Top 7 Front End Frameworks for Dynamic Web Applications

Front end frameworks play a crucial role in modern web development projects by providing structured foundations and reusable components that significantly expedite and simplify coding tasks. Developers benefit from the growing ecosystem of new frameworks released regularly, which cater to diverse design needs and enhance application performance.
If you are searching for the most suitable front-end framework for your upcoming IT projects, here are the top 10 options to consider, along with valuable tips to help you choose the best fit.
What is a Front-end Framework?
A front-end framework is a cohesive collection of tools, libraries, and prebuilt components intended to simplify the creation of a website’s or web application’s user interface (UI). It handles structure, layout, and interactivity and often includes reusable UI components such as buttons, forms, and navigation menus. By using a front-end framework, developers can build interfaces more efficiently, maintain consistency across pages, and accelerate development cycles.

How does a Front-End Framework work?
A front-end framework works by providing a structured architecture and a set of conventions that guide how UI components, state management, and events are handled — so developers don’t have to build everything from scratch.
- Component-based architecture: The framework divides the UI into modular, reusable components (e.g., header, list, card, form). Each component encapsulates its markup, style, and behavior — which improves maintainability and reuse across the project.
- State and data binding + rendering logic: When data changes (e.g., user input, API response), the framework automatically updates the relevant UI components — reducing manual DOM manipulation and improving performance.
- Routing, build tools, and integrations: Many frameworks include or integrate with routing, bundling, and build tools — enabling SPA (single-page application) behavior, code organization, optimization, and easier maintenance.
This workflow allows developers to focus on building business-specific logic and features rather than reinventing fundamental UI functionality every time.
5 Main Components of a Front-End Framework
Most front end development frameworks share some essential components:
- UI Components: These are pre-built, reusable building blocks for your UI, such as buttons, forms, menus, and interactive elements. Imagine a toolbox filled with ready-made UI components you can easily integrate into your application.
- Routing: This functionality manages how users navigate your application on the client side (their web browser) and how URLs are handled. It ensures a smooth user experience as they move between different sections of your web app.
- State Management: Front end frameworks provide tools for managing and updating the application’s state, which refers to the data displayed and interacted with on the screen. This ensures that all parts of your application stay in sync and reflect the latest data.
- Templating Engine: This feature allows you to define and render dynamic HTML templates based on your application’s data. Think of it as a mold that you can use to shape your UI based on the information your application needs to display.
- Development Tools: Many frameworks offer features like hot module replacement (updating code without reloading the entire page), code linting (identifying potential errors), and testing utilities to enhance the development experience and streamline the coding process.
Top 7 Best Frontend Frameworks for Enterprises
Choosing the best front end framework depends on your project’s specific needs & demands, but you can concentrate on some framework options that consistently rank high in popularity and developer satisfaction. Let’s explore 10 of the most popular front-end frameworks used today and see if your project can match the features of those frameworks:
1. React.js
React.js is a mature and widely adopted front-end framework (or technically a library) that uses a component-based architecture and virtual DOM to efficiently render user interfaces. It offers a vast ecosystem of third-party libraries, tools, and community support, which makes it a preferred choice for enterprises of all sizes. Recently, React has continued to lead the market share among front-end frameworks thanks to its flexibility, performance, and large developer pool.

Pros:
- Component-based architecture for modular, reusable UI
- Virtual DOM for efficient rendering and minimal UI lag
- Huge ecosystem and third-party library support
- Strong community and developer availability (easy hiring)
- Flexibility in architecture and integration with other tools or back-ends
Cons:
- Bundle size can grow significantly if not optimized (due to many dependencies)
- Requires careful state management in complex apps to avoid performance bottlenecks
- Steeper initial learning curve for proper architecture in large applications (especially with hooks, state, side-effects)
When to use:
- Large-scale single-page applications (SPAs) or enterprise web apps requiring a modular UI
- Projects needing a rich ecosystem and many third-party integrations
- Teams with existing React expertise or with plans to hire React developers quickly
- Applications requiring flexibility and custom architecture rather than opinionated frameworks
Example:
Facebook, the creator of React.js, extensively uses this framework for building its dynamic and responsive user interfaces, enabling seamless real-time interactions across its social media platform. The use of React has significantly improved Facebook’s web app performance and maintainability, facilitating frequent updates while delivering a smooth user experience to billions of users worldwide.
2. Vue.js
Vue.js is a progressive front-end framework that emphasizes simplicity and incremental adoption, making it easy for teams to pick up and integrate into existing projects. It offers declarative rendering, component composition, and reactive data-binding, balancing ease of use with robust capabilities for building interactive interfaces. Vue remains popular among startups and mid-sized companies, particularly in regions where developer availability is high and flexibility is desired.
Pros:
- Gentle learning curve and friendly syntax for rapid onboarding
- Reactive data-binding and declarative rendering for clean and maintainable UI logic
- Component-based structure supporting scalable apps without heavy boilerplate
- Lightweight compared to some full-featured frameworks — good for performance and quick load times
- Good flexibility: can be used for small widgets or a full SPA, depending on needs
Cons:
- Smaller ecosystem compared to React — fewer enterprise-grade libraries/plugins for extremely niche needs
- Potential limitations when scaling very large, complex applications (less “opinionated” structure)
- Less corporate backing compared to frameworks maintained by large companies (can affect long-term support in rare cases)
When to use:
- Startups or SMEs requiring quick time-to-market and flexibility
- Projects needing a balance between simplicity of development and dynamic UI capability
- Smaller to medium-scale web apps or progressive enhancements to existing sites
- Teams preferring ease of learning and fast prototyping over heavy architecture overhead
Example:
Alibaba, a global eCommerce giant, has adopted Vue.js for parts of its front-end development to create highly interactive and efficient user experiences. By leveraging Vue’s lightweight and flexible framework, Alibaba enhanced the speed and responsiveness of its web applications, contributing to increased customer engagement and sales conversions.
3. Angular
Angular is a full-featured, TypeScript-based front-end framework developed by Google, designed for building large-scale, maintainable single-page applications with strong architecture out of the box. Its built-in tooling, structured conventions, and opinionated architecture help enforce consistency across large codebases — a feature that appeals especially to enterprise teams. Overall, Angular remains a stable choice for complex projects that require robust state management, dependency injection, and long-term support.
Pros:
- Comprehensive built-in features (routing, forms, state management, DI) without the need for many external libraries
- Strong TypeScript support for maintainability and type safety
- Well-suited for enterprise-grade, large-scale applications with complex business logic
- Long-term support and mature versioning cycle backed by Google and the community
- Structured architecture that enforces coding standards and maintainable project layout
Cons:
- Steep learning curve for developers unfamiliar with TypeScript or Angular’s conventions
- Relatively heavier bundle sizes and runtime overhead compared to minimal frameworks
- Verbose boilerplate and sometimes rigid structure may slow down rapid prototyping
When to use:
- Enterprise applications requiring strict architecture, type safety, and consistent structure
- Large teams working collaboratively, needing enforceable coding standards and maintainability
- Applications with complex business logic, heavy data handling, or tight integration requirements
- Long-term projects that require stability, predictable upgrade paths, and scalability
Example:
Google uses Angular for several complex applications, including Google Ads, where it handles a vast amount of data and user interactions efficiently. Angular’s modular architecture allowed Google to maintain a scalable and robust platform, improving developer productivity and delivering consistent, high-quality user experiences.

4. Svelte
Svelte is a modern front-end framework that shifts much of the workload to compile time, producing highly optimized JavaScript output with minimal runtime overhead. Unlike frameworks that rely on a virtual DOM at runtime, Svelte compiles components into efficient vanilla JS, yielding smaller bundle sizes and highly performant UIs. In 2025, Svelte is gaining traction, especially for performance-critical applications and projects where a lightweight footprint and fast initial load matter.
Pros:
- Extremely small bundle size and minimal runtime overhead for fast load and runtime performance
- Clear syntax and a simpler reactivity model that reduces boilerplate and complexity
- Ideal for performance-critical web apps or pages needing fast Time-to-Interactive
- Lower memory and resource usage — beneficial for mobile or resource-constrained environments
- Ease of building small-to-medium apps without heavy setup or tooling overhead
Cons:
- Smaller ecosystem and fewer ready-made plugins/libraries compared to React or Angular
- Less established in large enterprise projects — may require more custom work or experienced developers
- Community and adoption are still less widespread compared to long-standing frameworks — potential risk for long-term support or scaling on very large teams
When to use:
- Performance-sensitive applications where speed, bundle size, and load times are critical
- Small-to-medium projects or landing pages needing fast responsiveness and minimal overhead
- Projects targeting mobile browsers or low-resource devices where efficiency matters
- Prototyping or smaller products seeking simplicity and rapid development
Example:
The New York Times has utilized Svelte in parts of its interactive web features, capitalizing on Svelte’s compile-time approach to generate minimal, optimized JavaScript. This results in faster page loads and a more fluid user experience, especially for readers accessing news content on mobile devices with limited bandwidth.
>>>Read more: Essential Java Web Frameworks
5. Solid JS
Solid.js is a modern and high-performance front-end framework that focuses on fine-grained reactivity and minimal runtime overhead, which allows it to achieve very fast rendering and efficient UI updates. It employs a reactive model similar to Svelte’s compile-time optimizations and is increasingly recognized for performance-first applications in recent years. Many performance benchmarks show Solid.js among the fastest frameworks for UI updates and hydration.
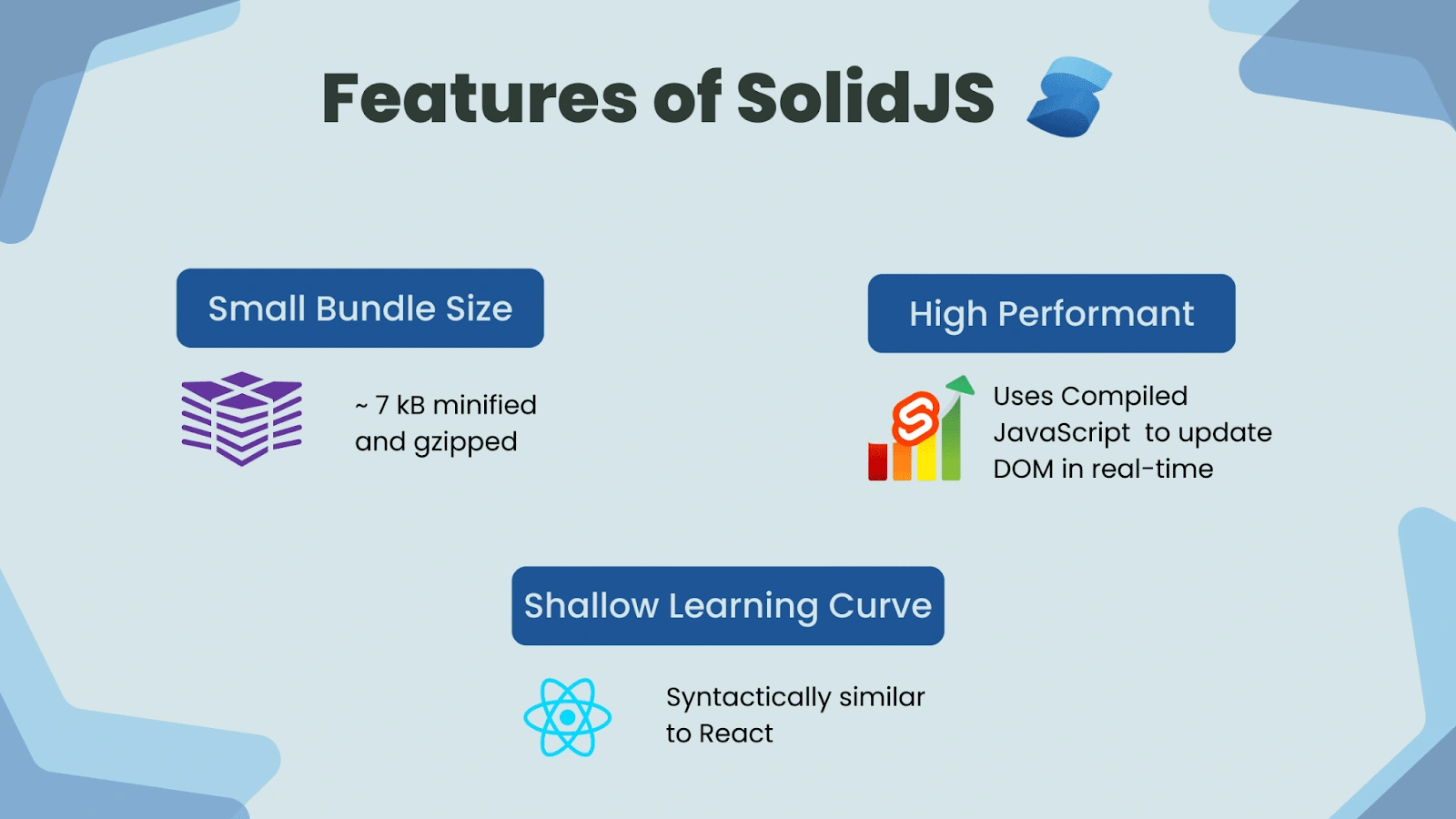
Pros:
- Very fast rendering and hydration thanks to fine-grained reactivity and minimal runtime overhead
- Efficient updates of UI without unnecessary re-renders, leading to a smooth user experience under heavy UI interactions
- Lightweight footprint, which helps performance, especially in large or complex UI applications
- High performance makes it suitable for real-time dashboards or dynamic interfaces with frequent state changes
- Growing but passionate community and increasing recognition among devs focusing on performance and scalability
Cons:
- Smaller ecosystem and fewer third-party libraries compared to mainstream frameworks like React or Vue
- Less developer availability, which may make hiring more challenging for large teams
- Being newer and less battle-tested in enterprise-scale projects compared to legacy frameworks — possible risk in long-term support or edge-case stability
When to use:
- Real-time applications or web apps with highly dynamic UI and frequent state changes (dashboards, data visualization)
- Performance-critical interfaces where rendering speed and efficiency are essential
- Projects prioritizing minimal bundle size and runtime overhead over extensive ecosystem or heavy abstractions
- Teams are comfortable with newer/less conventional frameworks and are willing to handle integration customizations if needed
Example:
Enzyme, a modern analytics platform, integrates Solid.js to build highly performant interactive dashboards. Solid.js’ focus on fine-grained reactivity reduces unnecessary re-renders, resulting in quicker data visualization updates and enhancing user productivity in data-driven decision-making processes.
6. Next.js
Next.js is a widely used meta-framework built on React that adds server-side rendering (SSR), static site generation (SSG), routing, and many performance optimizations out-of-the-box — making it ideal for web applications needing SEO, fast initial load, and flexible rendering strategies. As a result, Next.js continues to be a leading choice for enterprise web apps, content-heavy platforms, and scalable websites that require both performance and flexibility.
Pros:
- Built-in SSR/SSG support improves SEO and initial load performance
- Full compatibility with the React ecosystem and tooling, gaining the benefits of React plus extra optimizations
- Modular routing and file-based routing simplify project structure and navigation logic
- Good for large-scale web apps, content-heavy sites, or applications needing SEO and fast Time-to-First-Byte
- Support for hybrid rendering (static + server-rendered) offers flexibility depending on page needs
Cons:
- Slightly increased build complexity due to SSR/SSG setup and deployment requirements
- Larger initial learning curve compared to simple SPA frameworks, especially for server-side logic and data fetching
- Runtime server dependencies — which may require backend infrastructure rather than purely static hosting
When to use:
- Content-rich websites or blogs requiring SEO optimization and fast page load (marketing sites, news portals)
- Web applications needing the best possible SEO and performance (e-commerce front ends, public-facing apps)
- Projects where initial load speed and dynamic/ static content mix are both priorities
- Enterprises needing a stable, scalable web front-end with both SSR and SPA capabilities
Example:
Netflix leverages Next.js for its server-side rendering capabilities, enabling quick content loading and enhanced SEO performance on its streaming platform. This use of Next.js has led to faster page transitions and improved user retention, directly impacting overall viewer satisfaction and engagement metrics.
7. Nuxt.js
Nuxt.js is a meta-framework built on Vue.js that offers server-side rendering, static site generation, and powerful configuration for large-scale web applications or SEO-heavy sites. It combines the developer friendliness and simplicity of Vue with advanced web-app capabilities, making it ideal for businesses wanting both productivity and robust performance. Nuxt continues to gain adoption for content-heavy sites, SaaS platforms, or applications requiring SEO and scalability.
Pros:
- SSR/SSG support for improved SEO and performance
- Simple, intuitive development experience inherited from the Vue ecosystem
- Flexible configuration and capability for large-scale apps without heavy overhead
- Good for content-oriented or marketing-centric applications requiring SEO compliance
- Leverages Vue’s reactivity and simplicity, combined with enterprise-ready rendering features
Cons:
- Slightly steeper setup compared to plain Vue for static SPA projects
- Increased build complexity and deployment setup for SSR or static generation
- May introduce overhead in projects that only need a simple frontend without SSR/SSG
When to use:
- Content-heavy websites, blogs, or marketing platforms needing SEO and static generation
- Web applications combining dynamic interactivity with SEO/SSR needs (e.g., SaaS landing + app front-end)
- Projects requiring Vue simplicity but wanting server-side rendering or static generation flexibility
- Enterprises focused on SEO performance, fast page load, and easy maintainability with the Vue stack
Example:
GitLab, a leading DevOps platform, employs Nuxt.js to build its frontend with server-side rendering and static site generation. Nuxt.js’ capabilities have helped GitLab deliver a fast, responsive, and SEO-friendly interface, supporting a seamless developer experience and scalable infrastructure as the platform grows.
Besides these top 7 front-end frameworks, you may need to explore some popular backend frameworks as well to fulfill the design and coding of your products/ services.
Benefits of Front end Frameworks
The modern front end frameworks can offer a variety of benefits that make them invaluable tools for modern developers. Let’s dig into the key advantages that those frameworks can deliver to your projects.
1. Boosting Productivity
Front end frameworks provide a wealth of pre-built components and utilities, reducing the need for writing boilerplate code from scratch. This accelerates development time and allows developers to focus on building application-specific functionality.
2. Organized and Maintainable Code
Frameworks promote a structured and modular approach to code organization. This makes it significantly easier to manage and maintain complex web projects, especially as they grow in size. Imagine pre-built building blocks that can be easily reused throughout your application – that’s the power of components in a framework! By encouraging code reuse, frameworks reduce duplication and ensure consistency across your application’s codebase.
3. Smoother User Experiences
Many modern front end frameworks prioritize performance. They achieve this through techniques like virtual DOM and efficient rendering algorithms. These fancy terms essentially mean the framework works hard behind the scenes to deliver a smooth and responsive experience for users, even when interacting with intricate applications that handle a lot of data.
4. Cross-Platform Compatibility
A major advantage of many front end frameworks is their ability to work across different platforms. This is called being platform-agnostic. By using a framework with this feature, you can build web applications that function flawlessly on various devices and platforms, including web browsers, mobile phones, and even desktop applications.
5. Optimizing Performance
Many frameworks leverage advanced techniques like virtual DOM and efficient rendering to ensure your web application performs well, delivering a smooth and responsive user experience. The overall performance of the project is ensured as the front end frameworks deliver consistency throughout the coding and designing process.
6. Robust Ecosystem and Community Support
Popular front end frameworks benefit from large and active communities of developers. These communities contribute to the ongoing development and improvement of the frameworks. This translates to a wealth of resources readily available to you, including libraries, tools, and troubleshooting guides. With a strong community behind you, you’ll find it easier to overcome challenges and stay informed about the latest best practices in front-end development.
By understanding the benefits and various considerations of front end frameworks, you can make informed decisions to streamline your web development process and create exceptional web applications.
How to Choose the Right Front-End Framework for Your Project
Since you likely do not have time or resources to test all 10 popular front-end frameworks simultaneously, you need clear criteria to decide which framework best fits your business project. Below are essential factors to evaluate in a straightforward way:
- Project size & complexity — Projects with heavy UI, many interactive components, or complex state logic require robust frameworks with good state management and modular architecture; simpler sites or landing pages may benefit from lighter frameworks.
- Performance & load requirements — Applications needing fast load times, smooth rendering, or SEO optimization should favor frameworks delivering minimal runtime overhead and efficient rendering.
- Team skill & developer availability — The familiarity of your team with a framework (or the availability of developers skilled in it) strongly influences speed of development and long-term maintainability.
- Ecosystem, libraries & community support — A well-supported framework with a rich ecosystem of libraries, plugins, and documentation ensures easier integration and access to ready-made components or tools.
- Maintainability & long-term scalability — Frameworks with modular structure, clear conventions, and community maintenance make it easier to scale and update the project over time without technical debt.
- Cross-platform requirements or future expansion plans — If you anticipate expanding into mobile web, hybrid apps, or need responsive design across devices, choose frameworks that support such flexibility and compatibility with modern tooling.
Hire Front-End Developers from Newwave Solutions for seamless User Experiences
With the criteria outlined above, you now have a better understanding of how to select the most suitable front-end framework for your business’s project. However, choosing the right framework alone is not enough because front-end design and coding require extensive knowledge, technical skills, and diverse resources. If you face challenges during this process, Newwave Solutions is ready to assist you with our high-quality Hire Front-End Developers services.
As a trusted IT outsourcing partner with over 14 years of experience, Newwave Solutions enables your business to hire front-end developers who craft elegant, responsive interfaces and seamless user experiences. Our thorough recruitment process ensures the selection of experts skilled in React, Vue, Angular, or custom UI development who align well with your technical needs and team culture. When choosing to hire developers through us, your organization benefits from rigorous talent vetting, comprehensive support, robust security, and full transparency, ensuring your project’s demands are met with excellence.
Types of front-end solutions we offer include:
- Android Applications: We deliver user interfaces for Android app development that are intuitive and performance-oriented.
- iOS Applications: Our iOS front-end solutions focus on delivering smooth and engaging user experiences for Apple devices.
- Blockchain Software: Front-end development designed to interact securely and efficiently with blockchain backend systems.
- Web Applications: We build scalable and responsive front-ends tailored for modern web platforms using the latest frameworks.
- eCommerce Website: Custom eCommerce front-ends optimized for customer engagement, speed, and seamless transactions.
- CRM Software: User-friendly interfaces for CRM solutions that enhance client management and sales workflows.
- CMS Development: Tailored content management system front-ends that enable easy editing and dynamic content delivery.
- AI Solutions: Interactive and intelligent front-ends designed to complement AI-driven backend algorithms.
Partnering with Newwave Solutions ensures a smooth and effective front-end development experience that transforms your business ideas into successful digital products.
Conclusion
That’s all for the discovery of the most popular front end frameworks for enterprises and individual projects. Whether you prioritize blazing-fast performance, user-friendly development, or seamless scalability, there’s a framework perfectly suited to your needs. Choose wisely, and you can easily utilize the framework to deliver a user-friendly, seamless front-end experience for final users.
Connect with Newwave Solutions to explore how we can help you navigate the exciting world of front-end development frameworks and identify the perfect fit for your next project! Moreover, we can deliver additional quality React Native App development services and Java App development services to help you apply such popular front-end frameworks to your project effectively.
Contact Information:
- Head Office (Hanoi): 1F, 4F, 10F, Mitec Building, Cau Giay Ward, Hanoi City, Vietnam
- Branch Office (Tokyo): 1chōme118 Yushima, Bunkyo City, Tokyo 1130034, Japan
- Hotline: +84 985310203
- Website: https://newwavesolution.com
- Email: [email protected]
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply