Outsourcing vs Offshoring: Which Is Better for Making Strategic Business Decisions?

In today’s globalized economy, businesses are increasingly turning to offshoring and outsourcing as strategic tools to optimize operations, reduce costs, and enhance efficiency. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct business practices with varying implications.
This comprehensive guide will delve deep into outsourcing vs offshoring, exploring their definitions, differences, advantages, and potential pitfalls.
What is Offshoring and Outsourcing?
Outsourcing and offshoring are two terms frequently discussed in the business world, but they represent different strategies for managing operations. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses looking to optimize operations, cut costs, and improve efficiency.
What is Outsourcing?
Outsourcing refers to contracting specific business tasks or processes to third-party providers, which can be located either domestically or internationally. For instance, a company might outsource its customer service to a specialized firm, regardless of whether that firm is in the same country or overseas. This approach allows businesses to reduce costs, focus on their core activities, and leverage the expertise of external providers.
By outsourcing, companies can also improve efficiency and flexibility, as they can quickly adapt to changing market conditions without the need to hire additional staff. Outsourcing versus offshoring becomes relevant when comparing the benefits of outsourcing domestically versus moving tasks offshore.
Benefits of Outsourcing:

On the flip side, insourcing is the opposite of outsourcing, where a company chooses to bring previously outsourced tasks back in-house. This is often done to regain control over operations, enhance quality, or better align tasks with long-term business goals.
For those looking to enhance their technical capabilities or integrate sophisticated systems, knowing what specific Salesforce developer skills are necessary can make a significant difference.
What is Offshoring?
Offshoring refers to relocating business processes or services to another country, typically to benefit from lower labor costs or specialized skills available abroad. A typical offshoring example could be a company moving its customer service operations to India, or shifting manufacturing to China. These moves are driven by the need to lower costs while maintaining productivity.
The offshoring definition focuses on the cross-border relocation of operations, distinct from outsourcing which can occur domestically. Understanding what is offshoring is crucial for businesses considering expanding internationally.
Benefits of Offshoring:
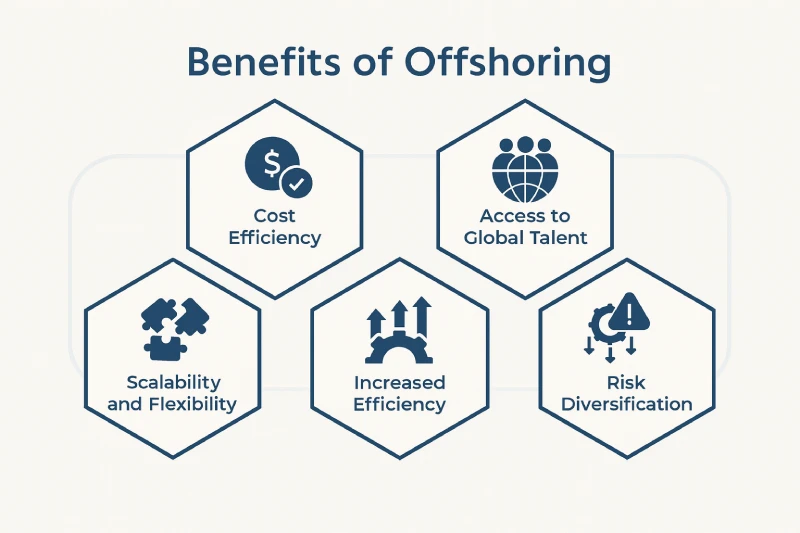
However, offshoring also poses risks, such as cultural barriers, language differences, and time zone challenges. Businesses must weigh the pros and cons of offshoring and outsourcing when deciding on the best approach for their needs.
The key difference between outsourcing and offshoring lies in the scope and location. Outsourcing is simply contracting work to a third-party provider, while offshoring involves physically moving business operations to another country. Therefore, offshoring is different from outsourcing because it always involves cross-border transactions.
Moreover, businesses need to understand offshoring vs offshore outsourcing, as the latter combines both practices: contracting a third-party provider based in another country.
Outsourcing vs Offshoring: A Quick Comparison
When deciding between outsourcing and offshoring, businesses often weigh several factors to determine which option aligns best with their strategic goals and operational needs. Here’s a clear comparison of outsourcing and offshoring presented in a table format:
|
Factor |
Outsourcing |
Offshoring |
|
Cost Efficiency |
Often focuses on flexibility and quality; may not significantly reduce costs. | Offshoring is appropriate for a business when it seeks substantial cost savings due to lower labor costs in certain countries. |
|
Control and Oversight |
Delegates control to external partners; less oversight of daily operations. | Requires direct management of overseas teams; involves navigating different cultures and regulations. |
|
Strategic Focus |
Allows a business to focus on core functions while leveraging external expertise. | Enables companies to expand market reach and access global talent. |
|
Risk Management |
Risks include service quality and data security due to reliance on external providers. | Involves geopolitical and regulatory risks alongside operational challenges. |
|
Scalability |
Supports agile operations; easy to scale up or down based on business needs. | May require more time and resources to scale due to infrastructure and regulatory considerations. |
|
Examples |
A company outsourcing customer support to a local provider for better service. | A tech firm offshoring software development to India for cost-effective skilled labor. Onshoring vs offshoring can also be a consideration here. |
This table summarizes the key differences between outsourcing and offshoring, making it easier to compare and evaluate which option might be best for a business’s specific needs and goals. Offshoring companies are often better suited for long-term, cost-intensive projects, while outsourcing might be ideal for flexible, short-term tasks.
For businesses seeking to optimize their development processes, consider programming outsourcing services to leverage specialized expertise and improve efficiency.
How Are Outsourcing and Offshoring Different in Business Strategy
When it comes to running a business, choosing between offshoring and outsourcing is not just about saving money. It’s also about how each approach affects the overall strategy and operations of the company. But what is the difference between offshoring and outsourcing? Let’s explore the differences in a business context.
Focus on Core Activities:
- Outsourcing allows businesses to focus on their core activities while letting specialized companies handle other tasks. For instance, a software company might outsource its accounting functions. This enables the software team to concentrate on product development without being distracted by administrative tasks.
- In contrast, offshoring refers to relocating certain business operations to another country, usually to capitalize on lower labor costs. However, offshoring may require businesses to invest in managing overseas operations, which can be resource-intensive and time-consuming. A good offshoring example is a tech firm that offshores its development to India; the firm might have to dedicate more effort to managing the offshore team rather than focusing solely on innovation.
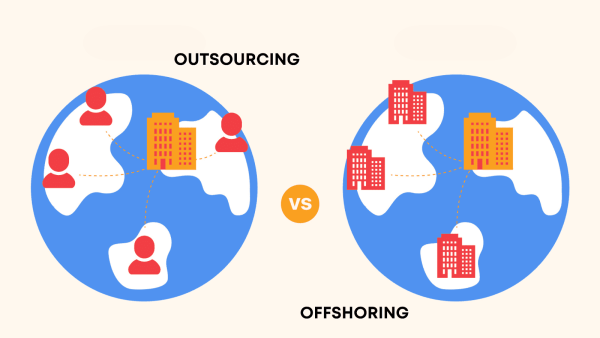
Cost Considerations:
Both strategies aim for cost reduction, but there’s a difference between offshoring and outsourcing in terms of how cost savings are achieved.
- Outsourcing can provide cost savings by allowing companies to avoid expenses related to hiring, training, and managing additional staff. For example, outsourcing IT services can lower costs by transferring the work to a specialized provider.
- Offshoring typically aims for even greater savings by taking advantage of lower wages in different countries. However, offshoring is different from outsourcing because it also involves higher initial investments, such as setting up infrastructure and complying with local regulations. Businesses must weigh whether long-term savings justify these upfront costs.
Control and Management:
A significant distinction between outsourcing vs offshoring is the level of control a business retains.
- Outsourcing transfers responsibility for certain tasks to a third-party vendor, which means less direct control over how those tasks are executed. Businesses need to vet partners carefully to ensure high standards.
- Offshoring, on the other hand, allows a company to maintain greater control over its overseas operations. This can be crucial for ensuring quality and consistency. However, managing offshore teams across different time zones and cultures presents challenges that require careful planning.
Risk Management:
Both outsourcing and offshoring carry risks, but they differ in nature.
- Outsourcing can lead to issues such as reduced service quality or data security concerns. A third-party vendor might not uphold the same standards, which could negatively affect the business.
- Offshoring introduces additional risks such as geopolitical instability, regulatory changes, and cultural differences. For example, offshoring takes place when corporations relocate operations to regions with more favorable economic conditions, but they must be prepared to navigate potential risks like political unrest or unexpected legal changes.
Growth Opportunities:
While both strategies offer growth potential, they differ in execution.
- Outsourcing can help a business scale quickly without the burden of hiring and managing additional staff. This flexibility is crucial for companies looking to adapt to fluctuating demands.
- Offshoring can facilitate market expansion by establishing operations in foreign markets, allowing businesses to tap into local talent and resources. For instance, many companies benefit from offshoring IT services to countries with highly skilled labor pools, such as India or the Philippines.
Understanding the pros and cons of offshoring and outsourcing is essential for making informed business decisions. Both offshoring and outsourcing play important roles in business strategy. Offshoring offers cost savings and growth potential but requires a more hands-on approach to management and risk mitigation. Outsourcing, meanwhile, provides flexibility and focus on core competencies but may result in less control over quality.
Moreover, it’s crucial to distinguish between offshoring vs offshore outsourcing. The latter combines elements of both approaches by outsourcing specific tasks to a third-party provider located in another country. This allows businesses to take advantage of cost savings while also benefiting from the expertise of external providers.
Types of Outsourcing/Offshoring Models
Outsourcing and offshoring models vary based on the nature of the services, the location of the service providers, and the engagement structure between the client and the service provider. Here’s a detailed overview of the common types of offshoring vs outsourcing models:
Outsourcing Models: Location-Based
|
Model |
Description | Pros |
Cons |
|
Onshore Outsourcing |
Contracting services within the same country | Easier communication, regulatory alignment, cultural similarities | Higher costs, less access to global talent |
|
Nearshore Outsourcing |
Contracting services to nearby countries with similar time zones and cultures | Moderate cost reduction, fewer zones of time, and cultural differences. | Higher costs compared to offshore outsourcing |
|
Offshore Outsourcing |
Offshore outsourcing definition is contracting services to distant countries for cost advantages | Significant cost savings, access to a broader talent pool | Cultural differences, time zone challenges, communication issues |
This table provides a concise comparison of location-based outsourcing models, helping businesses select the most suitable approach based on their specific needs and constraints.
Outsourcing Models: Relationship-Based
|
Model |
Description | Pros |
Cons |
|
Staff Augmentation |
Adding skilled personnel to augment an existing team | Flexibility, access to specialized skills, easier integration | Management overhead, dependency on external talent |
|
Dedicated Team |
Assembling a team dedicated solely to the client’s project | High control, deep understanding of the client’s business | Higher cost, significant management input required |
|
Project-Based |
Engaging providers for specific projects with defined timelines | Clear scope and deliverables, cost-effective for short-term needs | Less flexibility, integration, and long-term support challenges |
These relationship-based models help businesses scale quickly, but each one comes with trade-offs in terms of management effort, cost, and control over the team.
Outsourcing Models: Pricing-Based
|
Model |
Description | Pros |
Cons |
|
Fixed Price |
Pricing agreed upon before the project based on defined requirements | Predictable costs, minimized budget overrun risk | Limited flexibility, the potential for disputes due to scope changes |
|
Time and Materials (T&M) |
Pricing is based on actual time and resources spent | Flexibility, adaptability to changing requirements | Less predictable costs, potential budget overruns |
These pricing models allow businesses to choose between predictability and flexibility, depending on the nature of the project and their risk tolerance.
Offshoring Models
|
Model |
Description | Pros |
Cons |
|
Global Shared Services |
Centralized operations serving multiple business units globally | Economies of scale, standardized processes, cost efficiency | Initial setup costs, potential bureaucratic inefficiencies |
|
Hybrid Model |
Combining different offshoring models for optimal performance | Customizable, balanced risk and benefits | Complex management, integration challenges |
|
Multi-Sourcing Model |
Using multiple service providers across locations | Risk diversification, varied expertise, competitive pricing | Coordination complexity, potential quality inconsistencies |
|
Global Delivery Model |
Delivering services from multiple global locations | 24/7 operations, global talent access, redundancy | High management overhead, communication challenges |
|
Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) |
Setting up and running operations offshore, then transferring ownership | Risk mitigation, smooth transition, local expertise | Initial setup costs, transfer phase challenges |
These offshoring models offer various strategies for businesses seeking to leverage global resources, balancing flexibility, risk, and cost efficiency depending on the company’s goals.
Outsourcing vs Offshoring: When To Use?
Outsourcing/offshoring have become pivotal strategies for modern businesses aiming to optimize operations, reduce costs, and expand their global footprint. While both strategies aim to enhance business efficiency, the difference between outsourcing and offshoring lies in their scope and execution. Each approach offers distinct advantages depending on the business’s objectives and operational requirements.
For startups in particular, outsourcing has become a popular solution to streamline product development, reduce costs, and bring products to market faster. To explore more about how startups are leveraging this approach, you can refer to The Rise of Outsourced Product Development in Startups.
When To Use Outsourcing
Outsourcing involves delegating specific business functions or tasks to external vendors or service providers. This strategy is particularly beneficial in several scenarios:

- Cost Reduction: One of the main pros of outsourcing is the ability to lower operational expenses by contracting tasks to regions with lower labor costs. For example, a US tech startup might outsource software development to India for cost savings. This emphasizes the cost-effective nature of outsourcing vs offshore production, as tasks are delegated without moving the entire operation.
- Access to Specialized Skills: Businesses gain access to expertise that may not be available internally. For instance, a healthcare provider might outsource medical billing to a firm with in-depth knowledge of healthcare regulations. This highlights how outsourcing/offshoring provides access to global skill sets.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Outsourcing allows companies to scale operations easily without hiring additional staff, making it ideal for managing fluctuating workloads. This difference is key when comparing outsourcing versus offshoring, as outsourcing typically focuses on handling specific tasks rather than relocating entire operations.
- Focus on Core Competencies: By outsourcing non-core functions like IT support, businesses can concentrate on core product development and strategy activities. This is one of the advantages of offshoring and outsourcing — focusing on high-value activities while external teams manage routine tasks.
- Short-Term Projects: Outsourcing provides a cost-effective solution for temporary needs or specific projects. For example, a marketing agency might outsource graphic design for a short campaign. This flexibility is why businesses often choose outsourcing over offshoring for limited, project-based work.
If you weigh the decision between in-house and outsourced solutions, In House Vs Outsourcing: Which Suits Your Project Better? might provide valuable guidance.
When To Use Offshoring
Offshoring involves relocating business operations to another country to leverage cost benefits, access global talent, or expand into new markets. Let’s explore what is offshoring and when it should be used:

- Cost Savings: Offshoring takes place when corporations move operations to countries with lower costs of living and labor. For instance, manufacturing operations may be moved to China or Vietnam, offering significant savings. This defines offshoring vs outsourcing, as offshoring typically involves large-scale relocations.
- 24/7 Operations: By utilizing different time zones, businesses can provide continuous service. This is particularly beneficial in industries like IT support, where round-the-clock services are necessary. It’s one of the key benefits of offshore outsourcing that keeps businesses running non-stop.
- Access to Global Talent: Offshoring gives businesses access to specialized talent in regions where those skills are more prevalent. For example, Eastern Europe is renowned for its highly skilled software developers. What is offshore sourcing? It’s essentially a strategy to tap into global expertise that is scarce or expensive locally.
- Market Expansion: Offshoring allows companies to establish a presence in foreign markets, helping them adapt to local conditions and expand their international brand presence. Offshoring definition business expands on this as relocating operations to gain local market advantages.
- Control Over Operations: Unlike outsourcing, where tasks are handed off to external vendors, offshoring gives businesses control over their relocated operations. Offshoring is different from outsourcing because it typically involves maintaining direct oversight and management of operations, ensuring compliance and quality standards are met.
In summary, both offshoring and outsourcing are valuable strategies, but they serve different needs. Companies must weigh the pros and cons of offshoring and outsourcing to determine which approach best aligns with their long-term goals.
FAQs about Outsourcing and Offshoring
What are the risks of outsourcing?
Outsourcing can pose several risks, including loss of control over certain business processes, potential quality issues, and reliance on third-party vendors. Additionally, data security and confidentiality are significant concerns, as sensitive information may be exposed to external parties.
Companies should conduct thorough due diligence and establish clear contracts to mitigate these risks. This is especially true in situations involving offshoring, where companies must also navigate international regulations and cultural differences. Offshoring refers to relocating operations overseas, which can introduce challenges.
How does offshoring impact company culture?
Offshoring can lead to challenges in maintaining a cohesive company culture, as teams may be geographically dispersed. Differences in time zones, communication styles, and cultural norms can create misunderstandings. To address this, organizations should invest in regular communication, team-building activities, and efforts to align company values across locations.
Which industries benefit most from outsourcing?
Several industries have successfully leveraged outsourcing, including IT services, customer support, manufacturing, and healthcare greatly benefit from offshore outsourcing.
For example, IT services and software design are often offshored to countries like India and the Philippines, where labor costs are lower but the talent pool remains highly skilled. This practice allows companies to gain a competitive edge by reducing costs and accessing specialized expertise.
What are the pros and cons of offshoring and outsourcing?
Both offshoring and outsourcing offer significant cost savings, but they also come with challenges. Offshoring takes place when corporations seek to reduce operational costs, but it requires careful management of overseas teams and attention to compliance with local laws.
Outsourcing vs offshore operations involves different levels of risk and control. Outsourcing gives companies flexibility, but they may sacrifice some control over quality, whereas offshoring allows for greater control but requires significant investment in managing international teams.
Conclusion
Outsourcing and offshoring have become integral strategies for businesses seeking to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and tap into global talent. Understanding the distinct characteristics and benefits of outsourcing vs offshoring approach can help companies make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals.
In the dynamic global marketplace, outsourcing and offshoring depend on a company’s needs, goals, and operational context. By carefully evaluating these factors and implementing best practices, businesses can leverage these strategies to drive growth, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge.
Contact Information:
- Head Office (Hanoi): 1F, 4F, 10F, Mitec Building, Cau Giay Ward, Hanoi City, Vietnam
- Branch Office (Tokyo): 1-chome-11-8 Yushima, Bunkyo City, Tokyo
- Hotline: +84 98 531 0203
- Website: https://newwavesolution.com
- Email: [email protected]
To Quang Duy is the CEO of Newwave Solutions, a leading Vietnamese software company. He is recognized as a standout technology consultant. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

Read More Guides
Get stories in your inbox twice a month.
Let’s Connect
Let us know what you need, and out professionals will collaborate with you to find a solution that enables growth.




Leave a Reply