What is Microsoft SQL Server? Unpacking the Database Behind Your Data

You’re staring at spreadsheets scattered across dozens of files, desperately searching for that one crucial piece of customer data while your team waits for an answer that could close a million-dollar deal. Sound familiar? This chaos of unorganized information isn’t just frustrating—it’s costing businesses billions in lost opportunities, security breaches, and operational inefficiencies. What is Microsoft SQL Server? It’s the solution that transforms this data nightmare into a streamlined, secure, and powerful information management system. Unlocking everything you need to know about Microsoft SQL Server in this blog.
What is Microsoft SQL Server?
Microsoft SQL Server is a relational database management system (RDBMS) developed by Microsoft. At its core, this Structured Query Language‘s purpose is to store, manage, and retrieve data as requested by other software applications, which can run either on the same computer or on another computer across a network.
First launched in 1989 as a partnership with Sybase for OS/2 systems, SQL Server quickly became a cornerstone of Microsoft’s Windows NT strategy. Over the decades, it has shed its Sybase roots and undergone profound transformations, integrating with the .NET framework, embracing cloud-hybrid environments with Azure SQL, and incorporating cutting-edge features like in-memory OLTP, advanced AI, and machine learning capabilities directly within the database engine.
SQL Server is designed for three fundamental tasks:
- Storing: It provides a structured, secure, and highly reliable repository for data. Instead of saving information in flat files, it uses tables with rows and columns, enforcing data integrity and relationships.
- Managing: It gives you powerful tools to control who can see what data (security), ensure data accuracy (integrity), and perform routine maintenance like backups and performance tuning.
- Retrieving: It uses the Structured Query Language (SQL) to provide a powerful and efficient way for applications and users to ask complex questions of the data and get answers back at incredible speed.
Use Case for Microsoft SQL server
Understanding the practical applications of Microsoft SQL Server requires examining how different industries leverage its capabilities to solve real-world challenges:
1. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
This represents one of the most demanding use cases for SQL Server. Manufacturing giants like Ford utilize it to manage complex supply chain operations, tracking millions of parts across global facilities while maintaining real-time inventory visibility. The database simultaneously handles procurement data, production schedules, quality control metrics, and financial transactions, all while ensuring absolute data consistency across multiple time zones and regulatory environments.
Ready to build an ERP system that turns your unified data into a competitive advantage? Explore our expert ERP Development services to create a robust, scalable solution powered by SQL Server.
2. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms
These platforms showcase SQL Server’s ability to manage intricate, relationship-heavy data structures. Companies like Starbucks rely on it to maintain detailed customer profiles, purchase histories, loyalty program data, and preference analytics across thousands of locations. The system processes millions of transactions daily while providing marketing teams with instant access to the customer insights that drive personalized campaigns and significantly improve retention rates.
Need a CRM that does more than store contacts—it drives growth? Partner with Newwave’s CRM Development team to build an intelligent platform that transforms SQL Server data into customer loyalty.
3. Business Intelligence and Analytics
Modern implementations demonstrate SQL Server’s full analytical prowess. Healthcare organizations, for instance, use its advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities to identify patient care patterns, predict treatment outcomes, and optimize resource allocation. The platform’s seamless integration with tools like Power BI enables administrators to visualize complex data relationships—from patient flow patterns to pharmaceutical inventory optimization—ultimately improving both operational efficiency and patient outcomes.
4. E-commerce platforms
These platforms leverage SQL Server’s high-performance transaction processing capabilities to their fullest. Major online retailers depend on it to manage massive product catalogs, process thousands of simultaneous orders during peak traffic, and maintain real-time inventory synchronization across multiple sales channels. SQL Server’s robust handling of concurrent read and write operations is crucial, ensuring customers always see accurate product availability and preventing overselling situations that can damage trust and brand reputation.
Discover Newwave’s eCommerce Development solutions to create a high-performance, secure store powered by SQL Server.
How Does Microsoft SQL Server Work?
Microsoft SQL Server operates as a sophisticated multi-layered architecture designed to efficiently process, store, and retrieve data while maintaining consistency and performance across concurrent operations. Understanding this architecture reveals why SQL Server remains a preferred choice for mission-critical applications.
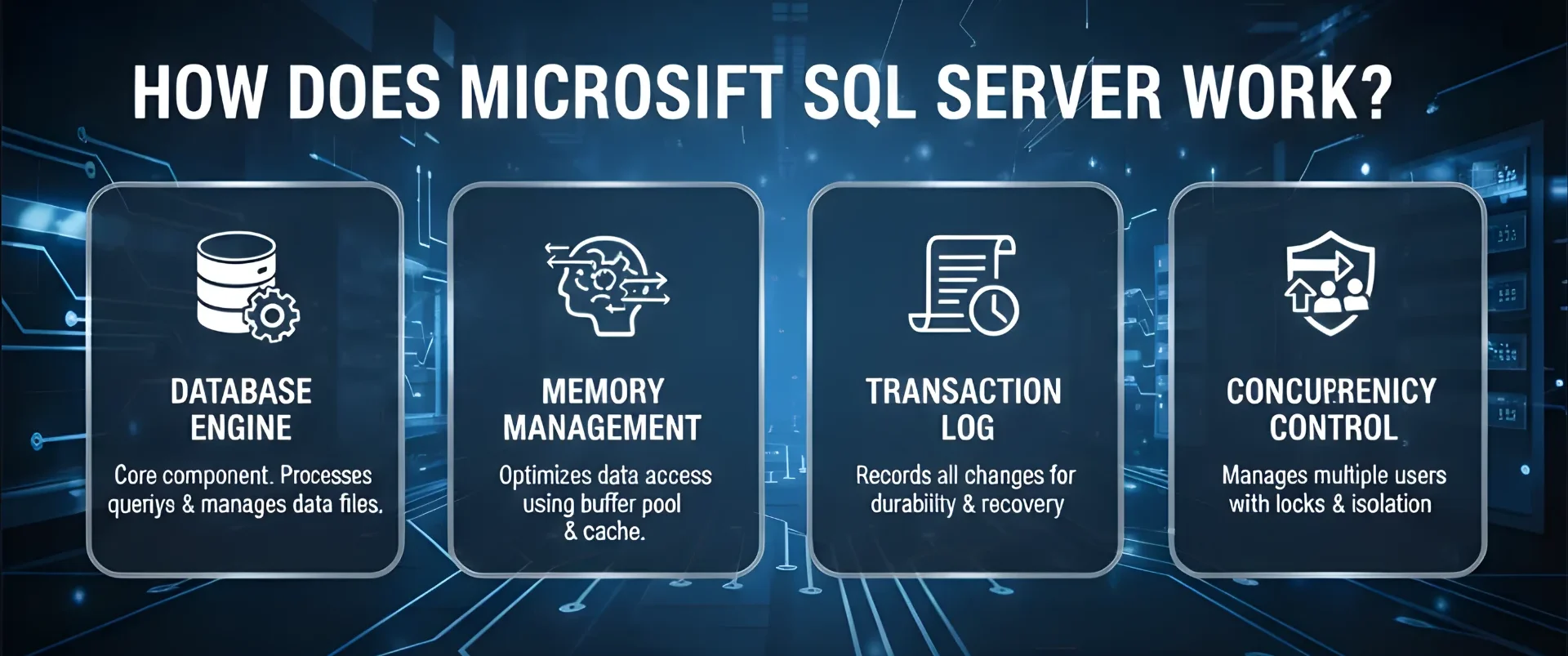
The platform’s core components work together seamlessly to deliver enterprise-grade performance:
- Database Engine: Serves as SQL Server’s central component, managing all data storage and retrieval operations. When you submit a query, the engine parses and validates SQL syntax, then develops an optimized execution plan considering available indexes, table sizes, and current system resources.
- Memory Management: Employs a sophisticated buffer pool system that keeps frequently accessed data pages in RAM for lightning-fast retrieval. The system intelligently predicts which data will be needed next, pre-loading information into memory before requests arrive, dramatically reducing disk I/O operations.
- Transaction Log: Ensures data integrity through a write-ahead logging system where SQL Server records intended changes before any data modification occurs. This approach guarantees that even if system failures occur mid-transaction, the database can either complete the operation or roll back to a consistent state.
- Concurrency Control: Enables multiple users to work with the same data simultaneously without conflicts through sophisticated locking mechanisms and isolation levels that balance data consistency with system performance. Users always see either the original version or the completed change, never an inconsistent intermediate state.
What Are the Key Benefits of Microsoft SQL Server?
Choosing a database platform is a strategic decision. Microsoft SQL Server offers a compelling set of benefits that deliver tangible value to organizations of all sizes, directly impacting efficiency, security, and the bottom line.
1. Unmatched Performance and Scalability
SQL Server is engineered for speed. Features like in-memory OLTP can make certain transaction processing workloads up to 30x faster by storing and processing data directly in memory, bypassing traditional disk I/O bottlenecks. Its sophisticated query optimizer almost always chooses the most efficient path to execute a request.
This means mission-critical applications run faster, user productivity increases, and customer experiences are smoother. You can scale up by adding more power to your existing server or scale out by implementing read-scale replicas or sharding, ensuring your database grows with your business needs.
2. Robust, Multi-Layered Security
In an era of constant cyber threats, SQL Server provides a “defense-in-depth” security model. It offers encryption both for data at rest (Transparent Data Encryption) and in motion (SSL). Features like Row-Level Security allow you to control access to specific rows in a table based on the user’s role, meaning an employee can only see data relevant to them. This is a powerful tool for achieving and demonstrating compliance with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, protecting not just data but also the company’s reputation and avoiding massive regulatory fines.
3. High Availability and Disaster Recovery
Downtime is expensive. SQL Server’s high availability solutions, like Always On Availability Groups, allow you to create redundant, synchronized copies of your databases (on-premises or in Azure). If your primary server fails, it automatically fails over to a secondary copy within seconds, minimizing disruption. This built-in resilience ensures that your key applications remain online, maintaining business continuity and customer trust even in the face of hardware failures or other unforeseen disasters.
4. Deep Integration with the Microsoft Ecosystem
For organizations invested in the Microsoft stack, SQL Server offers a native and seamless experience. Its integration with Windows Server, Active Directory for authentication, and the Visual Studio development environment simplifies administration and development. Power BI, Microsoft’s leading business analytics tool, connects to SQL Server with unparalleled ease. This ecosystem integration reduces the learning curve for IT staff, accelerates development cycles, and lowers the total cost of ownership by leveraging existing skills and infrastructure.
What Are the Potential Challenges of Microsoft SQL Server?
No technology is without its complexities. Being aware of these challenges allows for proactive planning and ensures you can fully leverage the platform’s strengths.
1. Managing Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
While there is a free version (Express Edition), the full-featured enterprise editions of SQL Server represent a significant investment. Costs include licensing fees (which are core-based and can be expensive on high-performance servers), the hardware to run it on, and the salaries of skilled database administrators (DBAs) to manage it. For businesses, the challenge is accurately forecasting this TCO and justifying the ROI. The solution often lies in careful licensing planning, considering virtualized environments to maximize core usage, or evaluating the cloud-native Azure SQL option to convert capital expenditure into a predictable operational expense.
2. Administrative and Performance Tuning Complexity
An out-of-the-box SQL Server instance will work, but to achieve optimal performance for a specific workload, it requires expert tuning. DBAs must monitor indexes, manage statistics, configure memory settings, and interpret query execution plans to identify and fix bottlenecks. This requires deep, specialized knowledge. The impact of poor performance can be slow applications and frustrated users. Businesses overcome this by investing in continuous training for their IT staff, leveraging Microsoft’s built-in performance tuning advisors, or considering managed cloud services that offload much of this operational overhead.
3. Navigating the Licensing Model
Microsoft’s licensing for SQL Server is powerful but can be notoriously complex. Understanding the differences between per-core and Server + CAL (Client Access License) models, and the features available in Standard vs. Enterprise editions, is critical. Making the wrong choice can lead to unexpected costs or limited functionality. The key to solving this is to work closely with Microsoft partners or licensing specialists during the planning phase to architect a solution that meets both technical and budgetary requirements.
FAQs
How much does Microsoft SQL Server cost?
The cost varies significantly based on the edition and licensing model. SQL Server Standard Edition can cost a few thousand dollars, while Enterprise Edition can run into tens of thousands, typically licensed per core. You must also factor in the cost of the Windows Server OS and the hardware. For precise pricing, it’s best to use the Microsoft licensing calculator or speak to a licensing partner, as it is a complex topic.
How do I start Microsoft SQL Server?
The most common way to start the core database service is through the “SQL Server Configuration Manager” tool. Here, you can locate the “SQL Server Services” node, find your specific instance (e.g., “SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER)”), right-click it, and select “Start.” You can also set the service to start automatically with the operating system.
How to connect to Microsoft SQL Server?
Connection requires four key pieces of information: the Server name (the computer name/instance name), the Authentication method (Windows or SQL Server Authentication), a valid Username, and its corresponding Password. This information is entered into a client tool like SSMS, Azure Data Studio, or even a custom application’s connection string.
What is the practical impact of the transaction log in SQL Server performance?
The transaction log is critical for data integrity and recovery, but it can become a major performance bottleneck. If the log is stored on a slow disk drive, every transaction (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) will be slowed down as the system must wait for the log write to complete. Furthermore, a poorly managed log that auto-grows in small increments can cause significant latency. Placing the log on its own dedicated, fast storage (like an SSD) and pre-sizing it appropriately are crucial for maintaining high performance.
How does the choice between Windows Authentication and Mixed Mode impact security?
Windows Authentication (Integrated Security) is widely considered more secure and is the recommended mode. It leverages Active Directory accounts, enabling strong password policies, Kerberos authentication, and centralized account management. It also eliminates the storage of passwords within SQL Server. Mixed Mode (which supports both Windows and SQL Logins) is often used when clients are non-Windows machines that cannot use domain authentication, but it requires managing separate, potentially weaker, passwords within SQL Server itself.
Can I uninstall Microsoft SQL Server?
Yes, you can uninstall it like most other applications through the Windows “Apps & Features” settings panel. However, extreme caution is advised. Uninstalling will remove the database engine and all its components, which will make any databases in that instance inaccessible unless they are backed up first. This action is permanent and can break applications that depend on it.
To sum up
Understanding what is Microsoft SQL Server goes far beyond a technical definition. It’s about recognizing a platform that has evolved for over three decades to become the bedrock of reliable data management. Whether you’re a developer building the next great application, a manager justifying the investment in a secure data platform, or an executive relying on accurate analytics to guide strategy, SQL Server’s blend of raw power, ironclad security, and ecosystem integration makes it a compelling choice.
Ready to architect a SQL Server environment that delivers peak performance and security for your platform? Contact Newwave’s database specialists to design, deploy, and optimize your mission-critical data infrastructure.
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply