Top 5 Python Backend Frameworks for Web Applications

As the demand for dynamic and scalable web applications continues to soar, Python has emerged as a frontrunner among programming languages for backend development. Its user-friendly syntax, vast library support, and cross-platform compatibility make it an ideal choice for crafting robust web solutions.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll embark on a journey through the realm of Python backend by introducing the five best Python backend frameworks, along with practical advice on choosing the suitable framework for your backend projects. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and insights to select the perfect Python backend framework for your next project.
What is a Python Backend Framework?
A Python backend framework is a collection of ready-made libraries, tools, and conventions that help developers build server-side logic, manage database interactions, route HTTP requests, and maintain application structure — all using the Python programming language. Such frameworks are widely used in real-world applications because they accelerate development, enforce best practices, and simplify maintenance.
Thanks to its readability, vast ecosystem, and strong community support, Python backend frameworks have become among the most popular choices for web services and enterprise-scale applications.
Key features of Python backend frameworks include:
- Built-in ORM and database abstraction — Many frameworks provide an Object-Relational Mapping layer that lets developers interact with databases without writing raw SQL, which enhances security and speeds up data modeling.
- Integrated authentication and session management — Frameworks often include modules for user authentication, authorization, session handling, and security, which simplifies building secure web applications.
- Routing and request-handling mechanisms — A robust routing system enables clean URL design, request parsing, and response handling, which helps organize backend endpoints clearly.
- Extensible plugin and library ecosystem — Developers can leverage a rich ecosystem of third-party packages for tasks such as data validation, caching, serialization, API building, and more, reducing custom code and increasing maintainability.
- Support for scalability and asynchronous operations — Some modern Python frameworks support asynchronous request handling and efficient concurrency models, which help applications manage high load and real-time operations more effectively.
>>> Related post: Python Software Development Complete Guide for Beginners
Different Types of Python Backend Web Framework
Choosing the right Python backend framework can significantly impact your web development project. Python offers a variety of frameworks, each with its own strengths and use cases. Let’s explore some popular options to guide you in selecting the best Python backend framework for your needs.
1. Full Stack Framework
For projects requiring a comprehensive solution, consider full-stack frameworks like Django. These frameworks act as a one-stop shop, providing built-in features for:
- Frontend development: Django Python framework handles the user interface (UI) aspects of your application.
- Backend logic: The framework takes care of the server-side operations that power your application’s functionality.
- Database management: The Django Python framework simplifies database interactions, allowing you to store and retrieve data efficiently.
- Additional features: Many full-stack frameworks offer functionalities like security measures, user authentication, and administrative tools.
This Django Python framework is ideal for large-scale applications where a Python backend web framework is needed alongside the frontend development aspects. If you’re looking for a Python backend framework list to kickstart development, Django is an excellent starting point.
2. Micro-framework
For smaller projects or situations where you value customization over built-in features, consider micro-frameworks like the Python web framework Flask. These lightweight frameworks provide the core components for web development, allowing you to tailor the application to your exact needs.
Here’s what makes micro-frameworks like Flask stand out:
- Minimalistic and lightweight: They are ideal for projects where a simple and efficient backend is essential.
- Flexibility: Micro-frameworks allow you to choose the specific libraries and tools that best suit your project requirements. This level of control is particularly attractive to developers who prefer a hands-on approach.
- Focus on essentials: Micro-frameworks prioritize core web development functionalities, making them a great choice for building APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) or smaller web applications.
3. Asynchronous Framework
As the complexity of web applications grows, handling multiple requests simultaneously becomes critical. This is where asynchronous frameworks like Hug come into play. These frameworks are built for performance optimization by utilizing asynchronous programming techniques.
Here’s how asynchronous frameworks excel:
- Concurrency: They efficiently handle multiple tasks at once, ensuring your application remains responsive even under heavy load. This is particularly beneficial for applications that deal with real-time data or require high user interaction.
- Non-blocking execution: Asynchronous frameworks prevent a single request from blocking the processing of others. This translates to a smoother user experience and improved overall application performance.
While asynchronous frameworks offer significant performance advantages, they might have a steeper learning curve compared to full-stack or micro-frameworks. Consider your project’s specific needs and your development team’s experience when evaluating asynchronous frameworks like Hug.
Choosing the right Python backend framework empowers you to build robust and scalable web applications. By understanding the strengths and use cases of full-stack frameworks, micro-frameworks, and asynchronous frameworks, you can make an informed decision that aligns perfectly with your project’s requirements.
Top 5 Python Backend Frameworks You Should Consider
Let’s explore some of the most common Python backend frameworks that various businesses and enterprises are applying today:

1. Django
Django is a full-stack, “batteries-included” Python backend framework that offers a comprehensive set of tools out of the box — including ORM, authentication, admin interface, and template engine. This framework enables developers to build robust, feature-rich web applications quickly, which makes it particularly suitable for complex projects such as e-commerce platforms, social networks, or enterprise web apps. Thanks to its maturity, large community, and extensive documentation, Django remains among the most widely used backend frameworks.
Key features:
- Built-in ORM & database abstraction — Django’s Object-Relational Mapping layer allows developers to interact with databases in Pythonic objects, avoiding manual SQL and simplifying data modeling.
- Comprehensive authentication & user management system — The framework includes ready-made modules for user registration, login, permissions, and groups — saving time on security and user management implementation.
- Integrated admin interface — Django automatically generates an admin panel for managing models and data, which accelerates backend management and reduces the need for custom dashboards.
- Template engine & view-layer support — The built-in templating system simplifies rendering dynamic HTML views, which helps build full web applications without separate frontend frameworks (or in hybrid mode).
- Strong security defaults and protection mechanisms — Django comes with built-in protections against common security risks like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF), which enhances application safety.
Pros & Cons:
|
Pros |
Cons |
| Robust full-stack features reduce the need for many external libraries. | The “all-in-one” approach may lead to a heavier codebase and structure unnecessary for small or simple apps. |
| Fast time-to-market for complex applications thanks to built-in components. | Less flexibility — default project structure and built-in conventions may feel restrictive when needing deep customizations. |
| Large community and vast ecosystem of plugins, libraries, and documentation. | Potential performance overhead compared to lighter frameworks, especially for very simple APIs. |
| High security standards and built-in protections out of the box. | Learning curve may be steeper for developers who need only minimal features (overkill for small projects). |
| Scalability and maintainability for enterprise-scale web applications. | Heavier memory/resource usage compared with micro-frameworks — might be suboptimal for minimal/microservices scenarios. |
Example:
Instagram utilizes Django as its primary backend framework to manage its massive scale of user interactions and content delivery. The framework’s built-in security features and ORM capabilities have enabled Instagram to handle billions of photos and real-time feeds efficiently, resulting in robust performance and rapid feature deployment.

2. Flask
Flask is a lightweight, minimalist Python micro-framework that provides essential web server and routing capabilities, leaving architecture, database, and other components up to developers’ choice. This design makes Flask highly flexible and straightforward, ideal for small to medium-sized applications or microservices where full-stack features are unnecessary. Because of its simplicity and modularity, Flask continues to attract developers who value control and minimal overhead.
Key features:
- Minimalist core with flexible extensions — Flask provides a basic web server, routing, and request/response management, and developers can choose libraries for DB, auth, or templating.
- Lightweight and easy to set up — The simplicity of Flask allows rapid prototyping, enabling teams to build APIs or small web services quickly.
- Modular architecture — Developers can structure applications in a modular way and integrate only needed components, which helps keep the code lean and maintainable.
- Full control over components and dependencies — Because Flask does not enforce any particular pattern or library, developers can choose the best tools for their needs (ORM, caching, security, etc.).
- Good for microservices and small-scale APIs — Its minimalism and flexibility make Flask suitable for light APIs, backend services, or internal tools where full-stack solutions would be overkill.
Pros & Cons:
| Pros |
Cons |
| High flexibility and control over dependencies and architecture. | Lack of built-in features means developers must assemble many components manually, which can increase development effort. |
| Very lightweight and fast setup — ideal for APIs, prototypes, or microservices. | The need to choose and integrate external libraries can lead to inconsistencies or maintenance overhead. |
| Minimal overhead and resource usage — suitable for simple or small apps. | Manual configuration of security, authentication, or other essential modules increases the risk of bugs. |
| Modular structure supports scalability via microservices architecture. | Less “out-of-the-box” functionality — not ideal for complex applications needing an admin panel, ORM, etc., without extra setup. |
| Easy to learn and flexible for small teams or solo developers. | For large-scale applications, manual setup and glue code can lead to inconsistent structure and higher maintenance costs. |
Example:
Pinterest employs Flask for several of its backend services due to the framework’s lightweight and flexible nature. This choice has allowed Pinterest to develop custom APIs quickly while maintaining high performance for visual discovery features, significantly improving user engagement and content recommendation accuracy.
3. FastAPI
FastAPI is a modern, high-performance Python framework designed for building APIs and asynchronous web services using Python 3.8+ with modern features such as type hints and async/await. This framework emphasizes speed, developer productivity, and reliability, which makes it particularly suitable for API-first applications, microservices, and backend services requiring concurrency. In 2025, FastAPI remains one of the most popular choices for developers who want performance comparable to Node.js or Go while staying in the Python ecosystem.
Key features:
- Type hints & automatic data validation — FastAPI uses Python type hints and Pydantic models to validate request and response data automatically, reducing boilerplate and runtime errors.
- Asynchronous support & high concurrency — Built on ASGI, FastAPI supports async/await, which enables handling many simultaneous requests efficiently — ideal for high-load APIs or real-time services.
- Automatic documentation generation (OpenAPI, Swagger UI) — FastAPI automatically generates interactive API docs, which speeds up API development and improves collaboration with frontend teams or external clients.
- High performance and low latency — Thanks to modern asynchronous design and minimal overhead, FastAPI delivers fast response times and efficient resource usage.
- Flexible routing and modular design — The framework allows modular structure, easy integration with third-party libraries, and clear separation of concerns — suitable for microservice-based or service-oriented architectures.
Pros & Cons:
| Pros |
Cons |
| Very high performance and ability to handle high concurrency. | Async programming introduces complexity, which can be challenging for developers unfamiliar with async/await patterns. |
| Automatic data validation and API documentation generation reduce errors and speed up integration. | Less mature ecosystem compared to Django — some plugins or packages may be unavailable or less stable. |
| Excellent for building fast, scalable APIs and microservices. | Requires careful design to avoid complexities in large monolithic applications when mixing sync/async code. |
| Modern developer experience and productivity — less boilerplate, clear code. | For applications needing full-stack features (auth, ORM, admin), additional libraries are often required. |
| Supports modern Python features and aligns well with current backend best practices. | As a newer framework, a smaller community than some older frameworks may affect long-term support or hiring talent. |
Example:
Uber leverages FastAPI for parts of its backend API development, capitalizing on the framework’s high performance and automatic API documentation. FastAPI’s asynchronous capabilities have enhanced Uber’s real-time ride matching and location services, reducing latency and improving overall service reliability.

4. Tornado
Tornado is a Python web server and framework known for its non-blocking asynchronous I/O and ability to handle many simultaneous connections — a design that addresses the classic “C10k problem.” This makes Tornado suitable for real-time applications, long-polling, WebSocket servers, or backends requiring high concurrency and persistent connections. Despite being older than some modern frameworks, Tornado retains relevance for projects where concurrency and performance matter most.
Key features:
- Non-blocking asynchronous I/O and high concurrency support — Tornado can handle thousands of simultaneous connections efficiently, which suits real-time web, chat, streaming, or long-polling applications.
- Built-in lightweight server and web framework — The framework includes its own server, which simplifies deployment without requiring external WSGI servers.
- Support for WebSockets and real-time communication — Tornado supports real-time protocols, enabling applications to offer live updates, push notifications, or interactive features.
- Flexible routing and request handling — Developers have low-level control over request handling and can fine-tune performance, middleware, and concurrency behavior.
- Compatibility with existing Python ecosystem and libraries — Despite its specialized nature, Tornado integrates well with Python packages, allowing developers to combine its concurrency strengths with standard libraries.
Pros & Cons:
|
Pros |
Cons |
| Extremely capable of handling high concurrency and real-time connections. | Lower-level abstractions demand more coding and architecture effort compared with high-level frameworks. |
| Suitable for WebSockets, streaming, chat, and real-time data — not just traditional HTTP apps. | Lacks built-in ORM, admin panel, or high-level abstractions — more manual work for database, sessions, etc. |
| Efficient resource usage and potential for high performance under load. | Steeper learning curve — asynchronous programming and manual wiring increase complexity. |
| Built-in server simplifies deployment and reduces dependency on external web servers. | Less suited for standard CRUD-based web applications which may be easier to build in full-stack frameworks. |
| Good fit for specialized real-time, concurrency-heavy applications rather than generic websites. | Smaller community and fewer ready-made plugins compared to mainstream frameworks like Django. |
Example:
Dropbox uses Tornado for handling high-concurrency operations in its file synchronization backend. The framework’s non-blocking I/O architecture enables Dropbox to manage millions of simultaneous file transfers efficiently, ensuring fast sync speeds and reliable service across global users.
5. Web2py
Web2py is an open-source, full-stack Python framework that emphasizes ease of deployment, simplicity, and rapid development with minimal configuration — making it attractive for developers who want to build web applications quickly without dealing with complex setup. The framework includes built-in components for database abstraction (DAL), form handling, session management, multiple protocol support (REST, SOAP, XML, etc.), and even a web-based administrative interface. For small-to-medium projects or when speed of deployment matters, Web2py remains a viable and efficient option for many enterprises.
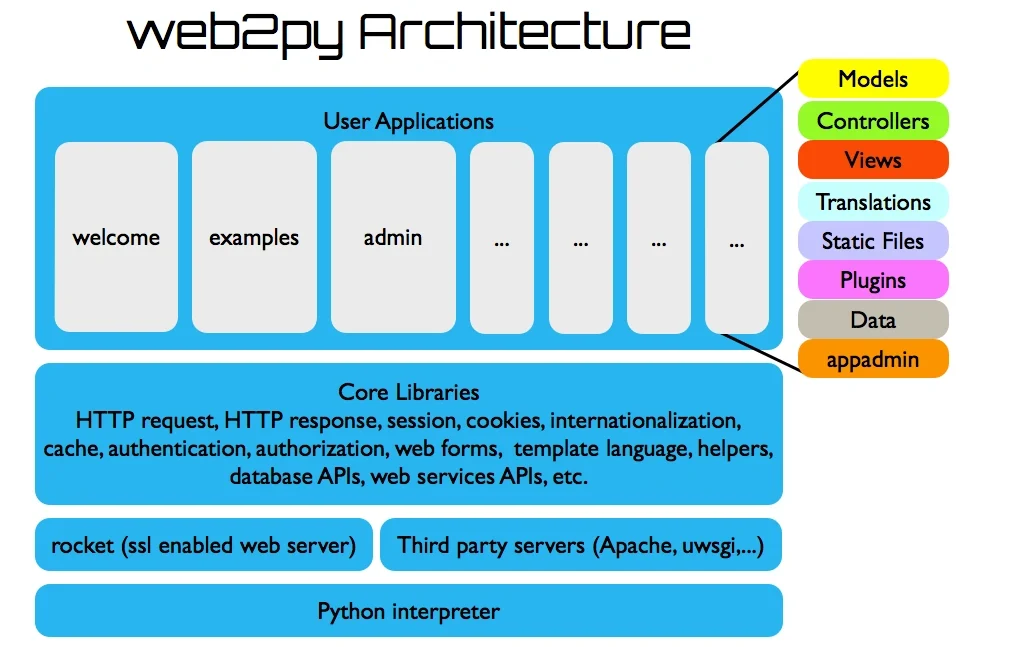
Key features:
- Database Abstraction Layer (DAL) — Web2py’s DAL dynamically generates SQL for various databases, allowing developers to work with databases without writing raw SQL and enabling easy switching between SQL backends.
- Built-in HTTP request handling, form processing, and session management — The framework directly handles HTTP, forms, sessions, cookies, user authentication, and more without needing many external dependencies.
- Support for multiple protocols and output formats — Web2py supports REST, SOAP, XML-RPC, JSON, CSV, and other output formats — giving flexibility for different kinds of web services and integrations.
- Integrated web-based IDE and administrative interface — Developers can perform debugging, testing, maintenance, and database administration directly through a web-based interface, which lowers setup friction and speeds up development.
- Convention-over-configuration philosophy to speed up development — Minimal configuration, default secure settings, and rapid scaffolding help developers launch web apps quickly — ideal for small businesses or MVPs.
Pros & Cons:
| Pros |
Cons |
| Very fast setup and minimal configuration — good for rapid prototyping or small projects. | Less modern ecosystem — fewer community plugins and slower updates compared to Django, Flask, or FastAPI. |
| Built-in DAL, session management, HTTP handling — reduces need for external dependencies. | The design and architecture may feel dated compared to more popular frameworks. |
| Support for multiple output formats and protocols — flexibility for different types of web services. | Less optimized for high performance or asynchronous handling under heavy load. |
| Web-based IDE and admin tools simplify management — suitable for small teams or solo developers. | Limited suitability for large-scale or enterprise-level applications requiring advanced architecture or microservices. |
| Lower learning curve and straightforward conventions — easier for developers new to Python web development. | Smaller community and less long-term support compared with mainstream frameworks, potentially making maintenance harder over time. |
Example:
Mozilla applies Web2py in some of its web application backends, benefiting from the framework’s full-stack capabilities and automatic deployment features. This implementation has streamlined Mozilla’s development process for tools like Firefox web extensions, accelerating release cycles and enhancing developer productivity.
Besides the above Python frameworks, you can explore other Backend Frameworks if you wish to view other programming language choices for your backend development
How to pick the right Python Backend Frameworks?
Choosing a fitting Python backend framework is critical to ensure that your backend runs smoothly and complements the front-end of your project efficiently. Below are several key criteria to guide that decision:
- Project complexity & functional requirements — The scale and complexity of your project should drive your framework choice, because a heavy-duty enterprise app will benefit from a “full-featured” framework with built-in tools, while a small API or microservice may prefer a lightweight, flexible framework for agility.
- Performance & scalability needs — The expected load, concurrency, and growth potential of your application should influence the selection of a framework that supports asynchronous operations, efficient request handling, and scalable architecture in order to avoid performance bottlenecks under high traffic.
- Community support and ecosystem maturity — A well-established framework with a robust community and a wealth of third-party libraries helps reduce development time, ensure better security, and simplify maintenance over time.
- Development speed and time to market — If you need to deliver quickly, frameworks with built-in features (authentication, ORM, admin panels) will accelerate development and reduce time to first release instead of building from scratch or assembling many small libraries manually.
- Flexibility and maintainability — The framework should allow clear code structure, modular design, and easy maintenance/upgrades as your application evolves, which helps lower long-term technical debt and adapt to business changes.
Is Python still Useful for the Backend?
In recent years, Python has increasingly affirmed its position as a top choice for backend development in both small-scale and enterprise-level projects. The language’s clarity and flexibility, combined with powerful frameworks, make it well-suited to handle complex server-side logic, database interactions, API creation, and data processing — all while allowing teams to maintain clean, maintainable codebases. As a result, many organizations now rely on Python for building robust, scalable, and secure backend systems.
Here’s how Python backend frameworks empower developers:
- Rapid Development: Python backend frameworks provide pre-built components and functionalities, accelerating development compared to building everything from scratch. This translates to faster time-to-market for your web application.
- Security: Peace of mind comes standard with Python backend frameworks as they often incorporate industry best practices and security measures. This inherent focus on security helps safeguard web applications from potential threats and vulnerabilities.
- Scalability: As your business flourishes, so too will your web application’s traffic and data demands. Python backend frameworks are built with scalability in mind, ensuring your application can seamlessly adapt and grow alongside your needs.
- Maintainability: Python backend frameworks promote well-organized and reusable code. This structured approach simplifies maintenance and future updates for your web application, keeping it running smoothly.
- Community Support: The widespread adoption of prominent Python backend frameworks fosters large and active developer communities. These communities offer invaluable resources, documentation, and ongoing support, making the development journey a breeze.
Overall, Python still remains very useful for backend development because it continues to rank among the top-used languages globally thanks to its readability, broad ecosystem, and strong support for web frameworks and backend services.
Hire quality Python developers from Newwave Solutions
Even when you select an appropriate Python backend framework, implementing a production-grade backend still requires experienced developers, proper resources, and deep technical knowledge. If your business lacks in-house expertise or past experience, outsourcing to a specialized provider can make a significant difference.
At Newwave Solutions, you have the option to hire skilled Python developers who are proficient at building robust backend systems, data pipelines, and AI-infused web applications. We make sure to cover the whole development cycle of your Python project, from idea generation to backend coding, design, and then the service release & maintenance later on.
Why choose Newwave Solutions’ Python developers:
- Deep Python knowledge: Access to developers with deep expertise in popular frameworks like Django and Flask, ensuring clean architecture and a scalable backend for both web and data-driven applications.
- Flexibility in engagement models: Developers of the projects can be hired on weekly, monthly, or long-term contracts, depending on your project scope and budget.
- High project security: Our developers guarantee that your project to achieve high enterprise-grade security, quality code standards, and transparent processes, which support secure deployment for business-critical applications.
- Capability to support wide-ranging services: custom Python web app development, enterprise applications, machine-learning integration, migration to Python, and ongoing maintenance & support.

By leveraging Newwave Solutions’ experienced Python team, you can accelerate your backend development while maintaining high code quality and scalability — even if your internal team lacks Python proficiency or necessary resources. Approach us soon and let our Python web development services help you from scratch!
Conclusion
These top-rated Python backend frameworks, ranging from comprehensive full-stack frameworks like Django to minimalist micro-frameworks like Flask, each offer unique strengths and functionalities. A thorough understanding of each framework’s core features and capabilities equips developers to make an informed decision and select the best backend framework suited perfectly for your specific web development projects.
Approach Newwave Solutions today to explore how our team of Python web development experts can assist you in selecting and implementing the ideal Python backend framework to propel your project toward success.
Contact Information:
- Head Office (Hanoi): 1F, 4F, 10F, Mitec Building, Cau Giay Ward, Hanoi City, Vietnam
- Branch Office (Tokyo): 1chōme118 Yushima, Bunkyo City, Tokyo 1130034, Japan
- Hotline: +84 985310203
- Website: https://newwavesolution.com
- Email: [email protected]
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply