What is MySQL: Top Relational Database for Web Apps & Scaling

The market demand for relational database management systems (RDBMS) to control and manage data has grown enormously, with many strong solutions available. Among them, MySQL stands out as one of the best options thanks to its balance of performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. If your business is evaluating what is MySQL for managing data or even big data, this Newwave Solutions blog will guide you through its features, pros and cons, real-world use cases, and a basic setup tutorial.
What Is MySQL?
MySQL is a widely used open-source relational database management system designed to store, organize, and manage data efficiently across different applications. Known for its speed, reliability, and ease of use, it has become one of the most trusted solutions for enterprises requiring scalable and cost-effective data management. When businesses ask what is MySQL server, the answer lies in its role as the core engine that powers websites, applications, and enterprise systems worldwide.
For example, Facebook has relied on MySQL to manage enormous volumes of user data, applying the technology to handle billions of daily interactions. This enables the platform to deliver high performance and reliability at a global scale.

Explore what is SQL and its insights first to understand MySQL clearly later on
7 Key Features of MySQL
In case you are curious about what MySQL can deliver to your business, here are the 7 main functions of the tool:
- Open-source and free licensing: MySQL is available under an open-source license, which allows businesses to use it without costly fees while still benefiting from a large global community for updates and support.
- ACID compliance for data integrity: By following the principles of Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability, MySQL ensures that all transactions are processed reliably, which is essential for financial, healthcare, and enterprise systems.
- Cross-platform support (Windows, Linux, macOS): MySQL runs seamlessly on all major operating systems, making it a versatile solution for enterprises with diverse IT environments.
- Replication and clustering for high availability: Businesses can replicate databases across servers or use clustering to minimize downtime, ensuring that applications remain accessible even during heavy traffic or hardware failures.
- Robust security with encryption and authentication: MySQL provides strong data protection through SSL encryption, role-based authentication, and password validation, helping companies meet strict compliance and regulatory requirements.
- Integration with BI tools and analytics platforms: MySQL connects easily with business intelligence tools such as Tableau and Power BI, allowing organizations to turn raw data into actionable insights for better decision-making.
- Cloud-native deployment support (AWS, Azure, GCP): MySQL is fully supported by major cloud providers, giving enterprises the flexibility to scale resources on demand and integrate seamlessly into modern cloud-native architectures.
Pros & Cons of MySQL
Like any technology, MySQL comes with its own strengths and limitations. While it is one of the most widely adopted relational database systems, it is wise for businesses to carefully evaluate both sides before making a decision. The table below presents the main pros and cons of MySQL in detail to help you decide if it fits your business needs.
|
Pros |
Cons |
| Cost savings through open-source licensing: MySQL is free to use, which eliminates expensive licensing costs and makes it highly attractive for startups and SMEs. | Performance challenges for very large datasets: MySQL may require extensive tuning and optimization to handle extremely high-volume or complex workloads. |
| Wide community and ecosystem support: With a large global developer base, businesses gain access to continuous updates, third-party tools, and support resources. | Fewer advanced features compared to competitors: Some enterprise-level functionalities, such as advanced partitioning or analytical capabilities, may be limited without premium editions. |
| Ease of integration with applications: MySQL works seamlessly with web technologies like PHP, Java, and Python, making it popular for powering websites and SaaS platforms. | Scaling limitations in certain use cases: While scalable, MySQL may not scale as efficiently as databases like PostgreSQL or Oracle for complex analytical workloads. |
| High availability options with replication and clustering: Businesses can use built-in replication and clustering to maintain uptime during failures or maintenance. | Migration complexities: Moving from commercial databases to MySQL can be challenging if organizations have a heavy reliance on proprietary features. |
4 Common Use Cases of MySQL
MySQL is a versatile database that can be applied across many industries and business scenarios. From managing customer data and controlling resources to powering online transactions and content delivery, it offers practical solutions for organizations of all sizes. Below are the most common use cases where businesses gain the most value from MySQL services.
1. Financial Services
In financial software development services, MySQL supports secure transaction processing, fraud detection, and real-time payment systems by handling large volumes of data with reliability. Its ACID compliance ensures every transaction is accurate, consistent, and secure.
A real-world example is PayPal, which has long relied on MySQL to power its global payment platform. By using MySQL, PayPal processes millions of secure transactions daily, ensuring fast and dependable service for customers worldwide.
2. E-commerce & Retail
Ecommerce development services or businesses use MySQL to manage product catalogs, inventory levels, and checkout processes efficiently. Its scalability allows retailers to handle peak shopping events while maintaining fast response times.
Shopify leverages MySQL to support its e-commerce platform that powers thousands of online stores. This adoption helps ensure smooth checkout experiences and reliable operations even during high-demand sales events.
3. Media & Entertainment
In the media and entertainment industry, MySQL enables companies to manage large content libraries, user profiles, and real-time streaming data. Its performance ensures users can access their favorite content quickly and without interruptions.
Netflix initially relied on MySQL for critical services that handled customer accounts and video metadata. This allowed Netflix to scale rapidly during its early growth stages while delivering consistent and reliable service.
4. Technology Startups
Startups often choose MySQL because it offers a cost-effective solution for building MVPs and scaling SaaS platforms. Its simplicity and integration with common programming languages help startups launch quickly while keeping expenses under control.
Slack and Airbnb both used MySQL during their early scaling phases to manage user data and support their platforms. The tool helped them expand operations rapidly without incurring the high costs of commercial database systems.
MySQL vs Other Databases
MySQL competes with other well-known database technologies such as PostgreSQL and Oracle. With so many options available, businesses often find it difficult to decide which solution best matches their needs. From our years of working with these systems, we have created a clear comparison table below to help you understand the main differences and make a more confident choice.
| Criteria | MySQL | PostgreSQL | Oracle |
| Cost | Free and open-source with optional paid support | Free and open-source with advanced features | Very expensive licensing and support fees |
| Ease of Use | Simple to learn and widely supported | Slightly more complex with advanced configurations | Complex system requiring expert administrators |
| Performance | Excellent for read-heavy and transactional workloads | Strong for complex queries and analytical workloads | Optimized for very large-scale enterprise environments |
| Scalability | Scales well for web apps and SMEs | Scales effectively both vertically and horizontally | Enterprise-grade scalability for mission-critical systems |
| Extensibility | Limited customization beyond core functions | Highly extensible with custom data types and plugins | Proprietary features with limited flexibility |
| Security | Provides encryption and authentication suitable for most industries | Advanced security with row-level control and auditing | Full enterprise security and compliance features |
Verdict:
- MySQL is the best choice for businesses that need a cost-effective, easy-to-use database for web applications, startups, and e-commerce platforms.
- PostgreSQL is ideal for organizations requiring advanced data handling, complex queries, or flexible customization.
- Oracle remains the strongest option for large enterprises that can afford premium licensing and demand top-tier scalability and compliance.
How to Set Up MySQL from Scratch
From our perspective, MySQL is considered straightforward once you become familiar with its structure, although some users find the initial setup a bit technical. If you are not sure where to begin, the following steps will provide a simple guide to help you get started quickly and understand how to use MySQL effectively.
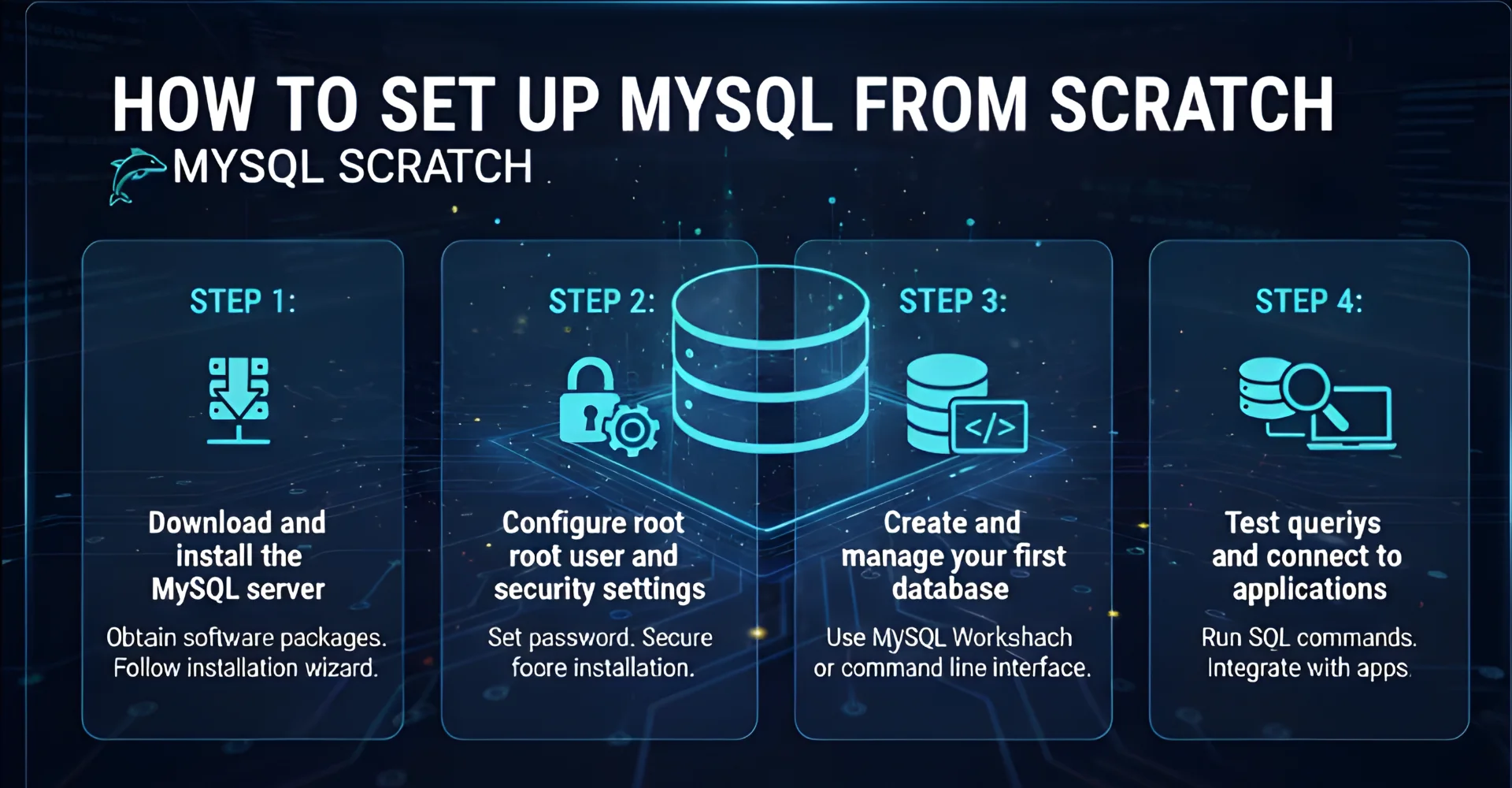
Step 1: Download and install the MySQL server
Visit the official MySQL website, choose the installer package suitable for your operating system, and follow the installation wizard. This step is essential if you are learning how to install MySQL, as the installer also includes helpful tools such as MySQL Workbench.
Step 2: Configure root user and security settings
During the setup process, you will be prompted to create a root user account and password. It is important to enable authentication methods and SSL options to secure your database from unauthorized access.
Step 3: Create and manage your first database using MySQL Workbench or the command line
Open MySQL Workbench for a graphical interface or use the command line if you prefer. Create a new database, define user roles, and set basic parameters to begin storing and managing your data.
Step 4: Test queries and connect to applications
Run simple SQL queries such as CREATE TABLE or SELECT * to confirm the database is working. You can then connect MySQL to your applications or websites, ensuring smooth data management and integration with your business systems.
5 Best Practices for Enterprises Adopting MySQL
MySQL can support a wide range of business tasks, from managing large datasets to powering critical enterprise applications. To help organizations maximize the value of this tool, below are the most common practices to adopt.
- Start with proof-of-concept deployment: Before rolling MySQL out across the entire organization, launch a smaller test project to validate performance and compatibility. This helps reduce risk and ensures the database aligns with your business needs.
- Use professional support or managed services for critical workloads: For mission-critical systems, relying on expert support or cloud-managed services ensures stability and minimizes downtime. These options also provide faster issue resolution and enterprise-level reliability.
- Regularly tune performance and indexes: Over time, databases can slow down if queries and indexes are not optimized. Regular tuning keeps performance high and ensures your applications run smoothly under heavy workloads.
- Implement backups and disaster recovery: Protecting data is essential for any enterprise system, and MySQL offers tools to automate backups. A strong disaster recovery plan ensures data can be restored quickly in case of failures.
- Monitor compliance and security configurations: Businesses in regulated industries must configure MySQL with strict security measures. Ongoing monitoring helps maintain compliance with standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS.
FAQs
1. Is MySQL free?
Yes, MySQL is free and open-source under the GNU General Public License (GPL). Businesses can use it without paying licensing fees, though premium support options are also available.
2. Why is the MySQL server slow?
MySQL can become slow if queries are not optimized, if indexes are missing, or if the server resources are limited. Regular performance tuning, indexing, and proper hardware allocation help maintain fast response times.
3. Can MySQL handle enterprise-level workloads?
Yes, MySQL can support enterprise workloads with high transaction volumes and large datasets. Many global companies, including PayPal and Facebook, have successfully used MySQL to power mission-critical systems.
4. How secure is MySQL?
MySQL provides robust security features such as SSL encryption, user authentication, and role-based access controls. With proper configuration, it can meet compliance requirements for industries like finance and healthcare.
5. Can MySQL run in the cloud?
Yes, MySQL can be deployed on all major cloud platforms, including AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. These managed services allow businesses to scale easily and reduce the burden of maintaining servers.
Conclusion
Understanding what is MySQL can help businesses see its value as a secure, flexible, and widely adopted database technology. While it is powerful and cost-efficient, enterprises should be mindful of performance tuning and choosing the right edition or managed service for their needs. With the right planning and support, MySQL can be a strong foundation for businesses across industries that want reliable, scalable data management.
In case you encounter difficulties with utilizing or implementing the MySQL system into your database management infrastructure, Newwave Solutions stands ready to provide comprehensive support tailored to your needs. Our team of seasoned experts, backed by over 14 years of experience in providing expert IT outsourcing services, possesses deep knowledge of database management systems like MySQL and can guide you through the entire deployment cycle—from initial installation and application integration to full deployment and ongoing maintenance.
Partner with Newwave Solutions today to seamlessly incorporate MySQL into your project’s database management, ensuring optimal efficiency, scalability, and performance for long-term success.
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply