgery (CSRF), SQL injection, and clickjacking.
Use Cases
Django is widely used for building a variety of web applications, ranging from content management systems and e-commerce platforms to social networking sites and data-driven applications. Its versatility and “batteries included” approach make it an excellent choice for projects of various sizes and complexities.
Example
Instagram relies on Django for its backend infrastructure to manage billions of daily photo uploads and user interactions efficiently. The framework’s robust ORM and admin panel have enabled Instagram to scale seamlessly while maintaining high security standards against spam and abuse. This implementation supports real-time feeds and global content delivery with minimal downtime.
2. Node.js (JavaScript)
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine, allowing developers to run JavaScript backend frameworks on the server side. Although not a traditional framework, the Node.js backend framework has gained immense popularity for its event-driven, non-blocking I/O model, making it highly scalable and efficient for building real-time applications. Overall, Node.js offers a lightweight and scalable foundation for building real-time applications and APIs that power React applications.
Key Features
- Event-Driven Architecture: Node.js utilizes an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model, which enables efficient handling of concurrent connections and real-time applications.
- Single-Threaded, Asynchronous Programming: Node.js employs a single-threaded, event-loop architecture, enabling asynchronous programming and efficient resource utilization.
- NPM (Node Package Manager): Node.js has a vast ecosystem of open-source packages and modules available through NPM, allowing developers to easily extend the functionality of their applications.
- Scalability: Node.js is known for its scalability, making it a popular choice for building high-performance, real-time applications that can handle a large number of concurrent connections.
- Java Backend Frameworks Everywhere: With Node.js, developers can use JavaScript on both the client and server sides, enabling code reuse and streamlining the development process.
Use Cases
Node backend framework is commonly used for developing various types of applications, including web servers, APIs, real-time chat applications, streaming platforms, and IoT (Internet of Things) applications. Its lightweight and scalable nature makes it particularly well-suited for applications that require high performance and real-time capabilities.
Example
Netflix utilizes Node.js extensively for its backend services, particularly in handling real-time recommendations and user profile management across millions of concurrent streams. Node.js’s event-driven architecture has significantly reduced latency in API responses, improving content delivery speed and user satisfaction worldwide. The framework’s scalability supports Netflix’s transition to a microservices architecture effectively.
3. Laravel (PHP)
Laravel is a PHP web framework known for its elegant syntax, developer-friendly approach, and robust set of features aimed at simplifying the development process. With a focus on expressive code and developer productivity, Laravel has gained popularity for building modern web applications.
Key Features
- Eloquent ORM: Laravel includes Eloquent, an advanced ORM that simplifies database interactions and allows developers to work with database records as objects.
- Blade Templating Engine: Laravel’s Blade templating engine offers a simple yet powerful way to create reusable, clean, and efficient templates for your application’s views.
- Artisan CLI: Laravel comes with Artisan, a command-line interface that automates repetitive tasks, such as database migrations, seeding, and testing.
- Middleware: Laravel provides middleware for filtering HTTP requests entering your application, allowing you to implement cross-cutting concerns like authentication, logging, and more.
- Routing: Laravel offers a simple and expressive routing mechanism that allows developers to define application routes using a concise and readable syntax.
Use Cases
Laravel is commonly used for building a wide range of web applications, including content management systems, e-commerce platforms, social networking sites, and enterprise software. Its elegant syntax, rich feature set, and vibrant ecosystem make it a popular choice for projects of all sizes.
Example
BBC employs Laravel for several backend systems, including content management and user authentication platforms serving global audiences. Laravel’s elegant syntax and built-in security features have streamlined BBC’s development process while ensuring compliance with strict broadcasting regulations. The framework enables rapid feature deployment for news portals and multimedia services.
4. Ruby on Rails (Ruby)
Ruby on Rails, often simply referred to as Rails, is a full-stack web application framework written in Ruby. Known for its convention-over-configuration philosophy and emphasis on developer happiness, Rails prioritizes simplicity and productivity, making it a favorite among startups and established companies alike.
Key Features
- Convention over Configuration: Rails follows the principle of “convention over configuration,” reducing the need for manual setup and configuration by enforcing best practices and standard conventions.
- Active Record: Rails includes Active Record, an ORM that simplifies database interactions by mapping database tables to Ruby objects and providing intuitive methods for querying and manipulating data.
- Scaffolding: Rails offers scaffolding generators that automatically create boilerplate code for common tasks like creating models, views, and controllers, speeding up the development process.
- RESTful Architecture: Rails promotes RESTful design principles, making it easy to build APIs and adhere to standard HTTP conventions for creating, reading, updating, and deleting resources.
- Gem Ecosystem: Rails has a vast ecosystem of gems (Ruby libraries) that extend its functionality, allowing developers to easily add features like authentication, authorization, and payment processing to their applications.
Use Cases
Ruby on Rails is widely used for developing web applications across various industries, including e-commerce, SaaS (Software as a Service), marketplaces, and social networking platforms. Its focus on developer happiness, productivity, and maintainability makes it a solid choice for projects that prioritize rapid development and scalability.
Example
GitHub powers its core platform with Ruby on Rails, managing code repositories, pull requests, and collaboration features for millions of developers. Rails’ convention-over-configuration approach accelerated GitHub’s growth from startup to enterprise scale while maintaining code readability and developer productivity. This foundation supports GitHub’s marketplace and CI/CD integrations seamlessly.
5. Express.js (JavaScript)
Express.js is a minimalist and flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a robust set of features for building web and mobile applications. As a lightweight framework, Express.js is highly customizable and allows developers to create APIs, web servers, and single-page applications with ease.
A minimalist Node.js web framework that provides a robust set of features for building web applications and APIs. Its flexibility and focus on core functionalities make it a popular choice for building the React backend framework.
Key Features
- Middleware: Express.js uses middleware functions to handle requests, perform tasks, and modify responses, allowing developers to modularize their code and create reusable components.
- Routing: Express.js offers a simple yet powerful routing mechanism that enables developers to define routes, handle HTTP methods, and execute callback functions based on incoming requests.
- Template Engines: Express.js supports various template engines like Pug, EJS, and Handlebars, making it easy to generate dynamic HTML content for web applications.
- Error Handling: Express.js provides built-in error handling mechanisms, middleware for error processing, and tools for debugging and logging errors, ensuring robustness and reliability in applications.
- Extensibility: Express.js is highly extensible, with a rich ecosystem of plugins and middleware available through NPM, allowing developers to add additional functionality and features to their applications.
Use Cases
Express.js is commonly used for building APIs, web applications, and microservices, as well as serving static files and proxying requests. Its flexibility, minimalistic approach, and strong community support make it a popular choice for developers looking to create lightweight and scalable applications.
Example
PayPal leverages Express.js for numerous microservices handling payment processing and transaction APIs with high reliability. Express.js’s minimalist design allows PayPal to maintain a lightweight backend while integrating complex financial compliance requirements efficiently. The framework’s flexibility supports PayPal’s global payment gateway operations across multiple currencies.
6. Spring Boot (Java)
Spring Boot is an opinionated framework built on top of the Spring framework for Java, designed to simplify the development of production-ready applications. With a focus on convention over configuration, Spring Boot eliminates much of the boilerplate code typically associated with Java development, allowing developers to quickly build robust and scalable applications.

Key Features
- Auto-Configuration: Spring Boot provides auto-configuration, which automatically configures your application based on dependencies and project structure, reducing the need for manual setup and configuration.
- Embedded Servers: Spring Boot supports embedded servers like Tomcat, Jetty, and Undertow, allowing developers to package their applications as standalone JAR files with embedded servers for easy deployment.
- Spring Ecosystem: Spring Boot leverages the broader Spring ecosystem, including Spring Security, Spring Data, and Spring Cloud, providing a comprehensive set of tools for building enterprise-grade applications.
- Actuators: Spring Boot Actuators offer production-ready features like health checks, metrics, and monitoring, giving developers visibility into the runtime behavior of their applications.
- Developer Tools: Spring Boot includes developer tools like automatic restarts, live reload, and enhanced debugging capabilities, improving developer productivity and workflow efficiency.
Use Cases
Spring Boot is commonly used for developing enterprise applications, RESTful APIs, microservices, and cloud-native applications in Java. Its seamless integration with the broader Spring ecosystem, robust features, and extensive community support make it a top choice for building scalable and maintainable Java applications.
Example
LinkedIn uses Spring Boot for its professional networking platform backend, managing member profiles, job recommendations, and messaging systems at a massive scale. Spring Boot’s auto-configuration and embedded servers have reduced LinkedIn’s deployment complexity while enabling rapid iteration of machine learning features. This architecture powers LinkedIn’s premium subscription services reliably.
7. Flask (Python)
Flask is a lightweight and versatile Python backend framework that provides the essentials for building web applications without imposing restrictions or requirements on developers. With a simple and modular design, Flask is easy to learn and allows developers to create a wide range of web applications, from simple prototypes to complex enterprise solutions.
Key Features
- Minimalistic: Flask follows a “micro” framework philosophy, keeping the core simple and lightweight while allowing developers to add extensions and libraries based on their specific needs.
- Jinja2 Templating: Flask uses the Jinja2 templating engine to render dynamic HTML content, making it easy to create templates, include variables, and control the flow of logic in views.
- Werkzeug WSGI Toolkit: Flask is built on the Werkzeug WSGI toolkit, which provides low-level utilities for handling HTTP requests, responses, and routing, giving developers fine-grained control over the application.
- Extensible: Flask has a rich ecosystem of extensions that add additional functionality, such as authentication, database integration, and API development, allowing developers to tailor their applications to meet specific requirements.
- RESTful Support: Flask supports building RESTful APIs out of the box, making it a popular choice for creating web services and backend systems that follow REST principles.
Use Cases
Flask is commonly used for developing small to medium-sized web applications, APIs, prototypes, and microservices in Python. Its simplicity, flexibility, and ease of use make it a preferred framework for projects that require rapid development, customization, and scalability.
Example
Pinterest implements Flask for various backend APIs handling image processing and recommendation algorithms serving visual discovery features. Flask’s lightweight nature allows Pinterest to customize data pipelines quickly while maintaining high performance for pin collections and boards. The framework supports Pinterest’s personalization engine effectively across global users.
8. ASP.NET Core (C#)
ASP.NET Core is a cross-platform, high-performance framework for building modern, cloud-based, and internet-connected applications using C#. Developed by Microsoft, ASP.NET Core offers a unified framework for developing web UIs, APIs, and real-time applications that run on Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Key Features
- Cross-Platform: ASP.NET Core is cross-platform and can run on Windows, Linux, and macOS, providing flexibility and portability for developers working on different operating systems.
- Modular Design: The .NET framework backend follows a modular design, allowing developers to include only the necessary components and dependencies for their applications, resulting in lightweight and efficient deployments.
- Razor Pages: ASP.NET Core includes Razor Pages, a page-focused programming model that simplifies building web UIs with clean and testable code, making it easy to create dynamic web pages.
- Entity Framework Core: ASP.NET Core combines Entity Framework Core, which is an ORM that streamlines database operations and enables developers to interact with databases using C# objects and LINQ queries.
- Dependency Injection: ASP.NET Core provides built-in support for dependency injection, making it easy to manage object dependencies and promote loose coupling between components in the application.
Use Cases
ASP.NET Core is commonly used for developing a wide range of applications, including web applications, APIs, microservices, and cloud-native applications. Its versatility, performance, and seamless integration with the Microsoft ecosystem make it a preferred choice for developers building applications on the .NET Framework backend platform.
Example
Stack Overflow relies on ASP.NET Core for its Q&A platform backend, supporting millions of daily questions, answers, and reputation calculations. ASP.NET Core’s cross-platform capabilities and high performance have enabled Stack Overflow to optimize database queries and caching strategies significantly. This implementation ensures fast page loads and reliable search functionality.

9. Ruby Grape (Ruby)
Grape is a REST-like API micro-framework for Ruby that provides a simple and fast way to create APIs with minimal effort. Designed for building lightweight and scalable API services, Grape offers a DSL (Domain-Specific Language) for defining endpoints, parameters, and response formats, making API development straightforward and efficient.
Key Features
- DSL for API Endpoints: Grape uses a DSL to define API endpoints, request parameters, response formats, and error handling, allowing developers to create APIs quickly and intuitively.
- Middleware Stack: Grape provides a middleware stack for processing requests and responses, enabling developers to add custom logic, authentication, and validation to their API endpoints.
- Versioning Support: Grape supports API versioning out of the box, making it easy to manage multiple versions of an API and introduce breaking changes without disrupting existing clients.
- Pluggable: Grape is highly pluggable, with a rich ecosystem of plugins and extensions that add functionality like caching, documentation generation, rate limiting, and more to API services.
- Integration with Rails: Grape can be integrated with Ruby on Rails applications, allowing developers to use Grape for building APIs while leveraging Rails for web application functionality.
Use Cases
Grape is commonly used for developing RESTful APIs, microservices, and backend systems that require a lightweight and flexible framework in Ruby. Its simplicity, speed, and focus on API development make it a popular choice for projects that prioritize building scalable and efficient API services.
Example
Airbnb utilizes Ruby Grape for its RESTful API layer that powers search functionality and booking systems across global listings. Grape’s lightweight routing and parameter validation have improved Airbnb’s API response times while simplifying integration with the Rails monolith. This micro-framework enhances Airbnb’s host-guest matching precision and availability management.
10. FastAPI (Python)
FastAPI is a modern Python web framework for building APIs with high performance, based on standard Python type hints. Leveraging the power of Python 3.6+ features like type annotations and asynchronous programming, FastAPI offers auto-generated OpenAPI documentation, data validation, and dependency injection, making API development fast, efficient, and reliable.
Key Features
- Fast Performance: FastAPI is built for speed, utilizing Starlette for asynchronous I/O operations and Pydantic for data validation, resulting in high performance and low latency for API endpoints.
- Automatic OpenAPI Documentation: FastAPI automatically generates interactive OpenAPI documentation (formerly known as Swagger) for APIs, allowing developers to visualize, test, and explore API endpoints with ease.
- Type Annotations: FastAPI uses Python-type hints for defining request and response data structures, enabling automatic data validation, serialization, and documentation generation without additional boilerplate code.
- Dependency Injection: FastAPI supports dependency injection, allowing developers to declare dependencies for route handlers, request handlers, and other components, promoting modularity and testability in applications.
- Compatibility with ASGI: FastAPI is compatible with the ASGI (Asynchronous Server Gateway Interface) specification, enabling seamless integration with ASGI servers and middleware for building asynchronous web applications.
Use Cases
FastAPI is ideal for developing high-performance APIs, microservices, and backend systems that require speed, scalability, and type safety in Python. Its combination of modern features, automatic documentation, and asynchronous capabilities makes it a top choice for developers looking to build efficient and reliable API services.
Example
Microsoft incorporates FastAPI in several internal services and Azure documentation tools due to its automatic API documentation and high performance. FastAPI’s async capabilities have accelerated Microsoft’s developer portal response times while providing OpenAPI specifications for seamless client integration. The framework supports Microsoft’s API-first development strategy effectively.
If your business wishes to develop front-end alongside back-end, you are going to need some quality front-end frameworks as well. Follow our latest blog to explore both aspects with the appropriate frameworks
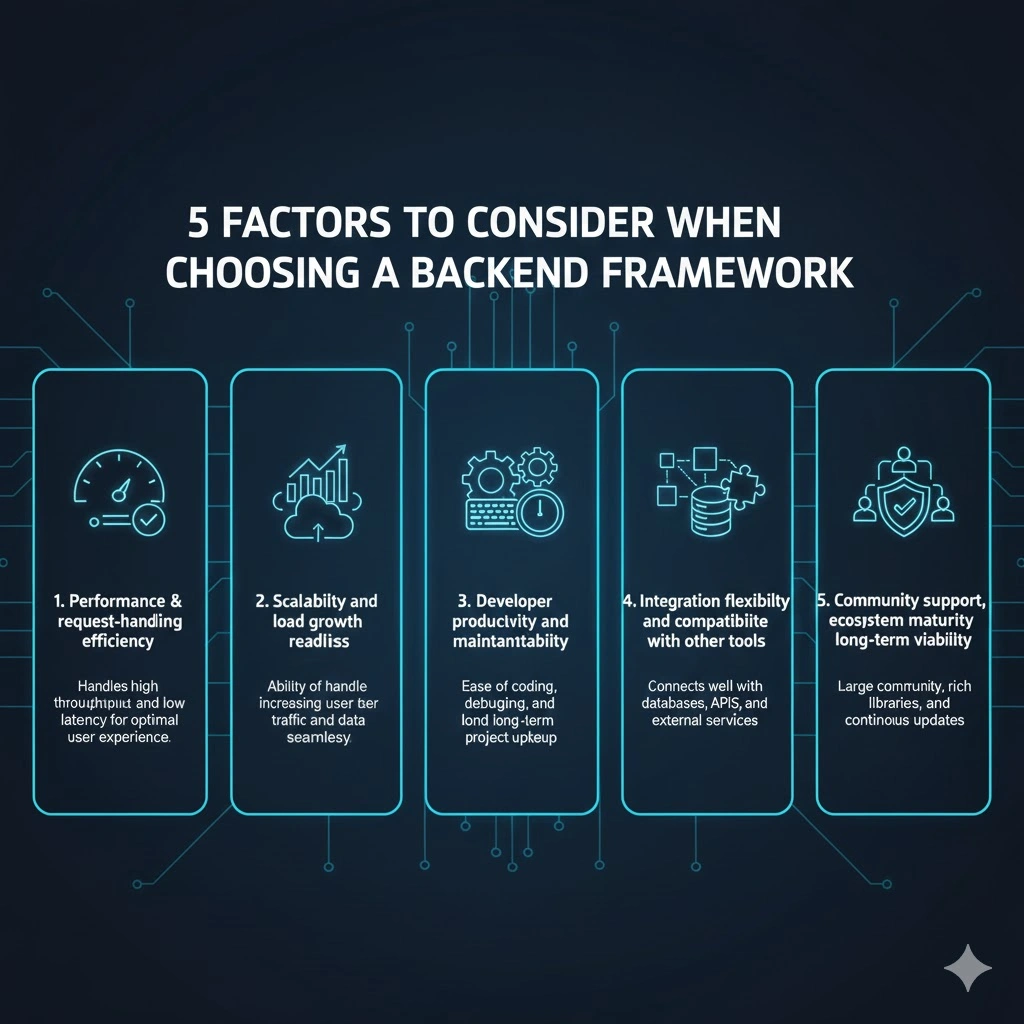
5 Factors to Consider When Choosing a Backend Framework
Selecting the appropriate backend framework can fundamentally influence the performance, maintainability, and scalability of your web application. The following factors should be carefully weighed to ensure that your choice aligns with both present requirements and future growth ambitions:
1. Performance & request-handling efficiency
The framework’s architecture and efficiency in handling HTTP requests — including routing, concurrency support, and resource management — determine how quickly and reliably the backend can respond under load. High performance becomes especially important when your application must serve large numbers of users or manage time-sensitive operations, thereby ensuring a smooth and responsive user experience.
2. Scalability and load growth readiness
The ability of the framework to support horizontal scaling, distributed deployments, database sharding or load balancing plays a critical role when the application’s user base or data volume expands. Choosing a scalable framework reduces the risk of bottlenecks, enables the system to grow gracefully, and supports long-term reliability even as traffic and functionality grow.
3. Developer productivity and maintainability
Clear conventions, well-structured architecture, comprehensive documentation, and intuitive syntax within the framework contribute significantly to developer productivity. Such qualities make it easier for teams to onboard new members, debug issues, implement features, and maintain the codebase over time with minimal friction — which is essential for long-lived projects.
4. Integration flexibility and compatibility with other tools
The selected framework should facilitate smooth interoperability with databases, third-party services, APIs, and other components such as caching, messaging, or micro-services. Compatibility and extensibility ensure that as your project needs evolve — for example, adding real-time updates, external integrations, or data pipelines — the backend remains adaptable without forcing major rework.
5. Community support, ecosystem maturity, and long-term viability
A strong, active community and a mature ecosystem of libraries, extensions, and security patches provide confidence that the framework will remain supported and safe over time. Such community backing often translates into faster issue resolution, availability of third-party modules, and collective knowledge, which reduces development risk and increases overall project stability.
Ultimately, the best backend framework depends on your specific project needs and team expertise. By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision that sets your web development project up for success.
Hire Backend Developers From Newwave Solutions
After selecting one or more suitable backend frameworks for your project development, businesses also require additional preparations, such as architecture design, database setup, security implementation, and skilled development resources to effectively design and develop the backend system. If your organization lacks experience or sufficient resources for these tasks, Newwave Solutions offers comprehensive Hire Backend Developers services that cover the full development cycle from inception to deployment.
Drawing on our meticulous recruitment process, Newwave Solutions hires only developers and experts who precisely match your business requirements and organizational culture. By integrating these highly-skilled professionals into your team, you accelerate project timelines while ensuring backend systems achieve long-term scalability and robust security. This strategic approach enables your business to concentrate on core growth initiatives as our dedicated experts manage all technical complexities with confidence and precision.
Main types of backend developers available from us include:
- Hire Node.js Developers: We deliver high-performance Node.js developers skilled in building scalable, real-time applications to accelerate your project’s backend infrastructure and API development.
- Hire Laravel Developers: Our Laravel specialists create elegant PHP-based backend solutions with robust security features to streamline complex web application workflows and database management.
- Hire PHP Developers: Experienced PHP developers from our team construct reliable server-side logic and custom CMS integrations to support dynamic content delivery and user authentication systems.
- Hire Python Developers: Python experts proficient in Django and Flask frameworks develop efficient data processing pipelines and machine learning integrations to power intelligent backend services.
- Hire .NET Developers: .NET professionals build enterprise-grade applications with seamless Microsoft ecosystem integration to ensure high reliability and cross-platform compatibility for business-critical systems.
- Hire ASP.NET Developers: ASP.NET specialists deliver optimized web APIs and MVC architectures to create responsive enterprise portals with advanced authentication and session management capabilities.
Overall, our services are committed to providing top-quality backend development teams that ensure your backend development process proceeds smoothly, efficiently, and is aligned with project objectives.
Besides providing back-end experts, we also deliver the “hire front-end developers” services for any business looking to cover a full-stack development. Contact us if you need assistance with either the backend or the frontend development process.
FAQs
1. How to Choose a Backend Framework?
When choosing a backend framework for your web development project, consider factors such as speed and efficiency, scalability, user-friendliness, interoperability, and community support. Evaluate the specific requirements of your project, the programming language you’re comfortable with, and the features offered by each framework to determine the best fit for your needs.
2. Which Backend Framework Is Most Used?
The most used backend frameworks vary depending on the programming language and the type of applications being developed. Some of the popular backend frameworks in 2024 include Django (Python), Node.js (JavaScript), Laravel (PHP), Ruby on Rails (Ruby), and Express.js (JavaScript). Choose a framework based on your familiarity with the language, project requirements, and desired features.
3. What Is the Hardest Backend Language?
The perceived difficulty of a backend language depends on individual experience and familiarity with the language’s syntax, concepts, and ecosystem. Languages like C++, Rust, and Haskell are often considered challenging due to their complex syntax, memory management requirements, and steep learning curves. However, with practice and dedication, developers can master any backend language and framework.
Conclusion
Choosing the right backend frameworks is a crucial decision that can significantly impact the success of your web development project. By considering factors like speed, scalability, user-friendliness, interoperability, and community support, you can select a framework that aligns with your project requirements and development preferences.
Ready to take the next step in your web development journey? Contact Newwave Solutions today to discuss your project requirements and explore how our dedicated development team can bring your vision to life. With expertise in a wide range of top ten backend frameworks and technologies, we’re here to help you build secure, scalable, and innovative web applications that propel your business forward.
Contact Information:
- Head Office (Hanoi): 1F, 4F, 10F, Mitec Building, Cau Giay Ward, Hanoi City, Vietnam
Branch Office (Tokyo): 1chōme118 Yushima, Bunkyo City, Tokyo 1130034, Japan - Hotline: +84 985310203
- Website: https://newwavesolution.com
- Email: [email protected]
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply