Bitcoin vs Ethereum: Core Differences and Which Is Better?

The discussion around Bitcoin vs Ethereum is not simply about price, performance, or popularity. At its core, this comparison represents two fundamentally different visions of what blockchain should be and how Blockchain technology should be used in the long term. Bitcoin was created to reduce money. Ethereum was built to redefine what can be built on top of a blockchain. Understanding this distinction is essential for investors, founders, and enterprises evaluating blockchain adoption, infrastructure strategy, or long-term technology investment.
What Is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is the first decentralized blockchain network and the foundation of the entire cryptocurrency industry. It was introduced in 2008 through a whitepaper published by the pseudonymous creator Satoshi Nakamoto and launched in early 2009.
Bitcoin was designed as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system that operates without centralized authorities. Over time, its role has evolved. Today, Bitcoin is primarily viewed as a decentralized store of value rather than a high-frequency payment network.
The Bitcoin protocol is intentionally conservative. Changes are rare, upgrades are slow, and backward compatibility is treated as a priority. This approach has helped Bitcoin maintain unmatched security and trust over more than a decade of operation.
Pros
Bitcoin’s strengths stem from its simplicity and rigid design philosophy. By limiting functionality, the network minimizes attack surfaces and operational risk.
From a practical perspective, Bitcoin offers:
- A fixed monetary supply capped at 21 million coins, reinforcing scarcity
- Extremely high security backed by Proof of Work and global miner distribution
- Strong decentralization with relatively low requirements for running full nodes
- Predictable issuance and monetary policy that is easy to model long term
- High liquidity and recognition across institutional and retail markets
Cons
The same characteristics that make Bitcoin secure also limit its flexibility. Bitcoin is not designed to evolve rapidly or support complex application logic.
Key limitations include:
- Very limited programmability compared to smart contract platforms
- Low transaction throughput and slower confirmation times
- Transaction fees that can become unpredictable during peak demand
- Minimal native support for advanced financial or application logic
- Innovation that largely occurs outside the base layer
Use Case & Potentials
Bitcoin’s value proposition is clearly articulated and specifically targeted towards several key functions within the financial ecosystem. As the first cryptocurrency, it serves not only as a pioneering digital asset but also as a robust store of value, akin to digital gold. Its decentralized structure offers a unique hedge against inflation and currency debasement, making it attractive during times of economic uncertainty. Furthermore, Bitcoin facilitates efficient cross-border transactions, eliminating the need for centralized intermediaries and thereby reducing transaction costs and time. As an asset for settlement in secondary layers, like the Lightning Network, Bitcoin exhibits versatility, enabling faster and more scalable transactions.
Common use cases include:
- Long-term store of value and digital asset preservation
- Hedge against monetary inflation and currency debasement
- Cross-border value transfer without centralized intermediaries
- Settlement asset for secondary layers such as Lightning Network
To fully understand how Bitcoin compares with programmable blockchains, it helps to look at Ethereum in depth. We already explored Ethereum’s architecture and ecosystem in our SOL vs ETH comparison, which provides additional context before continuing.
Bitcoin vs Ethereum: Which Is the Core Difference?

Although Bitcoin and Ethereum share blockchain fundamentals, their differences run deep. They were built to solve different problems and therefore make different tradeoffs.
Philosophy and Design Purpose
Bitcoin was created as a response to centralized financial systems. Its goal is to provide a neutral, censorship-resistant monetary network. Every design choice prioritizes security, immutability, and predictability.
Ethereum was created to extend blockchain beyond money. Its purpose is to act as a programmable platform where decentralized logic can be executed globally. This explains why Ethereum embraces change and experimentation more openly.
This philosophical split results in:
- Bitcoin prioritizing monetary certainty and minimalism
- Ethereum prioritizing flexibility and application enablement
Technology and Programmability
Bitcoin uses a deliberately constrained scripting system. It allows basic transaction conditions but prevents complex logic. This reinforces Bitcoin’s role as a settlement network.
Ethereum introduced a virtual machine that allows smart contracts to execute arbitrary logic. This capability underpins decentralized finance, NFTs, and autonomous applications.
This difference defines the contrast between Bitcoin blockchain vs Ethereum blockchain:
- Bitcoin focuses on secure value transfer
- Ethereum focuses on programmable state changes
Ecosystem and Innovation Pace
Bitcoin’s ecosystem evolves cautiously. Most innovation occurs at the infrastructure level, such as custody, scaling, and payment channels.
Ethereum’s ecosystem evolves rapidly. New financial primitives and application models often originate on Ethereum before spreading to other chains.
As a result:
- Bitcoin favors long-term stability
- Ethereum favors continuous innovation
Monetary Policy and Economic Model
Bitcoin’s issuance schedule is fixed and enforced by code. Halving events reduce supply issuance over time until the maximum supply is reached.
Ethereum uses a dynamic issuance model influenced by network activity. Fee-burning mechanisms tie ETH supply to usage, linking value directly to demand.
This creates:
- Passive scarcity for Bitcoin
- Utility-driven value for Ethereum
Summary Table for Comparison
| Aspect | Bitcoin | Ethereum |
| Primary role | Digital store of value | Programmable application platform |
| Supply model | Fixed and deflationary | Flexible with burn mechanism |
| Smart contracts | Very limited | Fully programmable |
| Ecosystem pace | Conservative | Rapid innovation |
| Upgrade philosophy | Minimal change | Continuous evolution |
So when to choose which one?
- Bitcoin is best suited for investors and institutions prioritizing long term value preservation, monetary certainty, and maximum security.
- Ethereum is better suited for builders, businesses, and investors focused on application growth, financial innovation, and active participation in decentralized ecosystems.
How Does Ethereum Work vs Bitcoin?
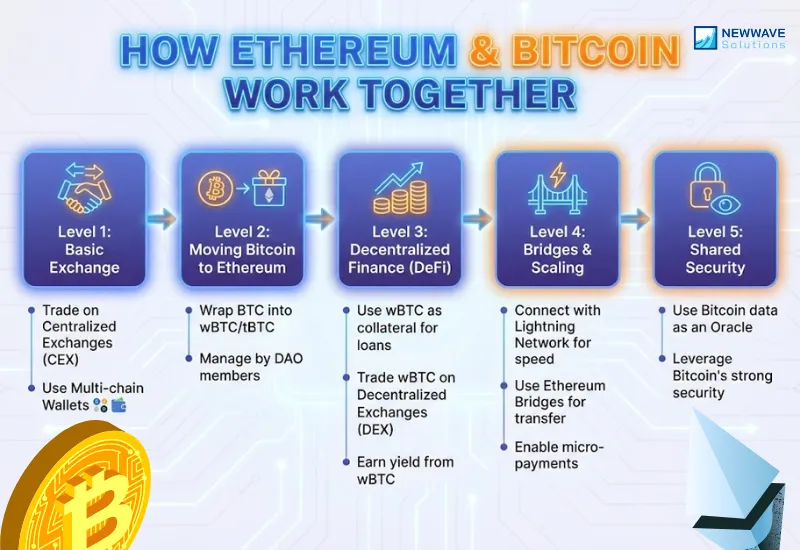
At a functional level, the difference between how Ethereum works versus Bitcoin comes down to what happens after a transaction is validated. Bitcoin confirms ownership transfers. Ethereum confirms ownership transfers and executes logic. This distinction becomes clearer when examined through layered system behavior.
Layer 1: Consensus and Network Security
Bitcoin secures its network through Proof of Work, where miners compete to validate transactions by expending computational energy. This creates strong security guarantees but limits throughput and energy efficiency.
Ethereum transitioned to Proof of Stake, where validators secure the network by locking up ETH. This shift reduced energy consumption and allowed Ethereum to focus on scalability through layered execution.
Key differences at this layer:
- Bitcoin uses computational work as security
- Ethereum uses economic stake as security
- Bitcoin prioritizes immutability
- Ethereum balances security with upgrade flexibility
Layer 2: Transaction Execution
Bitcoin processes transactions sequentially with a focus on settlement finality. Each block primarily confirms transfers of BTC between addresses.
Ethereum processes transactions as function calls within smart contracts. Transactions can modify state, trigger logic, and interact with other contracts within a single execution flow.
This means:
- Bitcoin transactions are simple and predictable
- Ethereum transactions can be complex and state changing
- Bitcoin confirms value movement
- Ethereum executes application logic
Layer 3: Programmability Model
Bitcoin’s scripting language is intentionally restrictive. It is not designed to support loops, complex conditions, or autonomous programs.
Ethereum supports Turing complete smart contracts written in a blockchain programming language, enabling applications to run without centralized control.
As a result:
- Bitcoin limits on-chain complexity
- Ethereum enables autonomous digital agreements
- Bitcoin discourages on-chain experimentation
- Ethereum encourages composability and reuse
Layer 4: Application and Ecosystem Layer
Bitcoin’s applications remain focused on payments, custody, and settlement solutions. Most advanced functionality exists off-chain or through secondary networks.
Ethereum supports a broad range of decentralized applications, including financial systems, digital identity, gaming, and asset tokenization. This layer is where Ethereum’s flexibility translates into real-world adoption.
This difference explains why:
- Bitcoin applications remain narrowly focused
- Ethereum applications span multiple industries
- Bitcoin acts as infrastructure for value storage
- Ethereum acts as infrastructure for digital economies
Layer 5: Economic Interaction and Value Flow
Bitcoin primarily functions as a static asset. Its value is held, transferred, or secured, but not natively productive.
Ethereum’s native asset plays an active role in the ecosystem. ETH is used to pay fees, secure the network, provide collateral, and participate in governance, linking its value to network activity.
This creates:
- Passive value behavior for Bitcoin
- Active value behavior for Ethereum
- Store-of-value economics versus utility-driven economics
Bitcoin vs Ethereum vs Solana: Which Is the Best?
Comparing Bitcoin vs Ethereum vs Solana requires understanding that these networks are not direct substitutes but complementary systems serving different layers of the blockchain stack.
Bitcoin anchors value and trust. Ethereum enables programmable finance. Solana optimizes performance and user experience. Here is the core comparison table for the best view:
| Criteria | Bitcoin | Ethereum | Solana |
| Core function | Store of value | Smart contract platform | High performance execution |
| Consensus | Proof of Work | Proof of Stake | Proof of History and Proof of Stake |
| Programmability | Minimal | Extensive | Extensive |
| Transaction speed | Slow | Moderate | Very fast |
| Primary users | Investors | Developers and enterprises | Consumer applications |
In conclusion:
- Bitcoin is ideal for value preservation.
- Ethereum is ideal for decentralized application development and financial infrastructure.
- Solana is ideal for high throughput consumer applications.
Together, they form a layered ecosystem where value flows between chains through bridges and wrapped assets, enabling collaboration rather than competition.
FAQs
Will Ethereum Outperform Bitcoin?
Whether Ethereum will outperform Bitcoin depends on how performance is measured. Bitcoin tends to lead as a long-term store of value due to its fixed supply, simple design, and strong security model. It is often favored in periods where capital preservation is the primary concern.
Ethereum, however, may outperform in terms of network growth and economic activity. Its value is closely tied to usage, including transaction volume, smart contract execution, and application adoption. As decentralized applications continue to expand, Ethereum benefits directly from increased demand on the network.
In practice, Bitcoin and Ethereum often outperform different market conditions rather than replacing each other.
Why Use Ethereum Instead of Bitcoin?
Ethereum is used instead of Bitcoin when blockchain is needed as a programmable platform rather than just a value transfer system. Bitcoin was designed for security and simplicity, which limits its ability to support complex logic.
Ethereum enables smart contracts and decentralized applications that can automate financial processes, governance, and digital asset management. This makes it suitable for building applications such as decentralized finance platforms, NFTs, and on-chain business logic.
Simply put, Bitcoin is optimized for storing value, while Ethereum is optimized for building and running decentralized applications.
Conclusion
The comparison between Bitcoin and Ethereum highlights how diverse and specialized the blockchain ecosystem has become. Bitcoin secures value. Ethereum enables innovation. Solana accelerates execution. Each plays a distinct role in the evolution of decentralized systems.
For businesses and founders exploring blockchain adoption, choosing the right platform is only the beginning. Success depends on architecture design, security, scalability, and long term maintainability across evolving ecosystems.
At Newwave Solutions, we support global clients in building scalable blockchain products across multiple networks. Our Vietnam based engineering teams deliver end to end dApp development solutions, custom token creation, and even fully self-hosted blockchain networks at the protocol level. We work across public and private chains, leveraging the right Blockchain platforms for each business case.
Whether you are building financial infrastructure, launching digital assets, or integrating blockchain into existing systems, our experience helps translate blockchain ambition into production ready systems with measurable business impact.
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply